Formal Charge: A bookkeeping device for electrons used to decide
advertisement
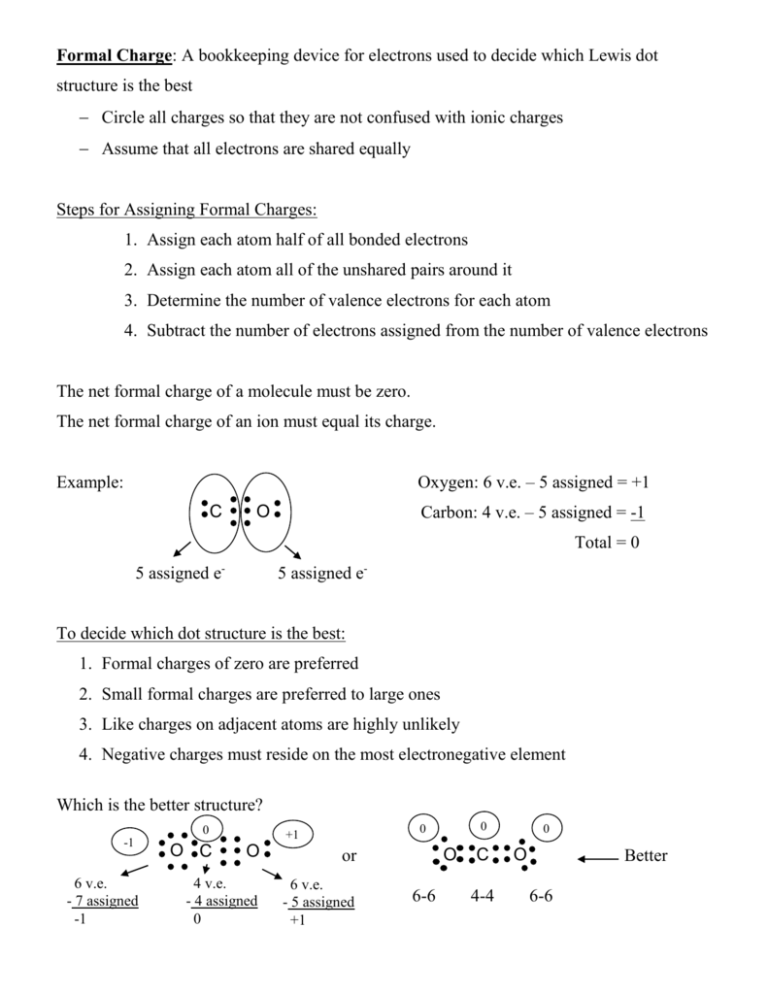
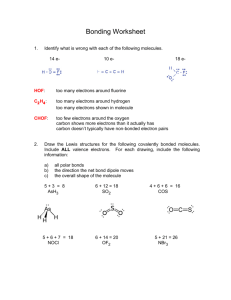
Formal Charge: A bookkeeping device for electrons used to decide which Lewis dot structure is the best Circle all charges so that they are not confused with ionic charges Assume that all electrons are shared equally Steps for Assigning Formal Charges: 1. Assign each atom half of all bonded electrons 2. Assign each atom all of the unshared pairs around it 3. Determine the number of valence electrons for each atom 4. Subtract the number of electrons assigned from the number of valence electrons The net formal charge of a molecule must be zero. The net formal charge of an ion must equal its charge. Oxygen: 6 v.e. – 5 assigned = +1 Example: C Carbon: 4 v.e. – 5 assigned = -1 O Total = 0 5 assigned e- 5 assigned e- To decide which dot structure is the best: 1. Formal charges of zero are preferred 2. Small formal charges are preferred to large ones 3. Like charges on adjacent atoms are highly unlikely 4. Negative charges must reside on the most electronegative element Which is the better structure? 0 -1 6 v.e. - 7 assigned -1 O C 0 0 +1 O or 4 v.e. - 4 assigned 0 6 v.e. - 5 assigned +1 O 6-6 C 4-4 0 O Better 6-6 Example: What should the central atom be in a molecule of CH2O? 0 0 O or 0 C H +2 -2 C O H H H 0 0 0 Carbon should be the central atom Example: Three possible structures for a thiocyanate ion -1 0 N -1 C 0 S N C 0 -2 S N 0 +1 A. Determine formal charges B. Which structure is preferred? Remember: Sum of all charges = -1 (charge of ion) N is the most electronegative, so it must be the negative charge You are looking for the lowest total charge structure -1 Answer: N C S More practice: Is hydrogen cyanate HCN or HNC? 0 -1 HCN -1 C S -1