Infant Motor Reflexes & Development Checklist
advertisement
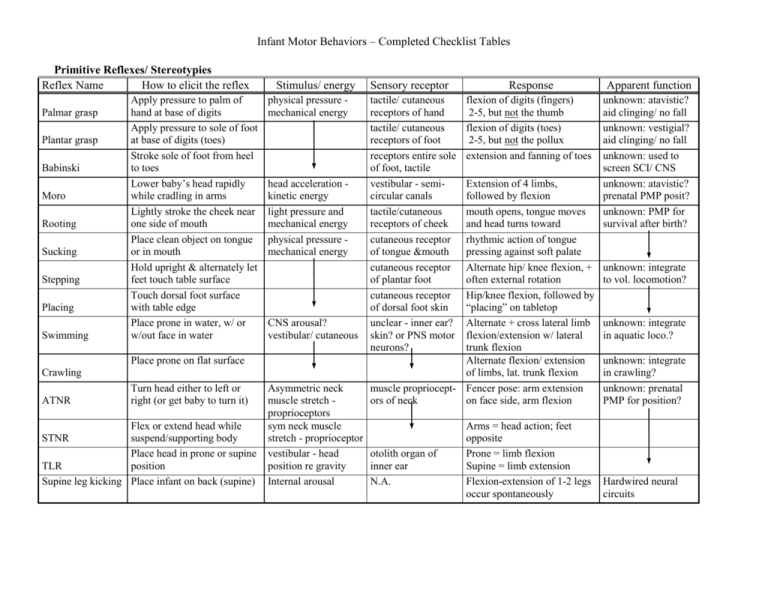
Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies Reflex Name How to elicit the reflex Palmar grasp Plantar grasp Babinski Moro Rooting Sucking Stepping Placing Swimming Apply pressure to palm of hand at base of digits Apply pressure to sole of foot at base of digits (toes) Stroke sole of foot from heel to toes Lower baby’s head rapidly while cradling in arms Lightly stroke the cheek near one side of mouth Place clean object on tongue or in mouth Hold upright & alternately let feet touch table surface Touch dorsal foot surface with table edge Place prone in water, w/ or w/out face in water Place prone on flat surface Crawling ATNR Turn head either to left or right (or get baby to turn it) Flex or extend head while suspend/supporting body Place head in prone or supine TLR position Supine leg kicking Place infant on back (supine) STNR Stimulus/ energy physical pressure mechanical energy head acceleration kinetic energy light pressure and mechanical energy physical pressure mechanical energy CNS arousal? vestibular/ cutaneous Sensory receptor tactile/ cutaneous receptors of hand tactile/ cutaneous receptors of foot receptors entire sole of foot, tactile vestibular - semicircular canals tactile/cutaneous receptors of cheek cutaneous receptor of tongue &mouth cutaneous receptor of plantar foot cutaneous receptor of dorsal foot skin unclear - inner ear? skin? or PNS motor neurons? Response Apparent function flexion of digits (fingers) 2-5, but not the thumb flexion of digits (toes) 2-5, but not the pollux extension and fanning of toes unknown: atavistic? aid clinging/ no fall unknown: vestigial? aid clinging/ no fall unknown: used to screen SCI/ CNS unknown: atavistic? prenatal PMP posit? unknown: PMP for survival after birth? Extension of 4 limbs, followed by flexion mouth opens, tongue moves and head turns toward rhythmic action of tongue pressing against soft palate Alternate hip/ knee flexion, + often external rotation Hip/knee flexion, followed by “placing” on tabletop Alternate + cross lateral limb flexion/extension w/ lateral trunk flexion Alternate flexion/ extension of limbs, lat. trunk flexion muscle propriocept- Fencer pose: arm extension ors of neck on face side, arm flexion Asymmetric neck muscle stretch proprioceptors sym neck muscle stretch - proprioceptor vestibular - head otolith organ of position re gravity inner ear Internal arousal N.A. Arms = head action; feet opposite Prone = limb flexion Supine = limb extension Flexion-extension of 1-2 legs occur spontaneously unknown: integrate to vol. locomotion? unknown: integrate in aquatic loco.? unknown: integrate in crawling? unknown: prenatal PMP for position? Hardwired neural circuits Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables Lifespan, Nondevelopmental Reflexes/ Stereotypies Reflex Name How to elicit the reflex Stimulus/ energy Pupillary shine bright light in eye after being in the dark Vestibulo-ocular Quickly spin person (nystagmus) around longitudinal axis intensity of light electromagnetic spectrum acceleration of head mechanical energy Heart rate Quickly move object toward eye or puff of air or foreign object (dust) Change emotional state; exercise; fright-fight Breathing Change emotional or exercise state of body varies, but involves increased excitatory nervous stimulation CO2 levels in arterial blood supply Epiglottal Swallow liquid or solid food physical pressure mechanical energy Eye blink Flexor withdrawl Firmly tap a relaxed, stretched tendon (eg patellar, Achilles) Noxious, painful, or tickle stimulus to extremity Crossed extension Elicit flexor withdrawl reflex in opposite limb Tendon stretch Startle Supine leg kick Sudden, unexpected, and/or intense light, sound, touch, etc. See previous sheet of primitive reflexes visual and/or mechanical any type of energy that is unexpected, intense, sudden Sensory receptor Response retinal cells especially cones Apparent function Pupil constricts with increased light intensity; dilates with low intensity semicircular canals “ramp movement”of eye of inner ear with slow, tracking mvt opposite rotation followed by saccade in rot. direction cutaneous receptors Rapid closing of eyelid over of eyeball eyeball; stimulation of tear duct to lub. cornea adjust light intensity to retinal image; protect cones unknown - link head eye motion; maintain balance; track objects? Thalamus/ hypothalamus and node of heart intracirculatory cells of CNS circulate sufficient O2 to tissues/organs laryngeal swallowing contractions muscles spindles/ GTOs of muscle cardiac muscle contractions increase rate with exercise or CNS activation increased ventilatory rate/ contractions of diaphragm or costal muscles epiglottis contracts and covers the bronchial opening rapid contraction of stimulated muscle protect muscles from overstretch cutaneous receptor flexion of entire limb of including free nerve stimulated extremity ending extension of entire limb opposite stimulated extremity visual, auditory, sudden, rapid limb extension gustatory,vestibular or “startle” reaction , proprioception protect corneal surface of eye provide adequate O2 exchange in lungs for circulation protect bronchia from foreign obj. remove limb from noxious stimulus support body during withdrawl “flight or fight” preparation - CNS activation Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables Postural, Equilibrium Reactions Reaction Righting Head Sagittal trunk pivot prone/Landau Derotative Parachute/propping Downward - arms How reaction is elicited Stimulus/ energy Body out of alignment w/ grav. gravitational force Place infant in prone position on head position in flat surface relation to gravity Sensory receptor vestibular apparatus otolith organ - inner ear Place infant in prone position on flat surface Response generically to align w/ gravity Head hyperextends at neck, raising face from surface Apparent function maintain upright posture Get head upright in space, aligned with gravity Trunk hyperextends, arching head and legs off surface Get trunk upright/ aligned and minimize energy use Place infant in prone position on flat surface Place infant supine and twist legs and/or shoulder girdle physical energy muscle stretch muscle receptors, esp muscle spindles Opposite segment “untwists” in direction of twisted segment To reduce muscle stretch/ keep segments aligned Downward - legs Sideward/ lateral body downward quickly Displace infant laterally in a quick motion Acceleration - kinetic downward acceleration/ kinetic energy lateral acceleration kinetic energy Forward/ anterior Quickly displace infant in the anterior direction/plane anterior acceleration/ kinetic energy hair cells of semicircular canals Arms extend anteriorly in direction of the fall Anticipate and cushion impact from forward fall Backward/ posterior Quickly displace infant in the posterior direction/plane posterior acceleration/ kinetic energy hair cells of semicircular canals Arms extend posteriorly in direction of the fall Anticipate and cushion impact from backward fall displacing support surface vestibular/propriocept adjustment of head/torso Keep alignment w/ grav. Prone In prone position, tilt support surface forward or backward head position in space + muscle stretch inner ear + muscle spindles otolith organ of inner ear + proprioceptors Head and trunk move away from direction of tilt Minimize energy use and maintain prone posture Supine In supine position, tilt support surface forward or backward Head and trunk move away from direction of tilt Minimize energy use and maintain supine posture Sitting In sitting position, tilt support surface to front/back/side Trunk and spine move in direction away from tilt Minimize energy use and maintain sitting posture All-fours On “all-fours,” tilt support surface to front/back/side Limb adjustment away from direction of downward tilt Minimize energy use and maintain all-four balance Standing In upright/stand, tilt support surface to front/back/side Trunk and legs lean away from direction of downward tilt Minimize energy use and maintain upright posture Tilting Body position changed quickly In vertical position, displace Get trunk upright/ aligned to maintain vertical vestibular apparatus extension in direction of mvt semicircular canals of Arms extend and abduct up reduce pot. impact forces Anticipate impact from vestibular apparatus hair cells of semicircular canals Legs extend and abduct + down falling downward Arms extend laterally in Anticipate and cushion direction of the fall impact from sideward fall Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables Voluntary Motor Skills (a.k.a. Motor Milestones) Motor skill Rolling over allow person to change prone to supine or vs. rotation of head, trunk, pelvis, leg action, arm action from inability to roll over to turn over to twisting during turn over Task factors movement characteristics surface characteristics, speed demands, original position, ATNR Sitting up position trunk in upright posture w/ pelvis-leg base trunk posture, head posture, leg position, arm action from inability to sit up independently to partial sit to upright sit sitting surface, presence of back or sit support, strength, CNS Crawling locomotion while in prone position – trunk contact head position, trunk in contact with from no crawling to initial attempts to surface, arm/leg actions advanced crawling with progress head position, trunk action, arm and leg actions head position, quadripedal surface contact, arm/ leg actions from crawling action w/trunk touching to rapid, all-4s creeping movement distance to cover, height of mvt space, type of surface, strength Standing Locomotion in prone position with quadripedal contact maintaining upright posture with feet as base of support head posture, trunk posture, leg action/posture; arm position/action inability to stand to standing with assist surface char., arm support, trunk to standing independently support, leg strength, balance Independent Walking upright locomotion on feet w/alternating leg action trunk/pelvic action, leg action, arm action no walking to cruising to independent walking to heel-toe action/alt. arms Creeping Goal/ function of skill Critical features/ components Changing movement characteristics surface characteristics, arm/trunk support, leg strength, balance Fundamental Motor Skills Jumping upright locomotion on feet from 2 feet to 2 feet Galloping/ Sliding Step + backward leap/ side facing Running/ Leaping upright locomotion alt. leg action w/ flight phase Hopping upright locomotion - w/ weight shift on 1 leg only Skipping Step and hop on alternate feet with uneven rhythm Throwing /Striking Projecting/sending away a ball from the hand of person or using implement Kicking Projecting a ball with foot trunk action, leg action, arm action; from no jump to step down to different phases of mvt momentary flight to bounce jump etc. Leg action, arm action From no leap and same lead leg to leaping with either leg leading trunk/pelvis action, leg action, arm from no run to momentary run to action, stance vs swing phase advanced run with different speeds leg action, arm action movement from pre-hop through 4 steps of leg components and 5 steps of arm actions Leg action, arm action From single side skip to 2-side skip on ball of foot landing; bilateral to oppos. foot/leg, trunk, forearm, humerus 4 steps in leg, 3 trunk, 3 forearm, 3 actions, backswing components humerus, 4 backswing components surface char., distance, height, time, leg strength Speed, direction, lead leg, obstacles Prep. backswing, step, trunk Segmented action to integrated Size of ball, distance, mvt. ball Catching Arms, hands, trunk 3 components with different levels Size, weight of ball, trajectory, distance, speed, color contrast speed, surface type, surface hgt, use of hands, clothing, body comp Rising to Stand from Supine Receiving or gathering in object getting up from lying supine to upright stand upper extremity, trunk(axial), lower 6 steps in upper extremity, 5 steps in extremity components trunk, 5 steps in lower extremity surface, speed, distance, leg strength distance to hop, speed, obstacles, leg strength, balance Distance to skip, speed, obstacles, leg strength, balance force/distance, ball-hand ratio, target size/accuracy/mvt, body size