Chapter 3
advertisement

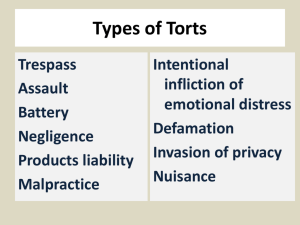
Name: Business Law Chapter 3 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. A tort is a wrong committed against an individual. 2. Public officials must prove actual malice to succeed in a defamation lawsuit. 3. Invasion of privacy is an unintentional tort. 4. Even the most careless conduct will not result in liability for negligence unless there is actual harm. 5. The main difference between intentional torts and negligence is that one is deliberate, while the other is usually caused by carelessness. 6. Although the reasonable person test is very subjective, it is used primarily in intentional tort cases. 7. The tortfeasor is the plaintiff in a lawsuit. 8. Mexican tort law does not provide for compensation for pain and suffering. 9. Current tort reform legislation includes survival statutes and wrongful death statutes. 10. If you are driving your car too fast on a rainy evening and have an accident, you might have committed an intentional tort. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 11. A wrongful injury to, or interference with, the property of another is a. nuisance. c. trespass. b. defamation. d. invasion of privacy. 12. A false statement made orally to a third party is a. slander. c. breach of duty. b. defamation. d. libel. 13. People who are engaged in extremely dangerous activities may be held liable even without negligence or malice; this is known as the doctrine of a. assumption of risk. c. unintentional liability. b. strict liability. d. dangerous liability. 14. To determine if the defendant's conduct was the proximate cause of the plaintiff's injury, the court applies the a. proximate cause test. c. forensic test. b. actual cause test. d. foreseeability test. 15. The negligence defense that might be used by a baseball club that is sued by spectators is a. contributory negligence. c. assumption of risk. b. comparative negligence. d. proximate cause. 16. The difference between a crime and a tort is that a crime is committed against the public good, while a tort a. is committed against a particular person or property. b. is caused when someone is being threatened. c. is considered a wrong against all of society. d. hurts all members of the community. 17. Examples of intentional torts include a. false imprisonment and disparagement. b. negligence and arson. c. assault and rape. d. forgery and proximate cause. 18. Your neighbor continues to play very loud music that is keeping you awake at night. This is an example of a. strict liability. c. product liability. b. an intentional tort. d. negligence. 19. Using explosives and keeping alligators as pets are examples of a. survival statutes. c. conversion. b. negligence. d. strict liability. 20. The remedies available in tort law usually include a. a public apology by the tortfeasor printed in the local newspaper. b. prison time for the tortfeasor. c. financial compensation to the victim for injuries caused by the tortfeasor. d. financial compensation for the victim and prison time for the tortfeasor. Completion Complete each statement. 21. When one person interferes with another's rights, either intentionally or negligently, a(n) ____________________ is committed. 22. Loud noises late at night, noxious odors, and fumes coming from a nearby house are all examples of ____________________. 23. The wrongful act of injuring another person's reputation by making false statements is known as ____________________. 24. If a wrongdoer has injured another party, a court will usually award ____________________ to the injured party. 25. ____________________ consists of lies about objects. 26. A(n) ____________________ is a wrong committed by a person who knows and wants the resulting consequences. 27. In a product liability case, both the seller and the ____________________ of the item are liable for injuries caused by the product. 28. Under the doctrine of ____________________, the amount of the plaintiff's recovery is reduced by the percent of his or her negligence. 29. Entering another person's land or property without permission is called ____________________. Matching Match each term with its definition. a. intentional tort f. b. strict liability g. c. nuisance h. d. defamation i. e. negligence j. duty of care proximate cause contributory negligence comparative negligence assumption of risk 30. The obligation to use a reasonable standard to prevent injury to others 31. Anything that interferes with the enjoyment of life or property 32. Negligence of each party is compared, and the amount of the plaintiff's recovery is reduced by the percent of his or her negligence 33. The failure to exercise the degree of care that a reasonable person would have exercised in the same circumstances 34. Behavior by the plaintiff that helped to cause the injury 35. Actions that are deliberate and cause hurt or embarrassment to others 36. When the plaintiff knew of the risk involved and still took a chance of being injured 37. The wrongful act of injuring another's reputation by making false statements 38. The legal connection between unreasonable conduct and the resulting harm 39. A legal doctrine that says some activities are so dangerous that liability will always follow Short Answer 40. What is the difference between a crime and a tort? Describe the three elements to any tort. Then discuss how tort law impacts business, and provide an example.