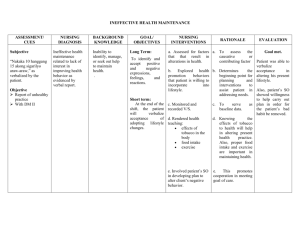
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE OBJECTIVES: GENERAL The students will develop the knowledge, skills, and attitude given a situation that includes medical surgical cases. This case presentation seeks to establish the student’s knowledge about the case of a 65-year-old woman who has congestive heart failure. SPECIFIC To understand the definition, epidemiology, signs and symptoms, treatment and management regarding the case. To understand the anatomy and physiology of the heart and relate it to the patient’s case. To trace the pathophysiology regarding the case of the patient. To implement the nursing care plan and gather the drug therapy that is related to the patient’s case. To formulate the discharge planning needed by the patient. INTRODUCTION Heart failure, sometimes called congestive cardiac failure (CCF), is a condition in which the heart muscle is weakened and can’t pump as well as it usually does. The main pumping chambers of the heart (the ventricles) can change size and thickness, and either can’t contract (squeeze) or can’t relax (fill) as well as they should. This triggers fluid retention, particularly in the lungs, legs and abdomen. The major causes of heart failure include coronary heart disease and heart attack, high blood pressure, damage to the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy), heart valve problems and abnormal heart rhythms. Of these, coronary heart disease and heart attack are the most common causes. Epidemiology: According to World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number 1 cause of death globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year. An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2016, representing 31% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% are due to heart attack and stroke while one third of these deaths occur prematurely in people under 70 years of age. Meanwhile, in the Philippines, hospitalization for congestive heart failure (CHF) was reported to be 1648 cases for every 100 000 patient claims in 2014. Data were obtained from representative government/private hospitals and a drugstore in all regions of the country. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMPS SHORTNESS OF BREATH FATIGUE AND WEAKNESS EDEMA PERSISTENT COUGH TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT Lifestyle changes: All heart failure treatment will involve lifestyle modifications including: Dietary changes Restrictions on salt intake Fluid intake restrictions Exercise Avoiding cigarettes, alcohol, and recreational drugs MEDICATION S U R G E R Y Coronary revascularization Ventricular Restoration Ventricular Assist Device Heart Transplant Patient’s Profile: Age: 65 year old Sex: Female Nationality: Filipino Religion: Roman Catholic Address: Valenzuela Date of admission: March 29, 2022 Time of Admission: 8:00am Chief Complaint: The patient was brought to the emergency room due to difficulty breathing. Condition started 2 days PTA when the patient had easy fatigability going to the comfort room. Admitting Diagnosis: Pulmonary edema and heart enlargement History of Illness: 10 year history of hypertension and diabetes NURSING HEALTH HISTORY ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY AND DIAGNOSTIC COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT ELECTROLYTES RENAL FUNCTION TEST DRUG STUDY NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT SUBJECTIVE: The patient stated “nahihirapan akong huminga”. OBJECTIVE: ·(+) Crackles from lower to mid portion of lungs ·Respiratory rate: 35 breaths per minute ·02 Saturation: 90 % ·Pale ·Diaphoretic DIAGNOSIS PLANNING Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion as evidenced by tachypnea and crackles from lower to mid portion of the lungs. After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient will be able to demonstrate deep breathing exercise. After 2 – 3 days of nursing intervention the patient will achieve the following: Establish a normal and effective breathing pattern as evidenced by: Respiratory rate of 12-20 cpm Oxygen saturation within normal range 95%-100% Absence of crackles upon auscultation INTERVENTION Independent: - Placed patient in a high fowlers position. -.Monitored vital signs, assessed and recorded respiratory rate and depth. - Auscultated breath sounds every 4 hours. - Educated and assisted in sustained deep breathing exercises. - Encouraged frequent rest periods RATIONALE - To permit maximum lung excursion and chest expansion. - To obtain baseline data. To detect early signs of respiratory problems. - Examine effectiveness of intervention and to detect decreased or adventitious breath sounds. - allow patient to participate in maintaining health status and improve Ventilation - Extra activity can worsen shortness of breath EVALUATION After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient will be able to demonstrate deep breathing exercise. After 2 – 3 days of nursing intervention the patient will achieve the following: Establish a normal and effective breathing pattern as evidenced by: Respiratory rate of 12-20 cpm Oxygen saturation within normal range 95%-100% Absence of crackles upon auscultation Hence, The Goal was partially met. - Utilized pulse oximetry to check oxygen saturation and pulse rate. Evaluated skin color and capillary refill. - To detect alterations in oxygenation. Lack of oxygen will cause blue/cyanosis coloring to the lips, tongue, and fingers Dependent: Administered oxygen as ordered. Supplemental oxygen is required to maintain PaO2 at an acceptable level. ASSESSMENT Subjective: “Namamanas ang mga paa ko umabot na dito sa tuhod ko” as verbalized by the patient Objective: BP 180/100 HR 110/min RR 35/min O2 sat 93% - (+) edema up to the knees area - *Hypothetical + 2 pitting edema bilateral lower extremities - oliguria - Elevated Serum Potassium: 6.1 - (+) crackles from lower to mid portion of the lungs. - CXR result showing pulmonary edema DIAGNOSIS PLANNING Excess fluid volume related to maladaptive compensatory mechanisms secondary to congestion of tissue perfusion as evidence by (+) edema, (+) crackles lung sound and CXR result of pulmonary edema. Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient will be able to acquire knowledge and understanding about the importance of diet modification (fluid intake restriction, low salt – low potassium diet) After 3 days of nursing intervention the patient will be able to achieve the following Vital signs within normal range: BP 90/60mmHg - 120/80mmHg HR 60 – 100 bpm RR 12 – 20 cpm O2 95 – 100% (Johns Hopkins Univ., 2022) b. (-) or absence of crackles sound from mid to lower portion of the lungs c. Urine output of within normal range d. Maintain normal fluid volume as evidence by absence of edema INTERVENTION - Monitored vital sign and assessed lung sound for baseline data - Measured and documented hourly I&O - Monitored weight regularly using the same scale and at the same time of day, wearing the same amount of clothing. RATIONALE - Provide an information base against which to monitor and assess progress and effectiveness during implementation of intervention. -To monitor fluid status; the normal range for 24-hour urine volume is 800 to 2,000 milliliters per day with a normal fluid intake of about 2 liters per day (MedlinePlus, 2022). - Elevated edematous of lower extremities, and handle with care -Sudden weight gain may mean fluid retention. Different scales and clothing may show false weight inconsistencies - Educate patient and family members the importance and strict compliance in proper nutrition, hydration, and diet modification. - Elevation decreases pressure and may help reduced edema. Edematous skin is more susceptible to injury. EVALUATION Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient acquired knowledge and understanding about the importance of diet modification. After 3 days of nursing intervention the patient achieved the following: ¾Vital signs: ·BP 140/90 ·HR 100/min ·RR 25/min ·O2 sat 95% ¾(+) crackles sound below mid portion of the lungs ¾Urine output of 250ml/day ¾+ 1 pitting edema in bilateral lower extremities Goal was partially met. Dependent: Administered diuretics as ordered, documented the response; Furosemide 40 mg IV stat - Increased excretion of excess fluids and electrolyte DISCHARGE PLANNING