CHAPTER 7 SECTION 1
advertisement

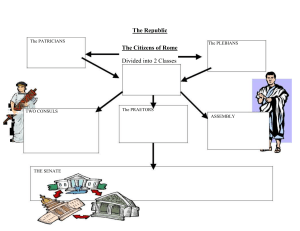
CHAPTER 7 SECTION 1 Founding the Roman Republic The land: Its geography and its importance Sheltered by Alps to north Toe and Heel in Mediterranean to south To east lies Adriatic Sea Able to control eastern and western halves of Mediterranean Apennine Mountains run full length—not very rugged Early trade and travel easy Alps separate Italy from rest of Europe o Several pathways cut through Alps Possible for enemies to invade o Long coastline open to attack from sea Rome and Beginning of an Empire People live here during Paleolithic period About 2000 B.C. invaders swept thru passes and overran peninsula o From north of Black and Caspian Sea Founding of Rome Mid 700s B.C. Latin’s move into west central Italy o Built villages along Tiber River Late 600s B.C. Rome came under control of Etruscan Kings from Northern Italy o Etruscans had written language o Crafted jewelry, fine clothing—metal, pottery and wood working o Knew how to drain swamps, pave roads, and construct sewers Etruscans helped Rome grow into a prosperous city—blended with Roman population Greek colonies in Southern Italy and Sicily became city states o Culture strongly influenced Romans Greek myths and gods—changed names Strategic Location Built on 7 hills along Tiber 15 miles inland from coast Built at crossroads of trade routes Early Roman Republic In 509 B.C. wealthy landowners overthrew Etruscan kings Established Republic—voters elect officials to run state o Only male adult citizens could vote and take part in government Three groups helped govern Republic o Senate Most influential and powerful Controlled public funds and foreign policy Sometimes acted as courts Approved dictators—could rule for 6 months in times of emergency Complete control of army and courts o Magistrates Included consuls, praetors and censors 509 B.C. 2 citizens elected to serve as consuls – or chief executive o Served 1 year term o Ran government, commanded armies, appointed dictators o Consuls governed w/ senate o Each consul could veto other o Checks and balances Praetors—helped consuls Commanded armies in war In peace oversaw legal system Censors Registered citizens according to wealth Appointed candidates to senate Oversaw moral conduct of citizens o Assemblies Voted on laws and elected officials Some voted to make war or peace Others served as courts Elected 10 tribunes—power over actions by Senate and public officials Conflict of the Orders Changes stemmed from many attempts of common people to win more rights Patricians versus Plebeians Patricians o Wealthy landowners who controlled government o Inherited power Plebeians o Made up majority of population Farmers and workers o Had few rights Could vote but not hold office o Could not know laws—were not written down Patricians served as judges o Increased power through demands and strikes Gained rights to join army, hold office and form own assembly Forced government to wrote down laws 450 B.C. 12 Tables established—placed in Forum for all to see o First plebeians appointed to government in late 400s B.C. o After 342 B.C. one consul position was always a plebian o By 300 B.C some plebeians became as powerful as Patricians—helped for Roman Nobility o Government positions were not paid—only wealthy could afford job Republic grows For 200 years fought wars against neighbors By 265 B.C. controlled all of Italy—south of Rubicon Extended Republic w/ well organized army and wise policies Role of Roman Army Every male citizen who owned land required to serve Major unit was called a legion o 4000-6000 soldiers or legionnaires Later established auxilia or army of non citizens In general army was well trained and morale was high Role of Wise policies Rome granted full citizenship to inhabitants of nearby Italian citizens Granted partial citizenship to more distant cities—Greek Colonies in Italy Partial citizens could own property and marry—but not vote Allowed allies to remain independent butt allies would provide soldiers to Roman army Also expected conquered people to give land to Roman farmers Helped Romans maintain control over conquered areas