Study Guide Micro-organisms and Cells 2015 Key Name: Date: KEY
advertisement

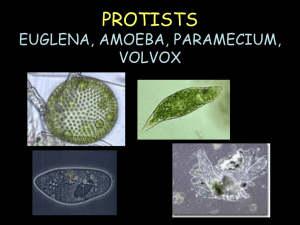
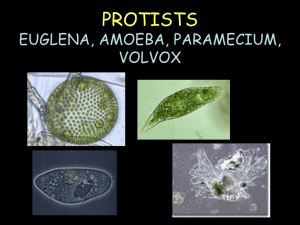
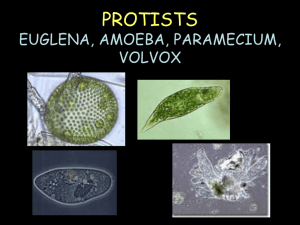
Study Guide Micro-organisms and Cells 2015 Key KEY Name: __________________ Date: ___________________ Homeroom: ______________ Core: ___________________ File: Study Guide Human Body systems and Micro-organisms 2013KEY.doc (Earth) 1, Compare the structures and functions (feeding, reproduction, movement and unique features) of Volvox, Paramecium, Euglena and Amoeba. Amoeba feed by extending the cytoplasm within them and pushing their cell membrane around potential prey consuming it. The amoeba reproduces asexually. Amoeba move by extending their cytoplasm (cytoplasmic streaming) and extending their pseudopods (false feet) dragging the rest of their bodies behind them. The unique feature of an amoeba is its false feet (pseudopods). Volvox feed by making their own food through photosynthesis (use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose – food for the volvox). The volvox reproduce by duplicating cells and depositing them inside the colonies of 500-60,000. The volvox move by moving their flagella in unisom with the other colony members. A unique feature of volvox is that is can also reproduce sexually – sharing genetic information to produce new offspring and asexually. Paramecium feed by moving their cilia (tiny hair-like projections) and directing their food to the oral grove. Paramecium reproduce by binary fission (they split in two creating an exact duplicate of themselves). Paramecium can however link together and share genetic information and then duplicate by binary fission later. Paramecium move by using the cilia to create a wavelike motion. The unique features of paramecium is they have two contractile vacuoles (water pumps that regulate the amount of water in the cells) and nuclei (Macronucleus contains its genetic information and controls how it uses energy). The micronuclei also contains the paramecium’s genetic information but is used strictly for reproduction. Euglena can ingest (eat) particles in water; however, they have chloroplasts (organelles which contain chlorophyll which allow them to produce their own food by using photosynthesis- autotrophic). Euglenas reproduce asexually by binary fission (split in two duplicating themselves). Euglenas move my using the Flagella (whip-like tail). The unique feature of the Euglena is that it can eat other particles (heterotrophic) in fresh water and make its own food by photosynthesis. You will need to know how to label each of these microorganisms: How do each of these micro-organisms: Amoeba: a. Extract (take/get) energy from food The Amoeba pseudopods surround their food particles and form a food vacuole where food is broken down and used by the Amoeba. Amoeba use contractile vacuoles to expel excess water from inside the cell them. b. Get rid of waste The Amoeba has no anus, so any spot on the outside of it’s cell membrane can open to release waste. Paramecium: a. Extract (take/get) energy from food The Paramecium has a gullet where food is placed in vacuoles and slowly digested. b. Get rid of waste The Paramecium have an anal poor that excretes waste. Volvox: a. Extract (take/get) energy from food The Volvox processes the sugar produced through photosynthesis. The Volvox has not stomach. b. Get rid of waste The waste product of photosynthesis is oxygen and it is released into the water supply after sugar is produced from combining water and carbon dioxide. The waste product of photosynthesis is oxygen and it is released into the water supply after sugar is produced from combining water and carbon dioxide. Euglena: a. Extract (take/get) energy from food Euglenoids can be heterotrophic (eating other organisms/materials) or autotrophic (making their own food – photosynthetic). b. Get rid of waste If the Euglenoid eats other materials it is digested in a food vacuole and expelled through a contractile vacuole. The waste product of photosynthesis is oxygen and it is released into the water supply after sugar is produced from combining water and carbon dioxide. Plant and Animal cell diagrams mitochondria produces energy through cellular respiration rough endoplasmic reticulum transport and storage ribosomes create proteins smooth endoplasmic reticulum creates lipids or fat chloroplast creates glucose during photosynthesis golgi apparatus synthesis, packages and releases concentrate proteins or lipids golgi body protein or lipid enters the cytoplasm cytoplasm where all chemicals take place liposome small membrane bounded transport vesicles peroxisome microbodies found in animal cells glyoxysome microbodies found in plant cells centrioles for cellular division and cellular reproduction cytoskeleton supports structure and helps move synthesized proteins lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes for digestion cilia hair like structures flagellum a whip-like tail contractile vacuole pump water out of cell vesicle moves protein, lipid and carbohydrate nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus Food vacuole contains food or water cell membrane separates cell contents from the environment nucleus information center of the cell nucleolus site of ribosome synthesis