Exam Review Sheet - Answer Key
advertisement
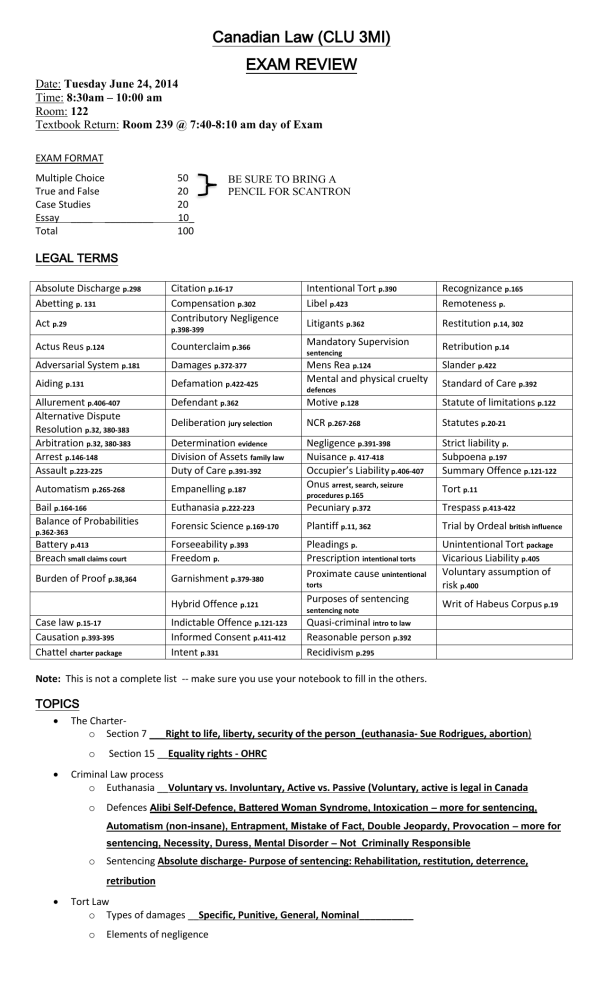
Canadian Law (CLU 3MI) EXAM REVIEW Date: Tuesday June 24, 2014 Time: 8:30am – 10:00 am Room: 122 Textbook Return: Room 239 @ 7:40-8:10 am day of Exam EXAM FORMAT Multiple Choice True and False Case Studies Essay ____ _________ Total 50 20 20 10_ 100 BE SURE TO BRING A PENCIL FOR SCANTRON LEGAL TERMS Absolute Discharge p.298 Abetting p. 131 Act p.29 Citation p.16-17 Compensation p.302 Contributory Negligence Actus Reus p.124 Counterclaim p.366 Mandatory Supervision Adversarial System p.181 Damages p.372-377 Aiding p.131 Defamation p.422-425 Mens Rea p.124 Mental and physical cruelty Allurement p.406-407 Alternative Dispute Resolution p.32, 380-383 Arbitration p.32, 380-383 Arrest p.146-148 Assault p.223-225 Defendant p.362 Motive p.128 Statute of limitations p.122 Deliberation jury selection NCR p.267-268 Statutes p.20-21 Determination evidence Division of Assets family law Duty of Care p.391-392 Strict liability p. Subpoena p.197 Summary Offence p.121-122 Automatism p.265-268 Empanelling p.187 Negligence p.391-398 Nuisance p. 417-418 Occupier’s Liability p.406-407 Onus arrest, search, seizure Bail p.164-166 Balance of Probabilities Euthanasia p.222-223 Pecuniary p.372 Trespass p.413-422 Forensic Science p.169-170 Plantiff p.11, 362 Trial by Ordeal british influence Battery p.413 Breach small claims court Forseeability p.393 Freedom p. Burden of Proof p.38,364 Garnishment p.379-380 Pleadings p. Prescription intentional torts Proximate cause unintentional Unintentional Tort package Vicarious Liability p.405 Voluntary assumption of risk p.400 Hybrid Offence p.121 Purposes of sentencing Indictable Offence p.121-123 Informed Consent p.411-412 Intent p.331 Quasi-criminal intro to law Reasonable person p.392 Recidivism p.295 p.398-399 p.362-363 Case law p.15-17 Causation p.393-395 Chattel charter package Intentional Tort p.390 Libel p.423 Recognizance p.165 Remoteness p. Litigants p.362 Restitution p.14, 302 Retribution p.14 sentencing defences procedures p.165 torts sentencing note Slander p.422 Standard of Care p.392 Tort p.11 Writ of Habeus Corpus p.19 Note: This is not a complete list -- make sure you use your notebook to fill in the others. TOPICS The Chartero Section 7 ___Right to life, liberty, security of the person_(euthanasia- Sue Rodrigues, abortion) o Section 15 __Equality rights - OHRC Criminal Law process o Euthanasia __Voluntary vs. Involuntary, Active vs. Passive (Voluntary, active is legal in Canada o Defences Alibi Self-Defence, Battered Woman Syndrome, Intoxication – more for sentencing, Automatism (non-insane), Entrapment, Mistake of Fact, Double Jeopardy, Provocation – more for sentencing, Necessity, Duress, Mental Disorder – Not Criminally Responsible o Sentencing Absolute discharge- Purpose of sentencing: Rehabilitation, restitution, deterrence, retribution Tort Law o Types of damages __Specific, Punitive, General, Nominal__________ o Elements of negligence Plaintiff has suffered actual damages Causation Lack of Reasonable Duty of Care Foreseeability o Forms of defamation- __Slander & libel o Defences for defamation Truth, Absolute Privilege, Qualified Privilege, Fair Comment o Defences for negligence Voluntary Assumption of Risk, Act of God, Contributory Negligence, Participation in Illegal Activities TRUE OR FALSE _T _ Trespass, libel and slander are intentional torts _T_ An action that is a tort might also be a crime _ F__ It is possible for people to consent to intentional torts being committed against them _ F __ The standard in a negligence case is measured by perfect conduct reason person _ T __ A plaintiff can be partially at fault in a civil suit __ T __ An employer can be responsible for damages received by an employee based on the principle of vicarious liability Driving company vehicle _ T __ Nuisance is the interference of the use and enjoyment of land _ T __ Defamation of character can only apply if the statement is written or spoken _T_ A landmark case for manufacturer’s liability is: Donahue v. Stevenson (1932) Standard of Care _ F __ A trespasser is anyone who enters another person’s property onto land without consent _T_ A law is a legal agreement which society believes in _ T __ Laws developed by Parliament are called statutes _ F __ An example of public law is tort law _ F __ Section 7 of the Charter deals with equality rights _ F __ The guilty mind or intent is actus reus mens rea _T_ An attraction for children is called an allurement – confusing to students (thought pedifile) _ F __ An offence that can be either an indictable or summary is a purebred _T_ A method of collection for a civil judgment is to garnish the wages _ T __ Foreseeability, causation and duty of care are terms associated with negligence _ F __ Youth in Asia = mercy killing Euthanasia _T_ Provocation is not a defence _ F __ Automatism, Sleep walking, mental disorders, drunkenness are all N.C.R. defences __ T _ Subpoena = summons _ F __ To ‘pay back’ = retribution Restitution __ T _ Concurrent means serving two sentences at the same time FILL IN THE BLANKS __Empanelling__ The process of jury selection __Special____ Damages that involve money _Occupier’s Liability__ The act that outlines property liability __Recognizance____ A ‘promise to appear’ ___Negligence_____ Breach of duty of care is: ___Adversarial_____ The justice system used in Canada __Reasonable Limits_ Section 1 of the Charter - ____________ _____________ Clause __Statutes ___ Laws created by parliament __Case ____ Laws created by court __Common _____ Laws defined by history and tradition Voluntary Assumption The defence for negligence where the plaintiff knew the risk but took the of Risk____ __Recidivism chance anyways __ ___Assembly___ Returning back -- as returning back to crime or prison Not religion, expression, or association but ______________________











