Plant Evolution Cladogram Worksheet
advertisement

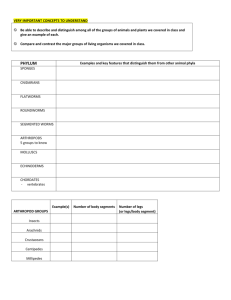
NAME _____________________________________DATE __________________________ PER __________ PLANT EVOLUTION CLADOGRAM Define the traits and types of plants in the table below. Make sure to use reliable resources. Trait Charophytes Bryophytes Pteriphytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophyll Seeds Fruit Pollen Vascular Tissue Cuticle Present Flower Dominant Sporophyte Definition Now that you know what the traits and types of plants are, mark an “X” in each box for the groups of plants that share that trait. Then using the information in the table, create a cladogram that outlines the evolution of plants. The traits are not in the order of evolution. Plant groups should be placed on vertical arrow. Traits should be located on horizontal lines. Charophytes Bryophytes Common Names Chlorophyll Seeds Fruit Pollen Vascular Tissue Cuticle Present Flower Dominant Sporophyte Pteriphytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms 1. What were the precursors to land plant? 2. In land plants, which of the taxa (groups) is the oldest? 3. What vascular land plant came next? 4. Looking at the chart, what type of land plants occurred next? 5. What was the last group of land plants to evolve? 6. What is a seed, and why was the evolution of the seed such an important innovation for plants? 7. How do the mechanisms by which sperm reach the egg differ between gymnosperms and seedless vascular plants? 8. Why was the flower such an important innovation? 9. What role do insects, animals and wind play in plant reproduction? 10. How does the pollination of gymnosperms and angiosperms differ? 11. Explain the difference between the following terms: a. Vascular and non-vascular plants: b. Angiosperm and Gymnosperm: 12. What are three differences between algae and land plants? 13. Name two adaptations that ferns have which they do not share with bryophytes. 14. Name one adaptation which gymnosperms have but ferns do not. 15. Name two adaptations, which angiosperms have, but gymnosperms do not.