ANSWERS 3
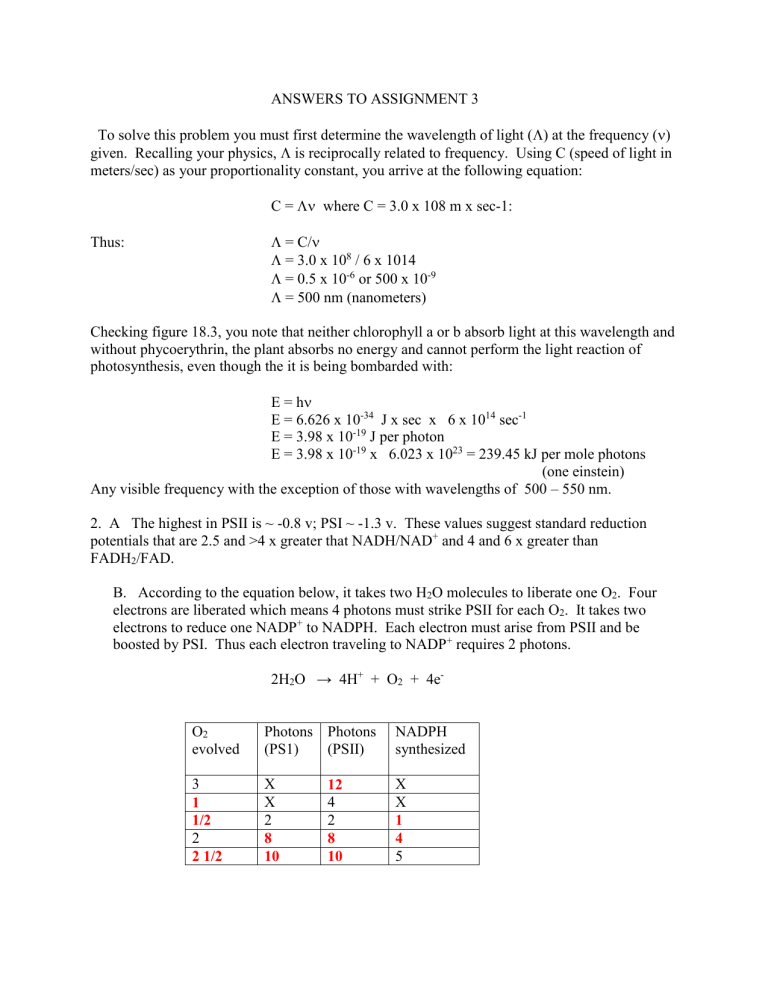
ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT 3
To solve this problem you must first determine the wavelength of light (
) at the frequency (
) given. Recalling your physics,
is reciprocally related to frequency. Using C (speed of light in meters/sec) as your proportionality constant, you arrive at the following equation:
C =
where C = 3.0 x 108 m x sec-1:
Thus:
= C/
= 3.0 x 10
8
/ 6 x 1014
= 0.5 x 10
-6
or 500 x 10
-9
= 500 nm (nanometers)
Checking figure 18.3, you note that neither chlorophyll a or b absorb light at this wavelength and without phycoerythrin, the plant absorbs no energy and cannot perform the light reaction of photosynthesis, even though the it is being bombarded with:
E = h
E = 6.626 x 10 -34 J x sec x 6 x 10 14 sec -1
E = 3.98 x 10
-19
J per photon
E = 3.98 x 10
-19
x 6.023 x 10
23
= 239.45 kJ per mole photons
(one einstein)
Any visible frequency with the exception of those with wavelengths of 500 – 550 nm.
2. A The highest in PSII is ~ -0.8 v; PSI ~ -1.3 v. These values suggest standard reduction potentials that are 2.5 and >4 x greater that NADH/NAD + and 4 and 6 x greater than
FADH
2
/FAD.
B. According to the equation below, it takes two H
2
O molecules to liberate one O
2
. Four electrons are liberated which means 4 photons must strike PSII for each O
2
. It takes two electrons to reduce one NADP
+
to NADPH. Each electron must arise from PSII and be boosted by PSI. Thus each electron traveling to NADP
+
requires 2 photons.
2H
2
O → 4H +
+ O
2
+ 4e
-
O
2 evolved
3
1
1/2
2
2 1/2
Photons
(PS1)
X
X
2
8
10
Photons
(PSII)
12
4
2
8
10
NADPH synthesized
X
X
1
4
5
The key compound is acetyl-CoA. You pathway should show glucose being broken down to pyruvate and from there to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is the gateway to lipid biosynthesis.
The oxidation reaction will generate 8 acetyl-CoAs, and 7 each of NADH and FADH
2
. With
12 ATPs for each acetyl-CoA, 3 for each NADH, and 2 for each FADH2 your total on the synthesis side is 96 + 21 + 14 = 131 ATPs. It cost one ATP to form palmitoyl-CoA, which brings your net total to 130 ATPs for each palmitate oxidized to CO
2
+ H
2
O.
The key intermediate is phosphatidic acid (phosphatidate) To form the triacylglycerols, the phosphoryl group must be hydrolyzed to make room for the addition of the third fatty acid. That reaction is catalyzed by a phosphatase enzyme. To make a glycerophospholipid, the phosphate is left on and an activated (CDP) group is added to the phosphate.