Intermolecular Forces Worksheet
advertisement

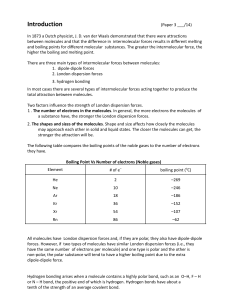
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet 1. For each of the following compounds, determine the intermolecular force(s) involved in each. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures for some of these molecules: Nitrogen carbon tetrachloride H2S sulfur monoxide N2H2 boron trihydride CH4O SiH2O 2. What is the strongest intermolecular force present for each of the following compounds? Water carbon tetrachloride ammonia carbon dioxide phosphorus trichloride nitrogen ethane (C2H6) acetone (CH2O) methanol (CH3OH) borane (BH3) FCN HCN 3. Explain why ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) has a higher boiling point (78.40 C) than methyl alcohol (CH3OH; 64.70 C). 4. Rank the following by from lowest to highest anticipated boiling point: C2H4, CH4, Ne, H3COCH3. Compd N2 CO Br2 ICl Mol. Wt. Boil Point -196 oC -192 oC 59 oC 97 oC 28 28 160 162 5. Using the chart above answer the following questions a. Which compound has the weakest force? b. Which compound has the strongest force? c. What force holds Br2 together in the liquid state? 6. How can non-polar molecules such as Br2, I2, and N2 condense to form liquids and solids? Molecule CH4 (methane) C2H6 (ethane) C3H8 (propane) C4H10 (butane) Boiling Point (oC) - 161.5 - 88.6 - 42.1 - 0.5 7. Using the chart above explain why the boiling points for the molecules above decrease as H’s and C’s increase