Chemistry Homework: Noble Gas Config & Periodic Trends
advertisement

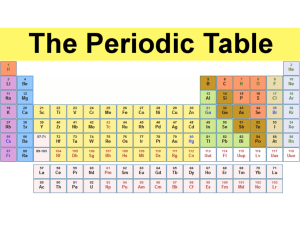
CH 5 HOMEWORK: Noble gas configuration: [Ne] 3s1 [Kr] 5s2 [He] 2s2 2p3 [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5 [Ar] 4s2 3d5 [Kr] 5s2 4d4 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d4 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p5 [Rn] 7s2 5f1 [Xe] 6s2 4f7 Na Sr N Br Mn Mo W Pb I Ac Eu Review: 1. Who is credited with discovering: Chemical periodicity – Mendelyeev The atomic number as the basis for the organization of the periodic tableMoseley 2. Explain the periodic law. When the elements are arranged by atomic number, elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals (2-8-8-18-18-32…) 3. Name the 4 changes to the periodic table after Mendeleev’s time. Organization by atomic number, addition of “new” elements, addition of group 18, separation of the rare earth elements. 4. What are main group elements. S and p block elements 5. What is the relationship among the elements within a certain group on the periodic table? Similar electron configurations, same number of outershell electrons, similar properties. 6. What name is given to each of the following groups of elements and what are the general properties of those elements: a) b) c) d) e) group 1 group 2 groups 3-12 group 17 group18 alkali metals; reactive, low density, low melting point, soft alkaline earth metals; not as reactive as group 1, higher densities transition metals; typical metals..high MP, dentity, strong halogens; reactive noble gasses; nonreactive 7. Explain each of the following and state the group and period trends for each: a) atomic radii radius of an atom; increases, decreases b) ionization energy energy required to remove an outershell electron decreases, increases c) electronegativity ability to attract and hold an additional outershell electron. decreases, increases. 8. Why are the noble gasses relatively nonreactive? Full energy level 9. What determines the length of each period on the periodic table? What orbitals are filled between the s and p. 10. What is the relationship between electron configuration and the period that the element is in? the period number is the principle quantum number for the s and p orbitals 11. What is an ion? An atom or group of atoms with a positive or negative charge. What is a cation? What is an anion? Positive ion; negative ion How is each formed? Cation-loses electrons; anion-gains electrons 12. What are valence electrons. Outershell electrons. 13. Write the noble gas configuration for: a) Li [He] 2s1 b) P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 c) Y [Kr] 5s2 4d1 d) Hg [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 e) U [Rn] 7s2 5f4 14. Based on the information below, give the group # (1 – 18), period #, block, and name of each of the following: a) [Ne] 3s2 3p1 13; 3; p; aluminum b) [He] 2s2 2; 2; s; beryllium c) [Ar] 4s2 3d10 12; 4; d; Zinc 15. By location on the periodic table, place the following elements in order by decreasing ionization energies: Li O C K Ne F Ne, F, O, C, Li, K 16. If an element has a high ionization energy will it also have a high electronegativity? Yes; except for Noble gases 17. Determine the charge of the ion most likely to be formed by each of the following: a) Li +1b) B +3c) O -2d) F -1e) Mg +2f) Al +3g) P -3 h) S -2 i) Br -1 j) Ba +2 k) Ne 0 18. Which of the following ions is least likely to form? I-1 Sr+2 Al+3 K+2 O-2 K+2 19. Write the electron configuration notation for the ions of oxygen and aluminum. O-2 1s2 2s2 2p6 Al+3 1s2 2s2 2p6