74 Evolution Vocab
advertisement

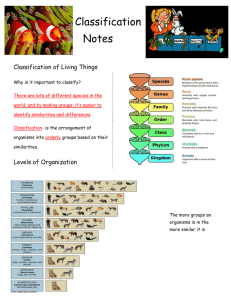
Name: __________________________________ Doc #: 91 Biology 2016 Classification and Microorganisms PRE-AP Review Sheet CLASSIFICATION/KINGDOMS Q1: Fill in the following chart regarding the cell walls of the different kingdoms: Kingdom Has a cell wall (answer NEVER, Cell Wall is made up of Prokaryote OR SOMETIMES or ALWAYS) (answer only if relevant) Eukaryote? Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Q2: What makes a prokaryotic cell different to a eukaryotic cell? ___________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Q3: List the taxonomic levels in order from GENERAL to MOST SPECIFIC and write the mnemonic (memory tool… think King Phil) sentence that you use to remember them: Names of the Taxon: ______________________________________________________________ Memory Sentence: _______________________________________________________________ Q4: Define Taxon: _______________________________________________________________ Q5: Scientists use binomial nomenclature to give organisms a common two part name. The first name, which is capitalized is the ___________ name and the second name, which is not capitalized, is the __________ name. Organisms that are closely related will often belong to the same genus so share the same first word but have a different second species word. Q6: From your notes on the characteristics of living things, list the 7 characteristics of living things: 1) ________________________________________________________________________ 2) ________________________________________________________________________ 3) ________________________________________________________________________ 4) ________________________________________________________________________ 5) ________________________________________________________________________ 6) ________________________________________________________________________ 7) ________________________________________________________________________ Q7: Define homeostasis: __________________________________________________________ Q8: A ________________ ________ follows a series of two option questions to identify organisms. Q9: Multicellular organisms organize cells into more complex structures: Place the following in order: Organs, Tissues, Cells, Organ Systems, Organism ____________ _____________ ____________ _______________ ________________ Q10: A hypothetical evolutionary tree is called a _________________. When drawing one, organisms on the same branch are more closely related than organisms on different branches. Q11: Fill in the boxes to complete a Kingdom Chart (you will need to have this memorized) KINGDOM CELL TYPE EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA PROTIST Prokaryote CELL STRUCTURES (Cell Wall) NUMBER OF Unicellular CELLS MODE OF NUTRITION 1 EXAMPLE MOVEMENT Cell wall without Peptidoglycan FUNGUS PLANT Eukaryote ANIMAL Eukaryote Cell walls with chitin Some unicellular, Some multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Autotroph Mushroom Some move with slime or flagella Monkeys Nonmotile VIRUSES Q12: Viruses are made up of two key parts: 1) a __________ which is the protein coat and 2) _______________ (genetic material) which contains instructions for making new copies of a virus. Q13: Viruses often target one type of cell. For instance, the influenza virus attacks upper respiratory cells. What type of cell does the HIV virus attack? _______________________________________ Q14: Why do you need a new flu shot every year? ________________________________________ Q15: Can a virus reproduce without a host? _______________________ Q16: The main reason viruses are classified as non-living is because they would not be able to reproduce in a normal environment (such as a sterile medium like agar plates). How do viruses reproduce then? ______________________________________________________________________________ Q17: What are 4 ways that a virus can be transmitted from person to person? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Q18: In the lytic life cycle of a virus, the cycle concludes with what? _________________________ What makes a lysogenic infection different from a lytic infection? ____________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ BACTERIA Q19: For each characteristic, write E if it is a characteristic of Eubacteria, A if it is a characteristic of archaebacteria and B if it is a characteristic of both: _______ Cell Walls made of Peptidogylcan _______ Cell walls NOT made of peptidogylcan _______ Is a prokaryote _______ Lives everywhere _______ Lives in extreme/harsh environments _______ Lack membrane bound organelles Q20: Bacteria are decomposers. What is a decomposer? ______________________________________________________________________________ Q21: Bacteria do lots of important things for the environment. They release oxygen when they carry out photosynthesis, they recycle nutrients and they also play a role in the nitrogen cycle. What do bacteria do in the nitrogen cycle? ____________________________________________________ Q22: Why do bacteria evolve/adapt more quickly than other living other organisms? ______________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Q23: How do bacteria aid in human digestion? ___________________________________________ This is an example of what type of symbiotic relationship? __________________________________ Q24: Some bacteria have chloroplasts. This means they can do what? _________________________ Q25: Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics. An example of a commonly used antibiotic that actually comes from a fungus is: __________________ Q26: Fill in the Venn Diagram comparing bacteria and viruses. You need at least 2 things in each area of the chart. VIRUS BACTERIA Q27: Memorize the Root Words from LIST 10 ROOT WORD MEANING ROOT WORD MEANING ADDITIONAL REVIEW FOR THE 9 WEEKS TEST (Mon 3/7 and Tues 3/8) 1. Staple your ECOLOGY and EVOLUTION review sheets to this review sheet. You need to know everything on all three review sheets. If there are any blanks on any review sheets, go through and fill them in. 2. Answer these additional questions on PROTISTS and FUNGUS which will be on the Nine Weeks Test: Why is Kingdom Protista sometimes referred to as a ‘Junk’ Kingdom or a Leftovers Kingdom? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ What is the one characteristic all protists have in common (hint: relates to the type of cell)? ___________________________________________________________ Protists are divided into broad categories based on who they are most like. For each type of protist, give examples: ANIMAL LIKE PROTISTS 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ PLANT LIKE PROTISTS 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ FUNGUS LIKE PROTISTS 1. ____________________________ The protozoan that causes malaria belong to which Kingdom? _________________ Explain how malaria is transmitted: _________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ What important role do fungi play in ecosystems? ______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ What is the only unicellular fungus? ______________________________________ Name two common diseases that are caused by a fungus. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. Memorize the Root Words from LIST 11 ROOT WORD MEANING ROOT WORD MEANING