Q3 Exam Review
advertisement
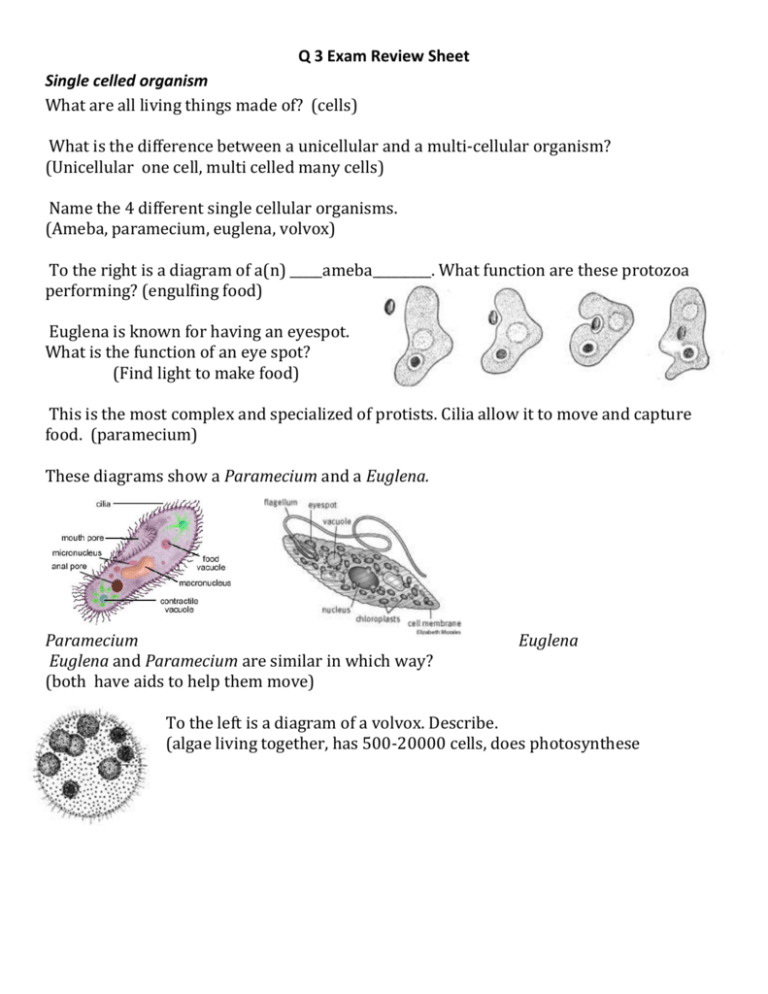
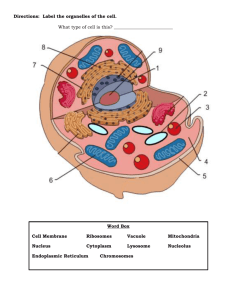
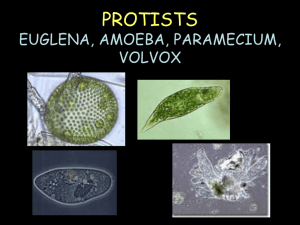
Q 3 Exam Review Sheet Single celled organism What are all living things made of? (cells) What is the difference between a unicellular and a multi-cellular organism? (Unicellular one cell, multi celled many cells) Name the 4 different single cellular organisms. (Ameba, paramecium, euglena, volvox) To the right is a diagram of a(n) _____ameba_________. What function are these protozoa performing? (engulfing food) Euglena is known for having an eyespot. What is the function of an eye spot? (Find light to make food) This is the most complex and specialized of protists. Cilia allow it to move and capture food. (paramecium) These diagrams show a Paramecium and a Euglena. Paramecium Euglena and Paramecium are similar in which way? (both have aids to help them move) Euglena To the left is a diagram of a volvox. Describe. (algae living together, has 500-20000 cells, does photosynthese Plant/animal cells Basic info to know • Cells are the basic units of function in all living things. • Cells in animals and plants have unique forms that allow each to take part in processes that are necessary for the cell and or/living thing to survive. • Organelles are to cells what organs are to the body. • They carry out the individual tasks of gaining and working with energy, as well as directing the overall behavior of the cells. Know the organelles and the function of each for both plant and animal cell Organelles : Function : Nucleus: Contains the DNA and RNA and manufactures proteins Nucleolus: In nuclei where ribosomes are synthesized. Centrioles: structure that appears during mitosis(cell division) Mitochondria: Energy producers of the cell Ribosomes: Produce proteins Golgi Bodies: Packages Proteins Chloroplasts: Involved in photosynthesis Vacuoles: Store waste, nutrients, and water Lysosome: Contains digestive enzymes, mostly in animal cells Endoplasmic Reticulum: Passageway that transports proteins from the nucleus Rough ER covered in ribosomes, Smooth ER is not Cell membrane: Semi-permeable lining that surrounds the cell Cell Wall: Is a stiff non-living wall that surrounds the cell membrane made of cellulose Cytoplasm: Jelly-like material surrounding the organelles Diffusion: How food, air, and water gets in and out of the cell. Cellular Respiration: How an animal cell gets energy. Photosynthesis: How a plant cell gets energy. Know the difference between and plant and animal cell Both contain: Nucleus, Nuclear Envelope, and Chromosomes- which carry the genes or the DNA, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Cell membranes Difference: Plant cells have non-living rigid cell walls, Plant cells contain chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll, a green chemical needed for photosynthesis, Plant cells contain a large vacuole; animal cells never contain large vacuoles, Plant cells are regular in shape; animal cells are irregular in shape. Human body Know the organization from cells to organism (Cells---tissues---organs---organ system---organism) Know what a lysosome does and how it compares to a body system (Digestive system) Understand what cytoplasm does and how it helps a cell Is located around the cell organelles and is located next to the nuclear membrane The most basic unit of life Cell Know examples of organs Heart, lungs, kidneys Know what the main function of each system does in the body Digestive-absorb nutrients- (small intestine) Respiratory –obtain oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Circulatory-bring blood to the heart and back around the body. Endocrine-send hormones throughout the body Nervous-send signals throughout the body Integumentary system(skin) protect the body, regulate the body’s temperature Immune system-kill disease and make antibodies Urinary system- clean out the waste for the body Skeletal system –gives support to the body, helps the nervous system send signals, and protects the organs, movement Muscular system-move the bones Know examples or organ systems Listed above! Know how the skeletal system and the muscular system work together Skeletal provides support and the muscles move the bone What does cellular respiration do for the body? Cells use oxygen to burn nutrients for energy