Cell Transport Study Guide
advertisement
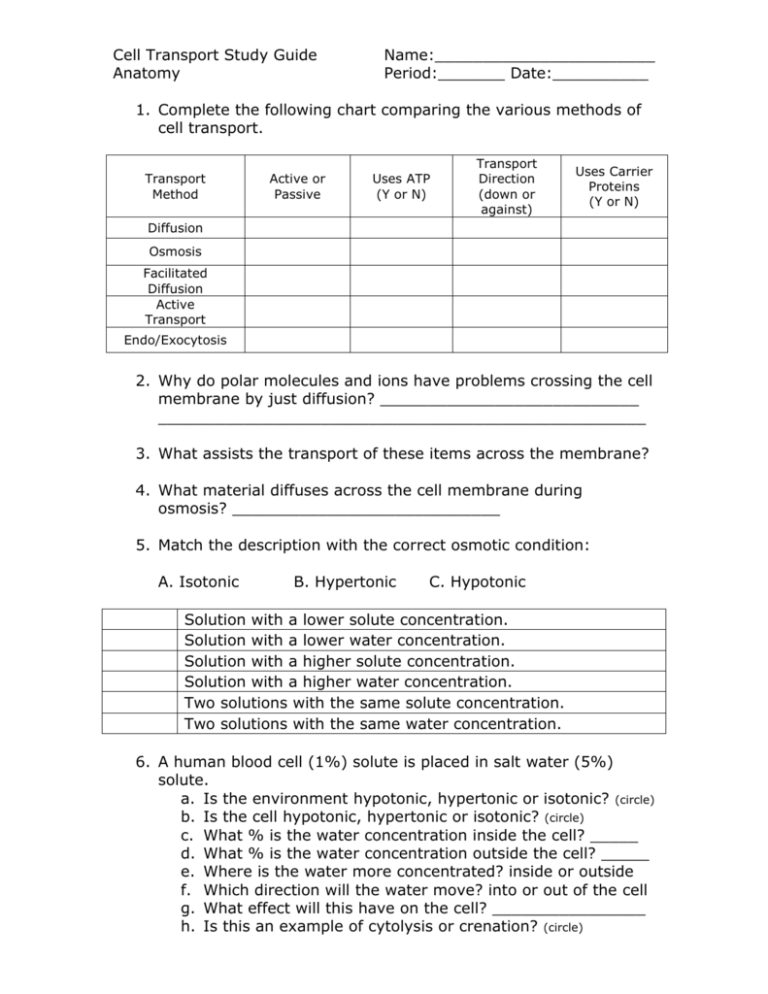
Cell Transport Study Guide Anatomy Name:_______________________ Period:_______ Date:__________ 1. Complete the following chart comparing the various methods of cell transport. Transport Method Active or Passive Uses ATP (Y or N) Transport Direction (down or against) Uses Carrier Proteins (Y or N) Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Endo/Exocytosis 2. Why do polar molecules and ions have problems crossing the cell membrane by just diffusion? ___________________________ ___________________________________________________ 3. What assists the transport of these items across the membrane? 4. What material diffuses across the cell membrane during osmosis? ____________________________ 5. Match the description with the correct osmotic condition: A. Isotonic B. Hypertonic C. Hypotonic Solution with a lower solute concentration. Solution with a lower water concentration. Solution with a higher solute concentration. Solution with a higher water concentration. Two solutions with the same solute concentration. Two solutions with the same water concentration. 6. A human blood cell (1%) solute is placed in salt water (5%) solute. a. Is the environment hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic? (circle) b. Is the cell hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic? (circle) c. What % is the water concentration inside the cell? _____ d. What % is the water concentration outside the cell? _____ e. Where is the water more concentrated? inside or outside f. Which direction will the water move? into or out of the cell g. What effect will this have on the cell? ________________ h. Is this an example of cytolysis or crenation? (circle) 7. A human blood cell (1%) solute is placed in distilled water (0%) solute. a. Is the environment hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic? (circle) b. Is the cell hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic? (circle) c. What % is the water concentration inside the cell? _____ d. What % is the water concentration outside the cell? _____ e. Where is the water more concentrated? inside or outside f. Which direction will the water move? into or out of the cell g. What effect will this have on the cell? ________________ h. Is this an example of cytolysis or crenation? (circle) 8. Sodium and potassium pumps maintain a high K+ and a low Na+ concentration inside nerve cells. In order to maintain this distribution of K+ and Na+ across the membrane, the sodium/potassium pumps must actively pump ________ ions out of the cell and _______ ions into the cell. 9. Identify the type of cell transport involved in each of the following descriptions. Use the key provided to indicate your answers. A. active transport B. diffusion C. exocytosis D. facilitated diffusion E. osmosis F. phagocytosis G. pinocytosis H. receptor-mediated endocytosis Movement of water across a semipermeable membrane down its concentration gradient. The movement of materials cross a semipermeable membrane down their concentration gradients with the assistance of carrier proteins. The movement of materials down their concentration gradients. Pumping of materials across a membrane against their concentration gradients through protein channels. Intake of small droplets of liquid by endocytosis. Occurs when a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane releasing the contents to the outside of the cell. The molecule to be transported binds to a receptor protein; the receptorprotein complex migrates to specialized coated pits pinching off and forming a vesicle. Low-density lipoproteins outside the cell bind to LDL protein receptor; LDL protein complex pinches off forming a vesicle inside the cell. Na+/K+ pumps maintain excess K+ inside the cell and excess Na+ outside the cell. Glucose binds to receptor protein and is carried into the cell, down its concentration gradient. A white blood cell engulfs a harmful bacterium. Drinking sea water causes the loss of water from cells lining the stomach and intestines.