ckfinder/userfiles/files/Grade 8 population revision guide
advertisement

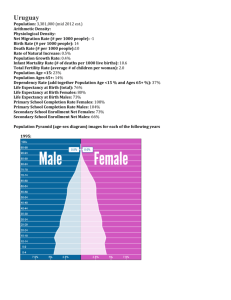
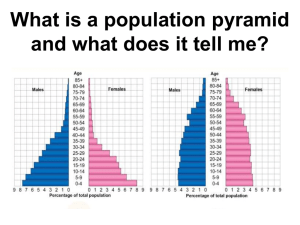
Grade 8 : Population Revision Guide NAME:___________________________________ CLASS: ___________________________________ 1 Figure 1 Figure 2 Sample Answers Level 4/5 work (giving specific examples and referring to the map) Figure 1 and 2 both show population density maps. Figure 2 is more detailed and how densely populated areas of the world are. It is clear that India and China are the most densely populated. Some areas in the East of China have a population density of over 5000 people per km squared, for example Shanghai. This is partly because the eastern part of China has more lowland which is easier to build on. In comparison some areas like Australia and Russia have a low population density with between 0 – 1 people per square km. This is because of the harsh landscape in each country. The desert in Australia is too dry for people to live in and the climate in Russia is too cold. Level 2/3 ( providing a basic overview of the map with very little detail) This map shows where people live. A lot of people live in Europe and Asia. Not as many people live in the top part of North America. It is too cold there. No people live in the North of Africa. Why do people live in some parts of the world and not others? Latitude – people often live near the equator because it is hot and not near the north or south pole because it is too cold. Altitude – it is easier to build on low land rather than mountains Coastal areas – people want to live beside the sea because they are trading points and the cool sea breeze. Migration – people prefer to live in some countries because they are safer than others Historical areas – which were once major trading points. 2 Population Growth Birth rates = the number of live births per 1000 of the population. Death rate = the number of deaths per 1000 of the population. Migration = the movement of people in and out of a country. Natural increase = the birth rate minus the death rate. LEDC = Less economically developed country MEDC = More economically developed country. If the birth rate is higher than the death rate, the total population will increase. If the death rate is higher than the birth rate, then the total population will decrease. Population growth rates are highest in LEDC, where birth rates are high but death rates are beginning to fall. Death rates are falling due to global improvements in health and medicine. Overpopulation With the population increasing rapidly, there is a threat of over population. If this happens there will be an impact on the following…. Food Waste Health care Education Water Energy Increased pressure on food supplies Increased number of deaths from malnutrition (not having enough food to eat). Increased numbers of dumps – which damage the environment. More incinerators (factories which burn rubbish) Longer waiting lists for operations/ appointments to see the doctor. Cost of medicine may increase if it is in short supply Overcrowding in hospitals (this is already happening in some countries) Increased class sizes Two tier day in schools ( some people may have to go to school from 2pm – 8pm Increased competition for university places. Increased pressure on water supplies. Quotas put in place on how much water you can use Cost of water will increase Water may also become more polluted Fossil fuels will run out Pressure to ensure renewable energy (solar/wind/ tidal power) will provide enough energy for the population. 3 4 Population Pyramids Population pyramids = used to show population structure. Life expectancy = how on, on average, a person is expected to live. Population pyramids can be drawn for a whole country or individual settlements (towns or villages). The shape of a population pyramid gives us information about birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy. A population pyramid also tells us about the number of dependents living in an area. Young dependants are children under the age of 15, who are still supported by their family. Elderly dependants are those people aged over 65, who on no longer work. Both of these groups are depend on the economically active (those of working age). Remember – population pyramids can change over time! The population pyramid of the UAE is very different than other countries. The most noticeable difference is that there are far males than females. This is certainly true for the 30 – 34 age bracket. In 2014, there were 645 thousand males and approximately 200 thousand females. There is a low birth rate and the life expectancy is lower than the UK. There are far more males than females because there are more jobs which attract male workers; for example, these are in construction and oil rigs. These types of jobs attract many migrant workers. M E D C The population pyramid for the UK is typical of an MEDC. The ratio of males to females is quite even. The low birth rate is due to access to good health care and education. The life expectancy is high, with people living to 85+. The low death rate is a result of many factors, such as improved medication, diet, new safety laws etc. 5 L E D C This population pyramid of Kenya is a good example on an LEDC 9(poor country). There is a very high birth rate, which is seen when the pyramid has a wide base. This is because there is a lack of contraception and poor education. Child immortality is high. The narrow top means that there is a high death rate. Food shortages, poor health care, lack of education all result in a lower life expectancy. Problems with an ageing population The population in most MEDCs is stable (they have low birth rates and low death rates). However, some MEDCs face the issue of having an ageing population. In Germany, the population is declining because the birth rate is lower than the death rate. Governments need to plan for an ageing population. More hospitals, retirements homes and public transport will be needed. Governments will also need to plan for pensions which means taxes may have to rise. 6 The bare bones! Birth rates = the number of live births per 1000 of the population. Death rate = the number of deaths per 1000 of the population. Migration = the movement of people in and out of a country Overpopulation causes problems for Food Water Homes Health care Waste Education Energy Problems on an ageing population More hospitals needed Better public transport needed Taxes will be raised to pay for pensions. Low birth rate Low death rate People live longer High birth rate High death rate People die at an early age. 7