Pesonal Income Taxes
advertisement

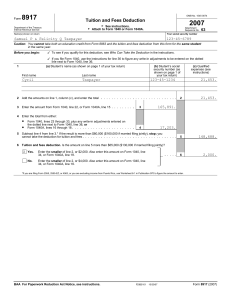
Name ___________________________ PERSONAL FINANCE PERSONAL INCOME TAXES – Review TERMS AND DEFINITIONS: Income tax – tax on wages, salaries, and self-employed earnings IRS – Internal Revenue Service - The federal agency that collects income taxes in the United States. File a Return - To mail or otherwise transmit to an IRS service center the taxpayer's information, in specified format, about income and tax liability. Form W–2 – Wage and Tax Statement - The form that an employer must send to an employee and the IRS at the end of the year. Reports an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from his or her paycheck. Form 1099 – INT - The form issued by all payers of interest income to investors at year's end. Form 1099-INT breaks down all types of interest income and related expenses. Payers must issue Form 1099-INTs for any party to whom they paid at least $10 of interest during the year. Form 1040 - The standard Internal Revenue Service (IRS) form that individuals use to file their annual income tax returns. Contains sections that require taxpayers to disclose their financial income status for the year in order to ascertain whether additional taxes are owed or whether the taxpayer is due for a tax refund. 1040 forms need to be filed with the IRS by April 15. Form 1040A - A simplified version of the 1040. No itemizing deductions, no business ownership, taxable income of less than $100,000 Form 1040EZ - An alternative to the 1040. Taxable income of less than $100,000, interest income of $1,500 or less, no dependents Tax Liability- The amount of tax that must be paid Refund - Owed to taxpayer if their tax payments (withholdings) are greater than total tax Tax Evasion - Failure to pay, or a deliberate underpayment of taxes. Dependent – a person who relies on someone else for support Exemption – A deduction from adjusted gross income for the taxpayer, the spouse, and qualified dependents Deduction – an expense that you can subtract from your adjusted gross income to figure your taxable income Standard Deduction - An amount, provided by law and bases on filing status, age, blindness, and dependency that taxpayers can deduct from their adjusted gross income before tax is determined Itemized Deduction – A specific expense that you can deduct from your adjusted gross income Gross Income - Money, goods, and property you received that must generally be reported on a tax return and may be included in taxable income. Earned Income - Wages, salaries, tips, and net earnings from self-employment and other income received for personal services Unearned Income - Income other than pay for work performed. Interest and dividends from savings or investments are common types of unearned income Interest Income - Income a person receives from certain financial accounts or from lending money to someone else. Adjusted Gross Income – A measure of income used to determine how much of your income is taxable. Adjusted gross income (AGI) is calculated as your gross income from taxable sources minus allowable deductions, such as unreimbursed business expenses, medical expenses, alimony and deductible retirement plan contributions. Taxable Income - The amount that is used to determine your tax liability History of Income Taxes: The first, known, written record of taxes dates back to ancient Egypt. At first paid in items such as grain, livestock, or oils. First income tax started 1799 in Great Britain to raise money for war First American income tax started in 1862 to pay for Civil War; repealed in 1872 In 1913, the 16th Amendment to the Constitution was passed, which allowed the first permanent income tax to be started and the first 1040 to be published. The Personal Income Tax Process: Earn wages and/or interest At end of year, receive a W-2 from your employer(s) and/or a 1099INT from your bank(s) Complete 1040EZ, 1040A or 1040 If you withheld more than you owe, receive a refund OR If you withheld less than you owe, make a payment by April 15th The usual filing date for all personal income taxes is April 15th Your W-2 Form: From whom is it received? From each employer for the year When received? Receive in January What information is included on it? Your identification information Employer information Income Withholdings The 1099 INT Form: From whom is it received? From each bank that pays your interest When received? In January What information is included on it? Your identification information Bank’s or payer’s information Interest received Withholdings (if any) The 1040 forms: Where to get a form: Library Tax preparation company such as H&R Block or a Certified Public Accountant Electronic tax program such as Turbotax Online at www.irs.gov Know the following differences/similarities between the 1040EZ and 1040A: Taxable income requirement – Less than 100,000 on both Interest requirement – Less than $1500 on 1040EZ, any amount on 1040A Dependents requirement – 1040EZ you cannot have a dependent, but you can be one; 1040A – you can have dependents Standard deduction – both (no itemized deductions) When do you need to file a 1040? When you have itemized deductions (such as mortgage interest, charitable deductions, or certain job expenses) or when self employed The 1040EZ: The form takes approximately 2 hours to complete Be able to complete two (2) 1040EZ forms – one as a dependent, one not as a dependent Be able to find taxable amounts on the tax table How do you find out where you should submit your 1040EZ form?