G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINNERING, NAGPUR (An
advertisement
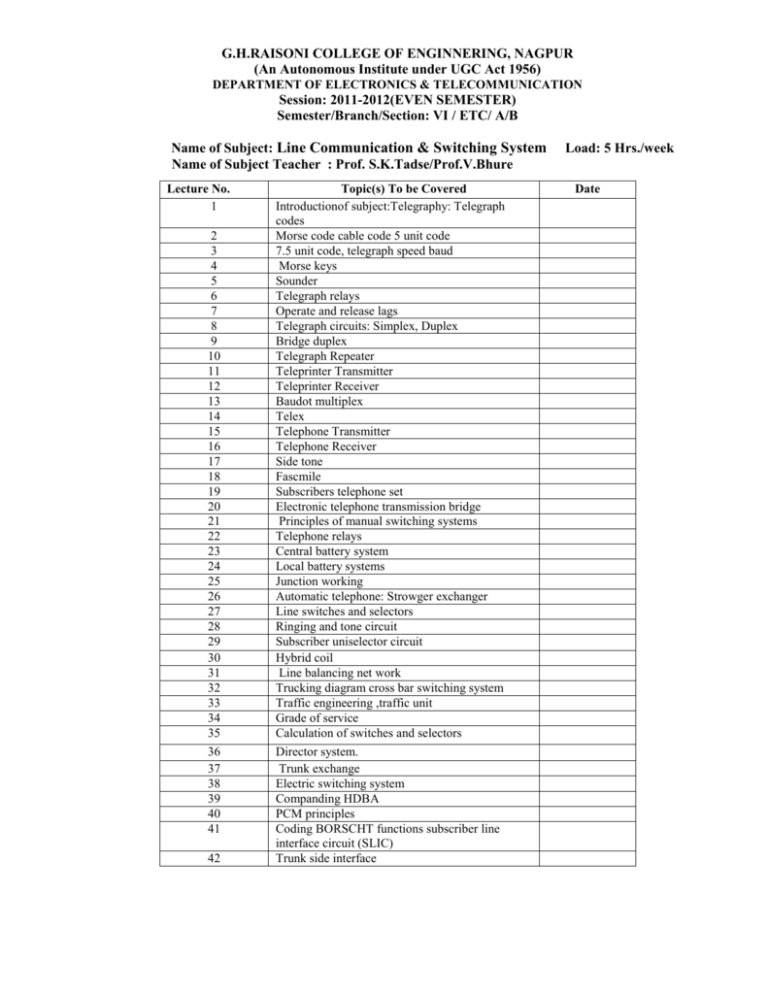
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINNERING, NAGPUR (An Autonomous Institute under UGC Act 1956) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION Session: 2011-2012(EVEN SEMESTER) Semester/Branch/Section: VI / ETC/ A/B Name of Subject: Line Communication & Switching System Name of Subject Teacher : Prof. S.K.Tadse/Prof.V.Bhure Lecture No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Topic(s) To be Covered Introductionof subject:Telegraphy: Telegraph codes Morse code cable code 5 unit code 7.5 unit code, telegraph speed baud Morse keys Sounder Telegraph relays Operate and release lags Telegraph circuits: Simplex, Duplex Bridge duplex Telegraph Repeater Teleprinter Transmitter Teleprinter Receiver Baudot multiplex Telex Telephone Transmitter Telephone Receiver Side tone Fascmile Subscribers telephone set Electronic telephone transmission bridge Principles of manual switching systems Telephone relays Central battery system Local battery systems Junction working Automatic telephone: Strowger exchanger Line switches and selectors Ringing and tone circuit Subscriber uniselector circuit Hybrid coil Line balancing net work Trucking diagram cross bar switching system Traffic engineering ,traffic unit Grade of service Calculation of switches and selectors Director system. Trunk exchange Electric switching system Companding HDBA PCM principles Coding BORSCHT functions subscriber line interface circuit (SLIC) Trunk side interface Load: 5 Hrs./week Date 43 44 45 46 Signaling ,cellular telephony Introduction to the ISDN Carrier communication, carrier equipments Attenuator equalizers filters 47 Long haul carrier telephone systems,BHCA 48 Power line carrier communication 49 Revision on above topics 50 Revision and Exam preparation G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering. Nagpur Dept. of Electronics &Telecommunication Engineering Session: 2011-2012(EVEN SEMESTER) Teaching Plan- VIth SEM /ETC/ SEC: - A / B Subject: CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING Name of subject Teacher: G.R.Walke/ R.H.Adware Lecture Unit Topics No. No. 1 Introduction about subject & its application 1 2 Closed loop system, examples 3 open loop system, examples 4 Positive feedback system, derivation, Negative feedback system, derivation 6 Block diagram reduction, rules 1 to 10 7 Examples on block diagram reduction 8 Examples on block diagram reduction 9 Definitions on signal flow graph, Examples on signal flow graph(SFG) 10 Mathematical modeling of electrical & electromechanical system 11 Examples based on modeling 12 Examples based on modeling 13 Examples based on modeling 14 Time response: Types of inputs in Time Response Analysis 2 15 Response of Ist order system to unit step input, ramp input 16 Response of second order system to unit step input, ramp input 17 Location of closed loop poles 18 Time response specification 19 Expression for overdamped, critically damped 20 Steady state error & error constants 21 Numericals based on first order system 22 Numericals based on second order system 23 Examples based on Time Response 24 Examples based on Time Response 25 Stability of System: Types of stability 3 26 Difficulty no.1 & 2 in stability 27 Hurwitz Criteria for Stability 28 Rouths Array for the stabilty 29 Numericals based on stability 30 Numericals based on stability 31 Root Locus definitions, Different Rules of Root Locus 4 32 Effect of addition of poles on Root Locus 33 Effect of addition of zeros on Root Locus 34 Numericals based on Root Locus 35 Numericals based on Root Locus 36 Frequency Response: Phase Lead Compensation, 5 Design of Lead Compensator, 37 Design of Lead Compensator using Bode plot, Root locus 38 Phase Lag Network, Design of Lag Compensator 39 Design of Lag Compensator using Bode plot, Root locus 40 Lag-lead compensator 41 Numericals based on Bode plots 42 Theory of Nyquist plot 43 Numericals based on Nyquist plot 44 Theory of polar plot 45 Numericals based on Polar plot 46 47 48 49 50 6 Definitions of state variables Physical state model, Phase state model, Canonical state model Eigen value & Eigen matrix Numericals based on state variables Numericals based on state variables G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINNERING, NAGPUR. (An Autonomous Institute under UGC Act 1956) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & TELE-COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Semester/Branch/Section: - VI /ETC/ A/B Session: 2011-2012(EVEN SEMESTER) Name of Subject: Communication Electronics Name of Subject Teacher: - Prof.S.S.Godbole/Prof.P.V.Puranik Lecture No. Syllabus To be Covered Lecture no. 1 Introduction to Communication, Modulation and its types. Lecture no. 2 Frequency spectrum of electromagnetic waves, their properties, bandwidth, Tuned Amplifiers, Lecture no. 3 noise, types, Lecture no. 4 Noise figure calculation Lecture no. 5 noise figure calculation Cont. Lecture no. 6 Problems on noise figure Lecture no. 7 AM modulators Lecture no. 8 series plated class C amplifier Lecture no. 9 SSB, SSB-SC modulation Lecture no. 10 AM demodulators Lecture no. 11 square law detector Lecture no. 12 Problems on AM Lecture no. 14 AM using transistors, detectors for SSB, SSB-SC AM signals Lecture no. 15 Detectors for SSB, SSB-SC AM signals Continued Lecture no. 16 Angle modulation Lecture no. 17 frequency modulation Lecture no. 18 FM Equation Lecture no. 19 Spectrum reactance tube Lecture no. 20 FET modulators Lecture no. 21 Armstrong method Lecture no. 22 Problems on FM Lecture no. 23 reactance tube Lecture no. 24 Spectrum reactance tube Lecture no. 25 FET modulators, Armstrong method Lecture no. 26 FM transmitters Lecture no. 27 Frequency stabilization methods, FM discriminator Lecture no. 28 Foster Seeley Lecture no. 29 , PLL detectors stereophonic FM Lecture no. 30 Pulse Modulation- PAM, Lecture no. 31 PPM, PWM Lecture no. 32 PCM, DM Lecture no. 33 PCM, DM Lecture no. 34 DELTA modulation Lecture no. 35 PCM Problems and MATLAB Intro Lecture no. 36 Radio receivers Lecture no. 37 TRE receivers Lecture no. 38 Super heterodyne receivers Lecture no. 39 Circuits of Mixer Lecture no. 40 RF stage, AGC, FM radio receivers Lecture no. 41 , IF stage, Detector Lecture no. 42 , AGC circuits Lecture no. 43 FM radio receivers Lecture no. 44 FM radio receivers Lecture no. 45 Problems on Radio Receivers Lecture no. 46 Problems on Radio Receivers Lecture no. 47 Line telephony- Lecture no. 48 Elemental Phone system, Simple exchange Lecture no. 49 TDM, Analog TDM TSI, Space Array Lecture no. 50 Revision G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINNERING, NAGPUR. (An Autonomous Institute under UGC Act 1956) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & TELE-COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Semester/Branch/Section: - VI /ETC/ A/B Session: 2011-2012(EVEN SEMESTER) Name of Subject: Fields & Radiating Systems Name of Subject Teacher: - Prof.R.T.Bankar/Prof.M.B.Babar Lecture No. Topics to be Covered UNIT I 1 Introduction of subject 2 Guided waves 3 Waves between parallel planes 4 Waves between TE, TM, TEM, waves 5 Characteristics of waves 6 Attenuation in parallel plane guides 7 Wave impedance UNIT II 8 Rectangular wave - guide 9 TM, TE waves in rectangular guides 10 Their characteristics 11 Wave velocity 12 Guide wave length 13 Wave impedance field configurations UNIT III 14 15 Transmission line parameters - Characterized impedance Propagation constant, Attenuation constant, Phase constant 16 Waveforms Distortion 17 Distortion less transmission lines 18 Loading of transmission lines 19 Reflection coefficient, VSWR 20 Equivalent circuits of transmission lines 21 Transmission lines at radio frequency 22 Open and short circuited lines 23 Smith chart, Stub matching UNIT IV 24 Scalar and vector potentials 25 Retarded potentials 26 Field due to a current elements 27 Power radiated, Its radiation resistance 28 For field due to a dipole 29 Power applied radiated 30 Its Radiation resistance 31 Reciprocity theorem applied to a antennas gain, 32 Aperture of antenna 33 Radiation intensity 34 Directivity and Antenna gain UNIT V 35 Two elements arrays 36 Directional characteristics 37 Linear arrays analysis 38 Broadside arrays pattern multiplication 39 End fire arrays pattern multiplication 40 Binomial arrays 41 Design of broadest array for a specific pattern UNIT VI 42 Basic principles of parabolic reflectors 43 Analysis and Power pattern 44 Lens antennas 45 Folded dipole turnstile 46 Yagi antenna 47 Log periodic antennas 48 Horn antennas 49 Traveling wave antennas 50 Cassegrain antennas





