Mitosis Lab - West Lake Eagles
advertisement

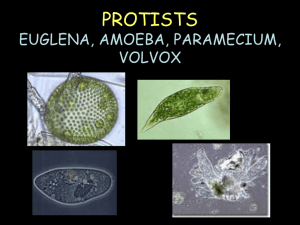
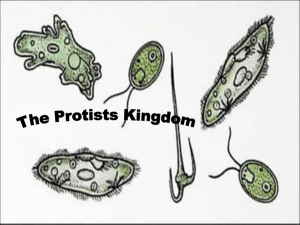
Name _________________________________ Period _____ Protista Lab Purpose: To identify the most common tpes of Protozoans. To have a better understanding of their cell structures, shape, and methods of locomotion. Background: 1. What are the 3 major kinds of Protists? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the major characterisitic that differs between organisms in each of the 3 groups? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Materials: Prepared slides of : Amoeba, Paramecium, and Euglena, microscope, & Virtual Labs for Euglena, Paramecium, and Amoeba http://labs.7bscience.com/protist-labs.html Procedures: Part 1: Prepared slide of Amoeba 1. Obtain a prepared slide of Amoeba proteus. 2. Find the pink or blue-stained Amoebas on the slide and focus on high 40x power. 3. Draw an Amoebas on your slide. On each drawing label the following parts: Plasmalemma, nucleus, pseudopod, and magnification. ** If the Amoeba that you are looking at doesn’t have a definite pseudopod, then DO NOT draw it. PART 2. Prepared slide of Paramecium 1. Obtain a prepared slide of Paramecium caudatum.. 2. Find the stained paramecium on the slide and focus on high 40x power. 3. Draw a paramecium on your slide. On each drawing label the following parts: Pellicle, macronucleus, cilia & magnification. Name _________________________________ Period _____ PART 3: Prepared slide of Euglena 1. Obtain a prepared slide of Euglena 2. Find the purple stained Euglenas on the slide and focus on high power 40x 3. Draw the Euglena on your slide. On each drawing label the following: Pellicle, chloroplast & magnificaiton PART 4: Volvox (colony of flagellates) 1. See Volvox See Handout (attached and Pictures of magnified Volvox on the front screen. Data and Results 1.Describe how an Amoeba moves. _______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2.What do we call the projections that the Amoeba uses for movement? __________________________ 3.What is the body symmetry of an Amoeba? ______________________________________________ 4.How does a Paramecium move? ________________________________________________________ 5.How would the Paramecium get a yeast cell into its body if it wanted to eat it? Explain in detail. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6.What structures are present in Euglenas, but are not found in the other two organisms. (2 pts) _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Name _________________________________ Period _____ 7.What structure does an Euglena contain that make it more “plant-like”? _____________________ 8.Why would a Volvox, which is a colony of single celled flagellates, be a beneficial way of living? _______________________________________________________________________________ 9.What is the colony symmetry of Volvox? ____________________________ Analysis: What different methods do the 3 major protists (Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena) studied in this lab use for movement (3 pts)? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ List some physical characteristics that are UNIQUE ONLY to the following protists: Amoeba: _____________________________________________________________ Paramecium: __________________________________________________________ Euglena: ______________________________________________________________