June 2015 Exam Review
advertisement
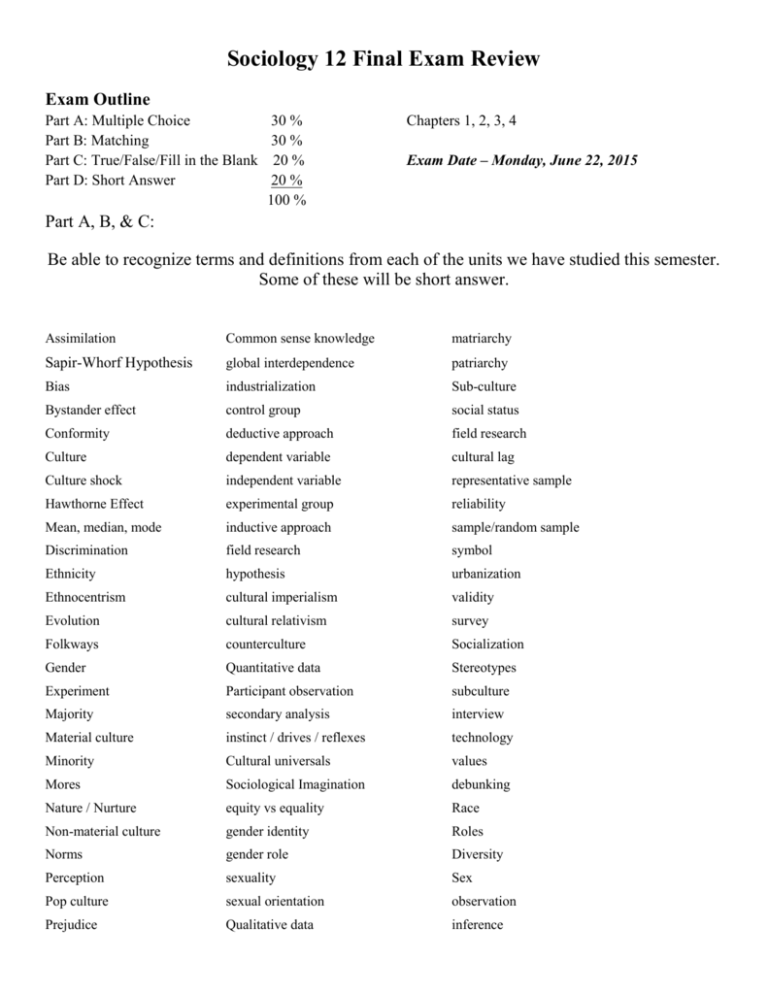
Sociology 12 Final Exam Review Exam Outline Part A: Multiple Choice 30 % Part B: Matching 30 % Part C: True/False/Fill in the Blank 20 % Part D: Short Answer 20 % 100 % Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4 Exam Date – Monday, June 22, 2015 Part A, B, & C: Be able to recognize terms and definitions from each of the units we have studied this semester. Some of these will be short answer. Assimilation Common sense knowledge matriarchy Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis global interdependence patriarchy Bias industrialization Sub-culture Bystander effect control group social status Conformity deductive approach field research Culture dependent variable cultural lag Culture shock independent variable representative sample Hawthorne Effect experimental group reliability Mean, median, mode inductive approach sample/random sample Discrimination field research symbol Ethnicity hypothesis urbanization Ethnocentrism cultural imperialism validity Evolution cultural relativism survey Folkways counterculture Socialization Gender Quantitative data Stereotypes Experiment Participant observation subculture Majority secondary analysis interview Material culture instinct / drives / reflexes technology Minority Cultural universals values Mores Sociological Imagination debunking Nature / Nurture equity vs equality Race Non-material culture gender identity Roles Norms gender role Diversity Perception sexuality Sex Pop culture sexual orientation observation Prejudice Qualitative data inference Concepts Why study sociology? What is society? What is culture? Sociological Perspectives: o Definitions: Sociology, anthropology, psychology o Sociological Imagination o Personal vs Social issues o Common sense o Five ways of knowing o Sociological perspectives: o o o o o Conflict theorist Functionalist Symbolic interactionist Feminist Post-Modern o Important Sociologists: o Auguste Comte - positivism o Max Weber – exclude personal values and economic interests o Emile Durkheim – social facts; anomie o Hebert Spencer – social darwinism o Harriet Martineau o Karl Marx – class conflict; bourgeoisie vs proletariat o George Simmel o Jane Adams o W.E. DuBois o Intellectual revolution vs political/economic revolutions o Industrialization vs urbanization o Compare high, middle, and low income countries o Descriptions o demographics o Scientific Method of inquiry and research o Vaccination issue o Research ethics (list – 7 parts) o Methods – surveys / experiments / participant observation / field research / secondary analysis o Research method steps Problem, review literature, form hypothesis, create operational definition, choose research design, collect data, analyze data, state conclusions. Empirical evidence – importance of sample (representative / size / randomness) Objective reality, research values, and biases – Hawthorne Effect Limitations of scientific sociology Observation vs inference validity vs reliability Quantitative vs qualitative research/data (mean / median / mode) Deductive vs inductive reasoning Open ended vs close ended questions Causation vs correlation independent vs dependent variables What is Culture? Importance How is culture disrupted Definitions: • race, ethnicity, class, sex, gender Cultural diversity o natural vs social circumstances o significance of power and privilege o intolerance, racism stereotype vs prejudice vs discrimination instincts vs reflex vs drives Cultural relativism Cultural imperialism • Ethnocentrism • Material culture vs Non material culture Visible vs non-visible aspects of culture Cultural universals appearance, activities, social institutions, practices • Pop culture vs High Culture fads, fashions, leisure activities Subculture vs counterculture Components of culture o Symbol, language, Values, beliefs, folkways, laws (civil vs criminal), norms and mores (taboos) o Norms Prescriptive vs proscriptive Formal vs informal o Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis Cultural Lag Culture shock What is the socialization process? What factors affect it? Explain the Nature versus Nurture debate. Social contral mechanism o Self family peers language institutions coercion Consequences of socialization (4) Agents of socialization o Family, media, peers, school, religion, sports Problems associated with social isolation and maltreatment Resocializtion Sociological Theories of Human Development 1. Psychoanalytic Theory (Id/Ego/Superego) 2. Object Relations Theory 3. Social Learning Theory 4. Functionalist Theory 5. Conflict Theory 6. Symbolic Interaction Theory Concept of self 4 parts o Physical, active, social, psychological o Socialization Theories of Self Locke – Tabula Rasa Cooley – Looking Glass Self Mead – Role Taking imitation Stage; play stage; game stage Piaget – Stages of cognitive development – sensorimotor, preop., concrete op., formal op.











