PE Studies 3AB - PE Studies
advertisement
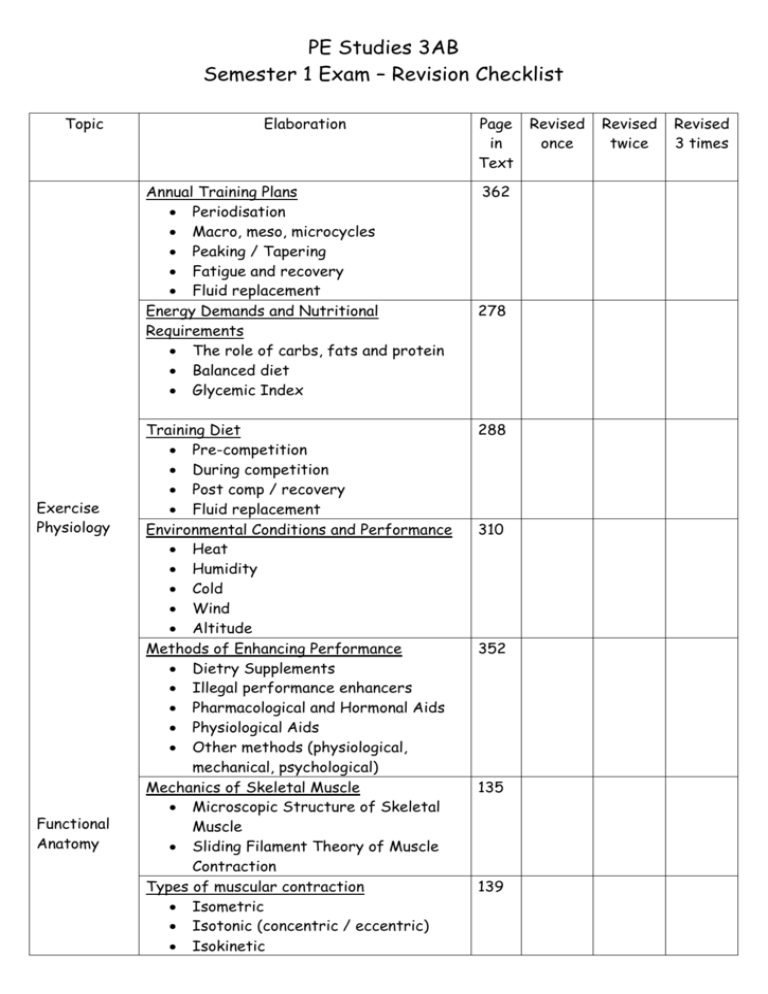
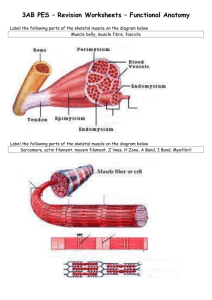
PE Studies 3AB Semester 1 Exam – Revision Checklist Topic Elaboration Annual Training Plans Periodisation Macro, meso, microcycles Peaking / Tapering Fatigue and recovery Fluid replacement Energy Demands and Nutritional Requirements The role of carbs, fats and protein Balanced diet Glycemic Index Exercise Physiology Functional Anatomy Training Diet Pre-competition During competition Post comp / recovery Fluid replacement Environmental Conditions and Performance Heat Humidity Cold Wind Altitude Methods of Enhancing Performance Dietry Supplements Illegal performance enhancers Pharmacological and Hormonal Aids Physiological Aids Other methods (physiological, mechanical, psychological) Mechanics of Skeletal Muscle Microscopic Structure of Skeletal Muscle Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Types of muscular contraction Isometric Isotonic (concentric / eccentric) Isokinetic Page in Text 362 278 288 310 352 135 139 Revised once Revised twice Revised 3 times Functional Anatomy Relationship between muscle contraction force–velocity force–length. 144 Muscle contraction and Nerve Function Motor Neurons Motor Units Neuromuscular Junction Muscle fibre types Type 1 Type 2a Type 2b 153 Biomechanical concepts in selected sports Conservation of momentum (Newtons 2nd Law) Impulse-momentum Coefficient of restitution Moment of inertia Angular momentum The use of levers in sport Torque 3 classes of levers Application of biomechanical principles to analyse skills Biomechanical analysis Biomechanics Qualitative v Quantitative analysis Subjective v Objective analysis Force-motion Force-time Inertia Range of Motion Balance Coordination Continuum Segmental Interaction Optimal projection Spin Biomechanical analysis of sports skills Sprinting High Jump Throwing Striking Fluid mechanics in physical activities Bernoulli’s principle The magnus effect Spin Drag 166 184 202 218 229 244 Don’t forget to revise the notes YOU wrote Extra Resources can also be found on the wikispace