108012 Latin I - Pitt County Schools
advertisement
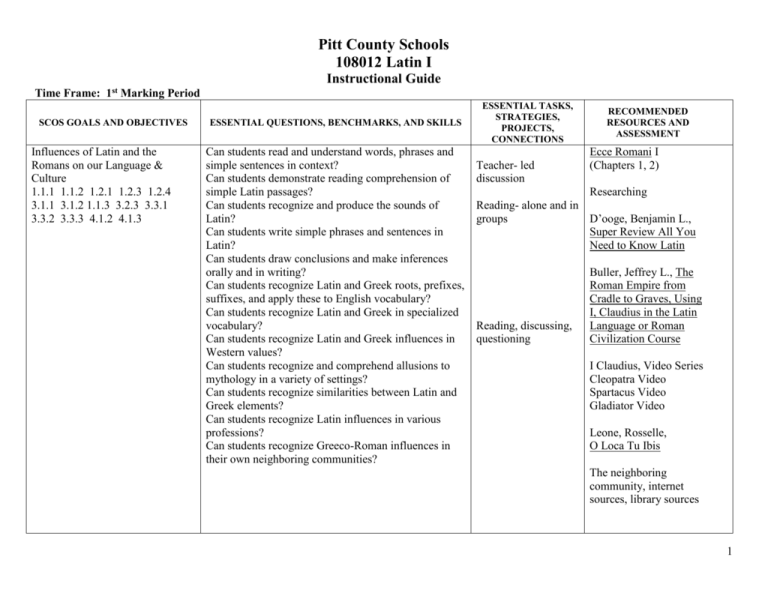
Pitt County Schools 108012 Latin I Instructional Guide Time Frame: 1st Marking Period SCOS GOALS AND OBJECTIVES Influences of Latin and the Romans on our Language & Culture 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.2.1 1.2.3 1.2.4 3.1.1 3.1.2 1.1.3 3.2.3 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.3 4.1.2 4.1.3 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS, BENCHMARKS, AND SKILLS Can students read and understand words, phrases and simple sentences in context? Can students demonstrate reading comprehension of simple Latin passages? Can students recognize and produce the sounds of Latin? Can students write simple phrases and sentences in Latin? Can students draw conclusions and make inferences orally and in writing? Can students recognize Latin and Greek roots, prefixes, suffixes, and apply these to English vocabulary? Can students recognize Latin and Greek in specialized vocabulary? Can students recognize Latin and Greek influences in Western values? Can students recognize and comprehend allusions to mythology in a variety of settings? Can students recognize similarities between Latin and Greek elements? Can students recognize Latin influences in various professions? Can students recognize Greeco-Roman influences in their own neighboring communities? ESSENTIAL TASKS, STRATEGIES, PROJECTS, CONNECTIONS Teacher- led discussion RECOMMENDED RESOURCES AND ASSESSMENT Ecce Romani I (Chapters 1, 2) Researching Reading- alone and in groups D’ooge, Benjamin L., Super Review All You Need to Know Latin Reading, discussing, questioning Buller, Jeffrey L., The Roman Empire from Cradle to Graves, Using I, Claudius in the Latin Language or Roman Civilization Course I Claudius, Video Series Cleopatra Video Spartacus Video Gladiator Video Leone, Rosselle, O Loca Tu Ibis The neighboring community, internet sources, library sources 1 Uses of Nouns and Present Tense Verbs 1.1.2 1.1.4 1.1.5 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 Can students draw conclusions and make inferences from selections they read? Can students read a variety of Latin passages? Can students read Latin aloud with accurate pronunciation, meaningful phrasing, and appropriate inflection? Reading silently and orally Contributions of Romans 1.2.3 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 Can students identify major historical and political figures and forms of Roman government and comprehend their significance in Roman history? Can students recognize architectural features, engineering products, art forms of Greeks and Romans? Can students identify food, clothing, and artifacts to make inferences about life and custom? Can students identify Greco and Roman deities, and mythological heroes and the stories associated with these? Can students recognize Latin vocabulary and structures as unique to the language? Can students demonstrate awareness of how Romans thought and acted? Can students demonstrate awareness on ancient influences on Western values? Can students identify the physical and geographical features of Rome, the Empire, and their role in history and culture? Can students identify the basic features of Roman daily life and comprehend their significance? Can students identify major writers and their works as reflections of their major historical settings? Research, projects, student creations Projects and student creations Ecce Romani I (Chapters 3, 4) Teacher rubrics for readings Ecce Romani I (Chapters 5, 6) Teacher – made rubrics for creations Internet sources, Latin Library sources Reading, research Edith Hamilton’s Mythology Composing dialogues between important Romans Composing plays about Romans Composing letters Romans could have written, maps they could have used – etc. Keller, Andrew and Stephanie Russell, Learn to Read Latin Materials on Roman Products Latin Library sources Teacher – made tests on Roman products Prior, Richard E. and Joseph Wohlbert, 501 Latin Verbs Wheelock’s, Latin Grammar Buller, Jeffrey L., The Roman Empire from 2 Cradle to Graves, Using I, Claudius in the Latin Language or Roman Civilization Course Teacher – made rubrics, projects Introduction to Structural Elements 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.2.3 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 2.2.5 Future Tense and Imperative Mood 1.1.5 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.1.5 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 3.1.1 3.1.2 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.3.1 Time Frame: 2nd Marking Period Extending Cultural, Family and Community Connections 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 3.1.2 The Past Tenses 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.1.5 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.3.1 Historical Events and Personalities 2.1.1 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.4 3.2.3 4.1.3 Can students demonstrate a knowledge of vocabulary, basic inflection systems, and syntax appropriate to reading level? Can students recognize examples of Greek and Roman architecture and art forms, engineering and urban camp design as representatives of cultures and of historical events? Can students recognize and use future tense and imperative mood? Can students recognize and use the three perfect tenses in indicative mood active and passive voices? Can students demonstrate increasingly complex knowledge of events and personalities? Demonstrations lectures, reading practices Ecce Romani I (Chapters 7, 8) www.mythfolklore.net Hands-on architectural construction w/appropriate accompanying dialogue Reading practice Ecce Romani I Teacher explanations (Chapters 9, 10) Student – made visuals and projects Projects, research, presentation both hand-made and Power Point Reading, recitations Ecce Romani I (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Projects, on-line and hand-on research Ecce Romani I (Chapters 16, 17, 18) Ecce Romani I (Chapters 14, 15) 3 Pluperfect and Future Perfect Tenses 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.1.5 Time Frame: 3rd Marking Period The Passive Voice 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 3.2.1. 3.3.1 Third Declension Nouns and Adjectives 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 3.2.1 3.3.1 Artifacts and Archaeology 2.2.1 2.2.3 4.2.1 4.2.2 Can students use and recognize pluperfect and future perfect tenses? Teacher instruction, presentations, rubrics for presentation and composition reading, comparing use voices in projects Ecce Romani I (Chapters 19, 20) Can students recognize and use the passive voice, indicative mood in a variety of venues? Teacher instruction, presentations, rubrics for presentation and composition reading, comparing use voices in projects Ecce Romani I (Chapters 21, 22 and 23) Wheelock’s Latin Grammar Can students recite, read, and write third declension nouns and adjectives? Recitations, Readings, and Compositions Ecce Romani I (Chapters 24, 25) Can students use knowledge of Latin and ancient civilization in leisure activities for personal enrichment? Can students explore topics of interest related to the Greco Roman world for personal enrichment? Composing and creating projects about popular videos Rubrics for evaluating compositions and projects using appropriate grammar Rubrics for evaluating projects Formulating compositions, incorporating constructions explained by teacher Ecce Romani I (Chapters 26, 27) Ecce Romani II (maps) 4 Wrapping It up 4.1.2 4.1.3 4.2.1 Can students share, exchange, and present information about their own language experience to others in the school, community, and beyond? Creating projects based on travel, firsthand research, and on-line research Prior, Richard E. Joseph Wohlberg, 501 Latin Verbs I Claudius, Video Series Cleopatra Video Spartacus Video Gladiator Video Keller, Andrew and Stephanie Russell, Learn to Read Latin Vergil, The Aeneid Ovid, Metamorphoses The Poems of Catullus Cicero, Pro Caelio Wheelock’s Latin Grammar Buller, Jeffrey L., The Roman Empire from Cradle to Graves, Using I, Claudius in the Latin Language or Roman Civilization Course 5