Nutrition Review
advertisement

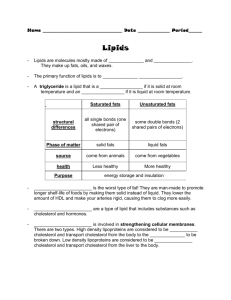
Review for Final Exam Nutr 12 General and introductory material (Chapters 1 and 2) Categories of nutrients: macronutrients vs. micronutrients, fat-soluble vs. water-soluble vitamins, major minerals vs. trace minerals Calorie sources, calorie content and percent calories from fat Definitions: inorganic vs. organic, essential nutrient, nutrient density (nutrients/kcal), energy density (kcal/g) Nutrient recommendations (DRI): RDA/AI, EAR, UL; how to determine whether a nutrient is essential Causes of nutrient deficiency; primary vs. secondary deficiency Food labels: how to read; significance of Daily Values Elements of research studies; controlled experiments vs. epidemiological studies Digestion and Absorption General terms related to digestion and absorption; functions of digestive organs and their secretions Products of digestion; pathway after absorption Cause of most intestinal gas (nutrients/substances that increase gas production) Carbohydrates Photosynthesis; elements combined to make glucose Sugars vs. starches: types, food sources Whole grains: white flour vs. whole wheat flour; purpose of enrichment; nutrients in enriched grains Lactose intolerance: cause, effects Storage of carbohydrate in the body; body’s requirement for glucose; depletion of body proteins in starvation due to need for glucose Sugar alcohols: examples, kcaloric content, reason they are used in foods, adverse effect of excess intake Artificial sweeteners: examples; kcaloric content (~zero) Fiber: definition; comparison of soluble vs. insoluble fibers (types, food sources, and health benefits); potential effects of high intakes Blood sugar regulation by insulin and glucagon, general effects of these hormones (including their general effects on triglycerides and proteins) Diabetes: symptoms and health effects, comparison of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes Glycemic index: definition; examples Lipids Comparison of triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols; roles of each type of lipid, general food sources Saturated vs. unsaturated fats and their properties and food sources; recommendations for heart disease Essential fatty acids: names, general structure (omega-3 vs. omega-6), roles, general food sources Hydrogenated fats: definition, purpose, and food sources, effect of hydrogenation on producing trans fats; health risks of trans-fatty acids Fish oils: names of omega-3 fatty acids in fish and their benefits Plant sterols: reason for addition to foods Fat transport: describe four categories of lipoproteins; their composition and roles in body; how lipoproteins affect heart disease risk Atherosclerosis: definition, effect of diet on lipoproteins and heart disease risk Protein Protein functions: enzymes, collagen, keratin, albumin, antibodies, etc. Protein’s amino acid order coded by DNA Protein RDA: calculations (using 0.8 g/kg), protein RDAs of average men and women (in grams) Fate of amino acid amine/carbon groups after consumption; how excess nitrogen is excreted Protein quality: characteristics of high quality proteins, sources of high quality vs. low quality proteins; definition of limiting amino acids Complementary proteins: definition, how protein complementarity is achieved, whether plant proteins (vegan intakes) are adequate for meeting protein needs Vegetarian diet categories; nutrient deficiency risks for vegans Nitrogen balance: influences, effects of dieting, disease, growth, protein intake, etc.; lack of effect of excess protein on positive N balance Symptoms and effects of marasmus and kwashiorkor Food allergies, definition of phenylketonuria (PKU) Final Topics: all material covered since last exam