File
advertisement

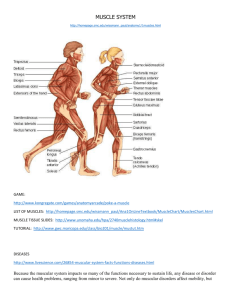
Muscular System Notes 3 Types of Muscle Tissue _____________ o Involuntary o Striated o Contains ________________ ___________ (allow for faster impulse transmission) o Found in _____________ _____________ o o o o Involuntary Non-striated Another name is _______________ Location: _____________________ _____________ o o o o Voluntary Striated Attached to bones by _____________ Primary muscle of system 4 Characteristics of all muscles ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Muscular System Notes Functions __________________ o Prime movers— o Antagonists— o Synergists— _________________ o __________ Contraction—partial contraction; counteracts the force of ______________ ___________ _________________ o _____% of body heat comes from muscle activity Gross Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Composed of ____________ muscle cells and ________________ tissue Involves ______ bones with an ______________ between them Origin— Insertion— **Insertion always moves toward origin** Tendons— Bursa— Synovial Memb./Fluid— Tendon sheaths— Muscular System Notes Microscopic Structure Muscle cells are called _____________ _____________. Bundles of muscle fibers are called _______________. Connective Tissue Components: o ___________________-o ___________________-o ___________________-- Parts of Muscle Fibers (cells) Sarcolemma— Sarcoplasm— Sarcoplasmic Reticulum— Many mitochondria Several nuclei Myofibrils/myofilaments 1) 2) 3) 4) _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ ________________—part of ______________; ________________ ____________; area between two _____________; Parts of sarcomere: A-bands— I-bands— H-zone— Muscular System Notes Muscle Contraction In a relaxed state, actin & myosin partially overlap. During contraction, myosin attaches to actin causing them to move toward each other. This is called the sliding filament theory. This shortens the sarcomere, which shortens the muscle fiber. When enough muscle fibers contract, the entire muscle will contract. 3 requirements: Nerve impulse Calcium ATP Process of Contraction Nerve impulse (__________________) is received. _____________ ions are released from SR into sarcoplasm. Ca++ combine with _______________. This allows ____________ __________ to attach to ___________. Filaments pull to center and sarcomere _______________. **If majority of muscle fibers shorten, then contraction occurs. Relaxation **Opposite of contraction Nerve impulse (____________________) is received. Ca++/troponin complex breaks up. This prevents myosin from binding to actin Filaments slide apart Muscular System Notes All-or-None Principle A muscle _______________ will contract fully or not at all. There is _____ partial __________________. Entire muscles CAN partially contract. Threshold stimulus— Subthreshold stimulus— Motor Unit…Nervous Tissue Component Motor Neuron o Dendrites—pick up _____________ thru receptors; carries impulse _______________ cell body o Cell body-–main part of cell that contains ______________ o Axon—carries impulse __________ from cell body toward the muscle fiber Muscle Fibers Neuromuscular Junction—space b/t ____________ & __________ fiber **KNOW DRAWING!!!! Muscular System Notes Fatigue Strength of contraction _________________ (no longer respond to _______) Uses up __________ & ______________ Creates ______________ ______________ & ___________ _____________ build-up (sore muscles) Types of Contractions Twitch— Tetanic— Isotonic— Isometric— **Flaccid—loss of muscle tone Effects of Exercise Negative: ______________ Positive: ________________—increase in muscle size; helped by ____________ _______________ (isometrics & weights) Endurance training —has a __________ _________ benefit; increases ___________ _________ & # of mitochondria in cell (more _________)