Respiratory Diseases
Asthma
Asthma is a respiratory disease in which spasm and
constriction of the bronchial passages and swelling of
their mucous lining cause obstruction of breathing.
It is often due to allergy, particularly to dust, animal
fur or feathers, moulds, and pollen. Asthma in adults is
less likely to be caused by allergy, and more likely to be
associated with respiratory infections and emotional
upsets.
Many people with allergic asthma also suffer from hay
fever.
Treatments?
Emphysema,
A progressive respiratory disease characterized by
coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing,
developing into extreme difficulty in breathing, and
sometimes resulting in disability and death.
Although the exact cause is unknown, bronchial spasm,
infection, irritation, or a combination of the three
seem to be contributory.
The highest degree of occurrence is among heavy
cigarette smokers, especially those exposed to polluted
air.
Children who suffer from bronchitis or asthma are also
susceptible.
In recent years emphysema has become a serious
public-health problem.
Lung Cancer
Growth of malignant cells affecting, initially, the lung.
Cancer forms when a lung cell undergoes alterations to
its DNA, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. Growth
continues until a tumour forms.
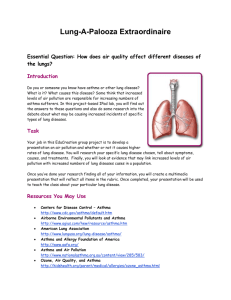
Martin Rotker/Phototake NYC
Cancerous Human Lung
This section of human lung tissue shows light-coloured cancerous tissue in the centre of the
photograph. At bottom centre lies the heart. While normal lung tissue is light pink, the tissue
surrounding the cancer is black and starved of oxygen, the result of a tar-like residue left by
cigarette smoke. Most lung cancer begins in the cells lining the main air passages, or bronchi.
In their cancerous state, these cells lack the cilia that normally catch and eliminate foreign
particles inhaled into the lung. Mucus ordinarily cleared by bronchial cilia becomes trapped,
blocking air passages. Cigarette smoking is directly responsible for 90 per cent of cases of
lung cancer.
Microsoft ® Encarta ® Reference Library 2002. © 1993-2001 Microsoft
Corporation. All rights reserved.
The process of metastasis (spread) takes place when
cells break off from the tumour and travel via the
blood or lymphatic system, lodging in other organs.
There they begin to multiply, forming other tumours.