Study Guide - Professor Fink
advertisement

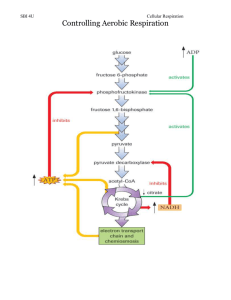
Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 1 Steven A. Fink; Instructor PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE 3: CELLULAR RESPIRATION True/False ____ 1. Oxidation is a type of catabolic reaction. ____ 2. Proteins are more important as an energy source than carbohydrates. ____ 3. Almost everything we eat is made-up of cells, or was made-up of cells. ____ 4. Most metabolic wastes produced by our body cells are excreted in the feces. ____ 5. As you begin to exercise, the rate of cellular respiration within the muscles speeds-up. ____ 6. The amount of O2 you consume is proportional to the amount of food that your body cells oxidize for energy. ____ 7. Diabetes is associated with a person having an abnormally low blood sugar level. ____ 8. Body heat results from the metabolic reactions occurring in the cells of the body. ____ 9. In the Electron Transport System, hydrogen atoms are attached to ATP molecules. ____10. During exercise, the blood sugar level increases. ____11. During cellular respiration, more than ½ of the chemical potential energy contained in a glucose molecule is released as heat. ____12. The amount of O2 that must be consumed after exercise depends upon the amount of lactic acid that was formed during exercise. ____13. One molecule of glucose contains more chemical energy than 6 molecules of CO2. ____14. The hydrogen atoms (& electrons) that are removed from sugars during cellular respiration, are attached to the oxygen that we inhale. 1 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 2 ____15. "Catabolic hormones" would stimulate the break-down of organic molecules in body cells for energy. ____16. The amount of CO2 you exhale is proportional to the amount of food that your body cells oxidize for energy. ____17. Most of the cells of the pancreas are involved in producing insulin. ____18. Carbon dioxide is produced during glycolysis. ____19. Lactic acid is one of the end-products of the Kreb's (Citric Acid) cycle. ____20. Glucose contains more chemical potential energy than two molecules of pyruvate sugars (pyruvic acid). ____21. The difference in the metabolic reactions occurring in nerve and muscle cells is primarily the result of differences in the kinds of enzymes produced in these two cell types. ____22. The mitochondria of a cell produce about twice as much ATP as is synthesized in the cytoplasm. ____23. The oxygen that we breathe is used within the cell to produce carbon dioxide. ____24. Under anaerobic conditions, fatty acids are broken-down for energy. ____25. Amylase is a digestive enzyme that breaks-down starch. ____26. "Anabolic" steroids stimulate the break-down of organic molecules in body cells for energy. Multiple Choice ____27. Substances in our diet such as Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and beta-carotene may slow the process of aging by: (a) the frequency of DNA replication (b) the frequency of DNA replication stimulating cell division of nerve cells (c) inhibiting the oxidation of organic compounds in our body by "free radicals” (d) reducing UV damage of the skin cells 2 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 3 ____28. During exercise, muscle cramps may develop due to the production of: (a) CO2 (b) citric acid (c) NAD-H2 (d) ATP (e) lactic acid ____29. After strenuous exercise an individual continues to breathe at an increased level because: (a) this breathing pattern prevents clogging of the airways with mucus (b) lactic acid must be eliminated via the lungs (c) accumulated lactic acid must be completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O using O2 (d) this breathing pattern acts to dissipate heat from the body (e) of purely psychological factors ____30. The reaction: ADP + Pi + energy ATP, is called: (a) phosphorylation (b) hydrolysis (c) dehydration synthesis (d) deamination (e) transcription ____31. The B-vitamins are primarily associated with: (a) brain function (b) hormone synthesis (c) cellular respiration (d) digestion (e) reproduction ____32. The pancreatic islets (Islets of Langerhans) secrete: (a) oxytocin & glucagon (b) glucagon & insulin (c) cortisol & insulin (d) insulin & adrenalin ____33. All of the following statements about ATP are correct EXCEPT: (a) ATP is used to provide energy in all cells of the body (b) ATP releases energy when its chemical bonds are split (c) ATP is a nucleotide (d) ATP contains phosphate groups (e) each ATP molecule contains more energy than each glucose molecule 3 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 4 ____34. ATP is: (a) a nutrient that is present in all foods that we eat (b) produced by the cells in our body by the break-down of food (c) both (a) and (b) are correct (d) none of the above ____35. The correct sequence for cellular respiration is: (a) Kreb’s Cycle Glycolysis Electron Transport System Transition Reaction (b) Glycolysis Electron Transport System Transition Reaction Kreb’s Cycle (c) Glycolysis Kreb’s Cycle Transition Reaction Electron Transport System (d) Glycolysis Transition Reaction Kreb’s Cycle Electron Transport System (e) Kreb’s Cycle Transition Reaction Glycolysis Electron Transport System ____36. When O2 is not present, muscle cells break-down ______ glucose molecules compared to muscle cells with O2 (in order to produce the same amount of ATP). (a) fewer (b) the same number (c) more (d) too variable to determine ____37. Most ATP is produced in what series of reactions? (a) Glycolysis (b) fermentation (c) Electron Transport System (d) Krebs Citric Acid Cycle (e) deyhydration synthesis (ab) gluconeogenesis ____38. The Electron Transport System is located in the: (a) mitochondria (b) cytoplasm (c) nucleolus (d) Golgi Complex (e) Endoplasmic Reticulum 4 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 5 ____39. The essential difference between combustion of gasoline in a car and the oxidation of organic molecules in cellular respiration is that: (a) O2 is not required for combustion of gasoline (b) no heat is produced in the combustion of gasoline (c) no CO2 is produced in the combustion of gasoline (d) the breaking of C-H covalent chemical bonds in cellular respiration is controlled and step-wise, and not explosive (e) there are no differences between oxidation of food and combustion of gasoline ____40. In which series of reactions is glucose converted into 2 molecules of pyruvate sugars (pyruvic acid)? (a) Glycolysis (b) the Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle (c) the Electron Transport System (d) the Transition Reaction (e) fermentation (ab) gluconeogenesis ____41. In which series of reactions are acetyl-CoA molecules converted into CO2? (a) Glycolysis (b) the Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle (c) the Electron Transport System (d) the Transition Reaction (e) fermentation (ab) gluconeogenesis ____42. Most CO2 is formed in what series of reactions? (a) Glycolysis (b) fermentation (c) Electron Transport System (d) Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle (e) Transition Reaction (ab) gluconeogenesis ____43. Which one of the following series of reactions occurs only when insufficient O2 is available to the cell? (a) glycolysis (b) Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle (c) fermentation (d) Electron Transport System (e) transition reaction (ab) gluconeogenesis 5 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 6 ____44. When sugars are broken-apart completely, only about _____% of the energy released is used to make ATP. (a) 5 (b) 25 (c) 40 (d) 80 (e) 100 ____45. In the Transition Reaction of Cellular Respiration: (a) pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is broken-down to acetyl-CoA (b) pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is broken-down to H2O (c) hydrogen atoms are transferred onto CO2 molecules (d) pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is converted to lactic acid (e) hydrogen atoms are transferred onto oxygen atoms ____46. Uric acid is formed from the break-down of: (a) glycogen (b) nucleic acids (c) lactic acid (d) glucagon (e) fat ____47. We must breathe O2 in order to survive because oxygen: (a) is used by the cells of our body to produce sugars & other organic molecules (b) is necessary for the formation of ethyl alcohol during fermentation (c) accepts the hydrogen atoms transferred from hydrocarbon molecules, as they are broken-down for energy (d) acts to attach the cells of a multicellular organism together (e) acts to carry electrical impulses in nerve fibers ____48. Whenever carbohydrates are not available for energy, the body: (a) can only break-down glucose anaerobically (b) converts pyruvic acid into lactic acid (c) breaks-down stored fats forming lactic acid (d) breaks-down stored fats forming ketoacids (e) uses B-vitamins for energy (ab) breaks-down stored starch into CO2 + H20 6 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 7 alcohol dehydrogenase C2H4O + NAD-H2 C2H6O + NAD ____49. Which one of the following statements about the above reaction is NOT correct? (a) C2H4O is the substrate (b) H atoms are transferred by NAD (c) C2H6O is the product (d) NAD acts as a coenzyme (e) alcohol dehydrogenase is used-up in the reaction ____50. Ketoacids are formed from the: (a) deamination of amino acids (b) incomplete break-down of fatty acids (c) break-down of glycogen (d) incomplete break-down of RNA (e) both (a) and (b) ____51. Which one of the following reactions does NOT occur in the Krebs cycle? (a) production of reduced coenzymes (b) production of carbon dioxide (c) generation of ATP (d) formation of lactic acid in the absence of oxygen ____52. Weight loss results from an: (a) anabolic and catabolic biochemical reactions (b) anabolic and catabolic biochemical reactions (c) anabolic and catabolic biochemical reactions (d) anabolic and catabolic biochemical reactions ____53. Which series of reactions actually uses oxygen? (a) Glycolysis (b) fermentation (c) Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle (d) Electron Transport System (e) protein synthesis (ab) gluconeogenesis 7 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 8 ____54. Within a living cell, the oxidation of one molecule is always coupled within the simultaneous __________ of another molecule. (a) phosphorylation (b) hydrolysis (c) deamination (d) reduction (e) oxidation ____55. When fats & proteins are used for energy, they are converted into: (a) acetyl-CoA (b) lactic acid (c) uric acid (d) prostaglandins (e) nucleotides ____56. The nitrogen-containing waste product formed from the break-down of proteins is called: (a) urea (b) ketone bodies (c) nitrogenous bases (d) pantothenic acid (e) ascorbic acid ____57. NADH dehydrogenase complex, cytochrome b-c1 complex, and cytochrome oxidase complex are all: (a) H-(“proton”) atom pumps embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria (b) enzymes of the Krebs cycle (c) enzymes of the Krebs cycle (d) kinases in the glycolysis reactions (e) molecules that transport pyruvic acid into the mitocondrion ____58. Diabetes is associated with: (a) hypoglycemia (b) hyperglycemia (c) hypothyroidism (d) hyperinsulinism (e) hypokalemia 8 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration ____59. Thyroxin hormone: (a) stimulates the reproductive organs (b) decreases the blood glucose concentration (c) stimulates lymphocyte white blood cell production (d) increases blood calcium concentration (e) stimulates cellular metabolic rate ____60. Diabetes is associated with a decreased level of: (a) lactic acid (b) urea (c) glucose (d) insulin (e) gastrin ____61. Which one of the following does NOT occur in diabetes? (a) increased catabolism of protein (b) increased catabolism of fats (c) hyperglycemia (d) increased production of ketoacids (e) increased catabolism of glucose ____62. A cell requires ATP for all of the following processes EXCEPT: (a) protein synthesis (b) active transport (c) cell division (d) contraction (e) osmosis ____63. In the Electron Transport System (of Celllar Respiration): (a) H+ + e- are transferred to oxygen to form water (b) pyruate sugar (pyruvic acid) is split into acetyl-Coenzyme A (c) glucose is split into pyruvate sugars (pyruvic acid) (d) acetyl-Coenzyme A is split into CO2 (e) pyruate sugar (pyruvic acid) is converted into lactic acid ____64. Synthesis of sugars from non-carbohydrates is called: (a) glycolysis (b) deamination (c) glycogenolysis (d) gluconeogenesis (e) glycogenesis (ab) transcription 9 9 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 10 ____65. "Oxidative Phosphorylation" is associated with: (a) glycolysis (b) formation of acetyl-Coenzyme A sugars (c) the Krebs (Citric Acid) cycle (d) Electron Transport System (e) protein synthesis ____66. A person who has elevated ketoacid levels in his bloodstream is probably: (a) using mostly fats & proteins for energy (b) producing large amounts of new protein (c) just starting to exercise (d) not inhaling enough oxygen (e) in kidney failure ____67. Glycogen is a(n): (a) monosaccharide (b) protein (c) carbohydrate (d) hormone (e) water-soluble coenzyme ____68. Urea is associated with which series of biochemical reactions? (a) deamination of amino acids (b) oxidation of glucose (c) glycogenolysis (d) fermentation (e) steroid synthesis ____69. Which one of the following stimulates glycogenolysis in the Liver? (a) gastrin (b) bile (c) pepsin (d) glucagon (e) insulin ____70. Our present atmosphere consists mostly of which gas? (a) oxygen (b) hydrogen (c) nitrogen (d) helium (e) carbon dioxide 10 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 11 ____71. Which one of the following Olympic class activities increases a person's endurance? (a) weight-lifting (b) shot-put throw (c) long-jump (d) pole-vault (e) 10,000-meter run ____72. The hormone Insulin serves to regulate: (a) the metabolic rate of the body (b) the heart rate (c) the sugar level in the blood (d) sexual development (e) red blood cell production ____73. As your blood sugar level increases, ________ is normally released into the bloodstream. (a) insulin (b) thyroxin (c) gastrin (d) glycogen (e) glucagon ____74. After eating a meal, the pancreas secretes _________ Insulin. (a) less (b) the same amount of (c) more ____75. The hormone Glucagon increases: (a) the splitting of glycogen into glucose raising blood sugar level (b) the conversion of glucose into glycogen lowering blood sugar level (c) the digestion of starch into maltose (d) the digestion of maltose into glucose (e) the storage of glucose ____76. When O2 is present, muscle cells produce ______ compared to muscle cells breaking-down the same number of glucose molecules without O2. (a) less ATP (b) the same amount of ATP (c) more ATP (d) too variable to determine 11 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 12 ____77. The hormone Insulin is produced by the cells of the: (a) gallbladder (b) liver (c) kidney (d) pituitary gland (e) pancreas ____78. Which molecule will undergo different biochemical reactions, depending on whether or not oxygen is available? (a) acetyl-Coenzyme A (b) citric acid (c) glucose (d) pyruvic acid (pyruvate) (e) fatty acids ____79. The Glycolysis reactions occur in the _______ of the cell. (a) cytoplasm (b) nucleolus (c) endoplasmic reticulum (d) mitochondria (e) Golgi complex (ab) lysosomes ____80. The total net gain of ATP molecules from the complete oxidation of glucose is: (a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 18 (d) 28 (e) 38 (ab) 42 (ac) 46 (ad) 100 ____81. The conversion of pyruvate sugar (pyruvic acid) to lactic acid in cells is called: (a) gluconeogenesis (b) fermentation (c) aerobic respiration (d) oxidative phosphorylation (e) glycolysis 12 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 13 ____82. Which one of the following is a catabolic process? (a) the synthesis (duplication) of DNA (b) the break-down of glucose for energy (c) protein synthesis from amino acids (d) the conversion of fatty acids into triglycerides (e) the synthesis of glucose into glycogen ____83. The blood vessel that carries nutrient-laden blood from the digestive tract directly to the Liver is the: (a) hepatic artery (b) hepatic vein (c) hepatic portal vein (d) bile duct (e) inferior vena cava ____84. Exhaled air contains ___________ than inhaled air. (a) less O2, but more CO2 (b) less O2, and less CO2 (c) more O2, and more CO2 (d) more O2, but less CO2 (e) the same amount of O2 and CO2 ____85. The molecules entering at the beginning of the Kreb's Cycle are: (a) lactic acid (lactate) (b) pyruvate sugars (pyruvic acid) (c) acetyl-Coenzyme A (d) ATP (e) ketoacids (ketone bodies) (ab) NAD-H2 ____86. Amino acids are converted by deamination into: (a) sugars (b) ketoacids (c) fats (d) uric acid (e) polypeptides (ab) steroids 13 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 14 ____87. Lactic acid may be formed as an end-product of: (a) glycolysis (b) the Kreb's (Citric Acid) cycle (c) the Electron Transport System (d) gluconeogenesis (e) transcription ____88. Enzymes are chemically: (a) nucleotides (b) vitamins (c) proteins (d) prostaglandins (e) steroids ____89. Most hydrogen atoms are carried to the Electron Transport System by: (a) ATP (b) NAD (c) oxygen (d) Coenzyme-A (e) calcium ____90. For each glucose molecule broken-down in glycolysis, there is a net gain of ____ ATP produced. (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 28 (e) 38 (ab) 50 ____91. Glucose is split into 2 pyruvate sugars (pyruvic acid) during: (a) the Kreb's (Citric Acid) Cycle (b) the Transition Reaction (c) glycolysis (d) oxidative phosphorylation (e) fermentation ____92. Which one of the following is a catabolic process? (a) glycogen glucose (b) amino acids protein (c) nucleotides nucleic acids (d) fatty acids triglycerides (e) vitamins minerals 14 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 15 ____93. The names of enzymes usually end with the suffix: (a) -ide (b) -ose (c) -ase (d) -ine (e) -one ____94. Oxidation is the: (a) loss of hydrogens (& electrons) from a molecule (b) gain of hydrogens (& electrons) to a molecule (c) loss of an amino group from a molecule (d) loss of oxygens (& electrons) from a molecule (e) removal of water from a molecule ____95. The substance that an enzyme changes is called the __________ . (a) coenzyme (b) product (c) substrate (d) inhibitor (e) ribosome ____96. Sugars are broken-down into pyruvic acid (pyruvate) in the ________ of a cell. (a) lysosomes (b) mitochondria (c) cytoplasm (d) ribosomes (e) centrioles ____97. Which one of the following is an example of a "catabolic process"? (a) buffer reaction (b) condensation reaction (c) dehydration synthesis reaction (d) reduction reaction (e) hydrolysis reaction ____98. Each gram of fat produces about _____ the calories of energy that sugars do. (a) the same aount of (b) 2 times (c) 4 times (d) 10 times 15 Physiology Study Guide 3: Cellular Respiration 16 ____99. Ketoacids: (a) are formed as a result of catabolism of monosaccharides (b) are the result of abnormal protein metabolism (c) are the result of a decreased rate of fatty acid catabolism (d) are metabolized by cells throughout the body, but at a limited rate ____100. Substances in our diet such as Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and beta-carotene may slow the process of aging by: (a) the frequency of DNA replication (b) the frequency of DNA replication stimulating cell division of nerve cells (c) inhibiting the oxidation of organic compounds in our body by "free radicals” (d) reducing UV damage of the skin cells 16