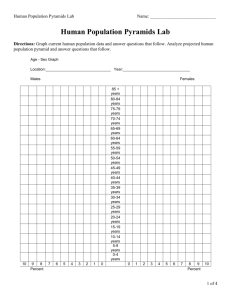
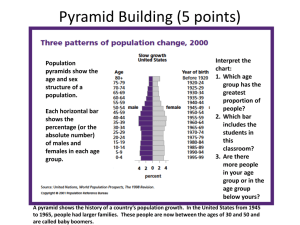
Pyramid Building: Population Pyramid Data Table
advertisement

Pyramid Building (Lesson taken from the Population Reference Bureau) 1. Show the chart, "Three Patterns of Population Change," on the overhead. If you use the figure with the Democratic Republic of Congo and Germany pyramids, cover these up for the first part of the lesson. Explain that a population pyramid shows the age and sex structure of a population. Point to the horizontal bars, which show the percentage (or the absolute number) of males and females in each age group. 2. Have students interpret the chart. Which age group has the greatest proportion of people? (35-39) Which bar includes the students in this classroom? (10-14 or 1519) Are there more people in your age group or in the age group below yours? Explain that a pyramid shows the history of a country's population growth. In the United States from 1945 to 1965, people had larger families. These people are now between the ages of 30 and 50 and are called baby boomers. Point to this group on the pyramid. 3. Now show them pyramids for Congo and Germany. Have them describe Congo's population structure. How is Congo's pyramid different from that of the U.S.? (There are more people in the younger age groups.) Which age group in Congo is the largest? (0-4) What proportion of the population is in this age group? (Almost 20 percent; about 9 percent are males and 9 percent females.) Now look at Germany. How is it different? (The age groups are closer to being equal.) How is it different from Congo? (There is a greater proportion of older people.) 4. Ask students: Why would a country 's leaders want to know the proportion of the population in different age groups? What difference does the age of the people in a country make? (People of different ages have different needs.) What kinds of products do young people use? What kinds of services do they need? (diapers, day care, toys, health care, schools, etc.) What about older people? (different kinds of health care, different foods, different products) Is it important for a government leader or planner to know the age of the population they are serving? 5. Explain that each student is going to draw a population pyramid for a specific country. However, the class will practice first with the U.S. Explain that the pyramid will have only four age categories instead of 16 like the ones shown. 6. Pass out copies of a blank Modified Population Pyramid outline. Put the corresponding transparency on the overhead. Point out that males are on the left, females on the right and they are measured as a percentage of the population. Read off the age categories. Tell students that 14 percent of females are ages 019. Have them draw a line from the bottom of the box at 14 percent up to the next line. Demonstrate. Do the same for the males and continue in the same manner for the other age groups. US Population by Age 2000 (percent) AGES MALES FEMALES 0-19 15% 14% 20-39 15% 14% 40-59 13% 13% 60+ 7% 9% Source: U.S. Census 2000. 7. Next, distribute copies of the Population Pyramid Data Table and another copy of the blank Modified Population Pyramid outline. Organize the class into groups of four to six students each. Then assign students to graph the pyramids of particular countries, identified by numbers. (Assign the countries in numerical order. Each group will then be graphing a variety of pyramid styles.) 8. Have students share their pyramids with the other students in their group. They should discuss similarities and differences in the shapes of their pyramids. What might be some of the reasons for different shapes? For example, Country #12 has many more males than females in the 20-39 age group (male workers migrating from other countries). 9. Now have students group themselves by pyramid shape. (You may wish to post large copies of the different styles of pyramids and then say, "Everyone with a pyramid that looks like Congo come to the front of the room…") Students should then line up by pyramid type, with broad based, narrow-topped pyramids (rapid growth) on the left side of the room, slow-growth pyramids in the center, and negative growth on the right side. 10. Students should look at the list of possible countries and guess which country they represent. After students have made their guesses, the teacher (using the Population Pyramid Data Table Teacher's Key) should identify each of the pyramids graphed by the students. 11. Students should seek patterns among the graphs within the regions. Pyramid Building: Population Pyramid Data Table Males Country 0-19 1 2 3 14 27 17 Females 2039 15 14 19 4059 13 6 10 60+ 0-19 7 2 4 14 26 17 2039 14 15 18 4059 14 7 10 60+ 10 3 5 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 10 26 20 14 28 11 13 19 28 11 16 22 27 14 14 24 13 17 22 30 13 25 25 21 15 16 27 19 23 13 27 25 12 20 15 15 17 15 14 14 15 15 15 15 18 16 14 18 15 16 14 18 16 13 14 16 16 17 15 14 15 16 17 16 15 17 15 18 13 12 9 13 6 14 14 10 5 14 12 9 6 11 12 9 13 11 8 5 13 8 7 9 12 12 7 10 7 12 6 7 13 9 10 2 3 7 2 10 7 6 2 10 4 4 2 7 7 3 9 5 3 2 9 3 3 3 7 7 2 5 3 8 2 2 8 4 9 25 19 14 28 10 12 18 27 10 14 21 27 14 13 23 12 16 21 29 12 23 24 20 15 15 25 18 21 12 26 24 11 19 15 12 17 15 13 14 15 15 15 14 17 15 14 18 15 15 14 17 17 13 14 16 16 17 15 14 14 17 17 15 15 15 14 17 13 5 10 13 6 14 14 11 5 13 12 9 6 12 13 9 13 11 8 6 13 7 7 9 12 12 7 11 8 13 6 7 14 9 14 2 4 9 2 13 9 8 2 14 6 4 3 7 12 3 12 5 4 2 12 3 3 4 8 9 2 5 4 11 3 3 12 5 Teachers Key: Pyramid Building: Data Table Teacher's Key Males Females Poland Haiti Thailand Italy Saudi 5 Arabia 6 Brazil 7 Australia 8 Ethiopia 9 Japan 10 Canada 14 27 17 10 2039 15 14 19 15 14 26 17 9 2039 14 15 18 15 26 15 12 2 25 12 5 2 20 14 28 11 13 17 15 14 14 15 19 14 28 10 12 17 15 13 14 15 4 9 2 13 9 11 Argentina 19 15 10 6 18 15 11 8 12 Kenya 13 Germany South 14 Korea 15 India 16 Nigeria 17 Cuba 28 11 15 5 2 15 14 10 27 10 15 5 2 14 13 14 16 18 12 4 14 17 12 6 22 27 14 16 9 4 14 6 2 18 11 7 21 27 14 15 9 4 14 6 3 18 12 7 18 Lithuania 14 15 12 7 13 15 13 12 19 Egypt United 20 Kingdom 21 China 22 Mexico 24 16 9 3 23 15 9 13 14 13 9 12 14 13 12 17 22 18 11 5 16 8 3 16 21 17 11 5 17 8 4 13 5 29 13 6 0-19 1 2 3 4 Dem. Rep. 23 of the 30 Congo 4059 13 6 10 13 9 13 6 14 14 60+ 0-19 7 2 4 10 3 7 2 10 7 2 4059 14 7 10 13 10 13 6 14 14 60+ 10 3 5 14 3 2 24 France 14 13 9 12 14 13 12 25 Bangladesh 25 16 8 3 23 16 7 3 26 Iran 25 16 7 3 24 16 7 3 27 Indonesia 21 17 9 3 20 17 9 4 28 Ireland 29 Cyprus 30 Pakistan 15 16 27 15 12 7 14 12 7 15 7 2 15 15 25 15 12 8 14 12 9 14 7 2 31 Sri Lanka 19 16 10 5 18 17 11 5 32 Vietnam 33 Romania 23 13 17 7 3 16 12 8 21 12 17 8 4 15 13 11 34 Honduras 27 15 6 2 26 15 6 3 Papua New 25 Guinea 17 7 2 24 15 7 3 15 13 8 18 9 4 11 19 14 14 12 17 9 5 35 36 Hungary 37 Turkey 13 12 20