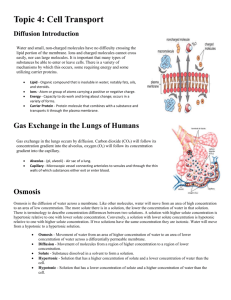
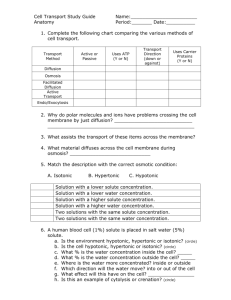
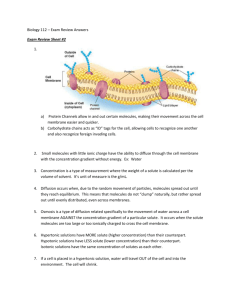
3 Diffusion and Osmosis Notes
advertisement
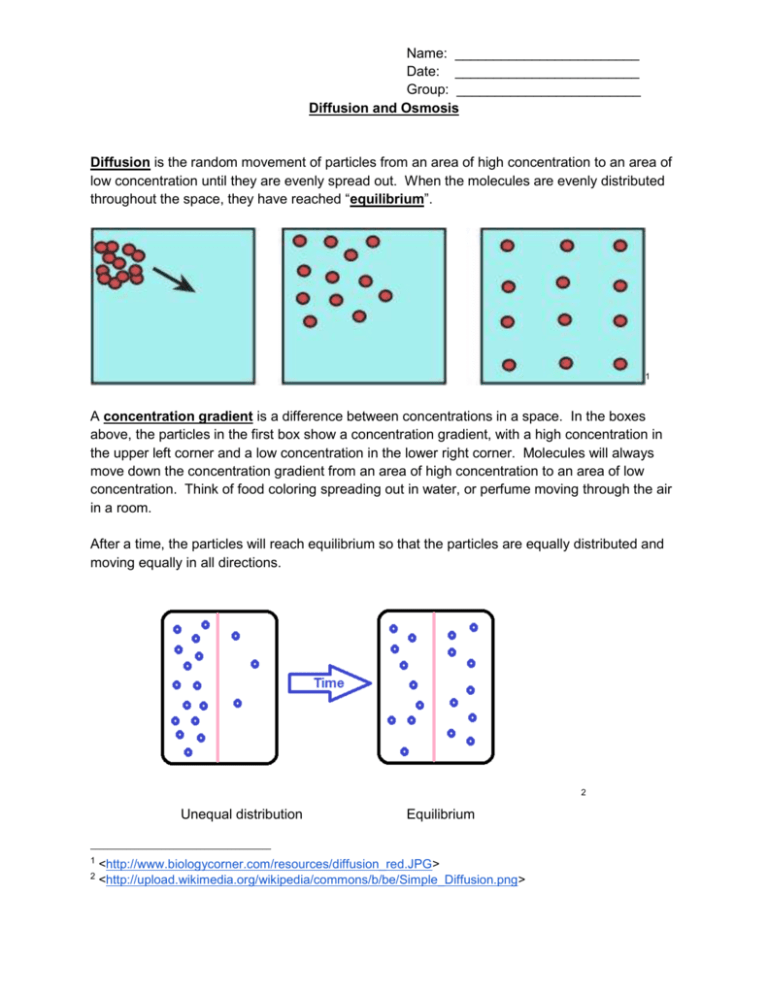
Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Group: ________________________ Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion is the random movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until they are evenly spread out. When the molecules are evenly distributed throughout the space, they have reached “equilibrium”. 1 A concentration gradient is a difference between concentrations in a space. In the boxes above, the particles in the first box show a concentration gradient, with a high concentration in the upper left corner and a low concentration in the lower right corner. Molecules will always move down the concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Think of food coloring spreading out in water, or perfume moving through the air in a room. After a time, the particles will reach equilibrium so that the particles are equally distributed and moving equally in all directions. 2 Unequal distribution 1 2 Equilibrium <http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/diffusion_red.JPG> <http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/be/Simple_Diffusion.png> Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Group: ________________________ Osmosis Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane. A semi-permeable membrane acts like a filter that allows some substances to pass through but not others. Water can pass through the membrance, and always moves from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration). Types of Solutions Solutions separated from one another by a semi-permeable membrane are named based on the relative amounts of solute in each solution. We label solutions as either isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic. These names help us understand the direction that water will move, which is especially helpful when discussing cells and their surrounding environments. 1. Isotonic Solution The prefix “iso-” means “the same”. In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute is equal on both sides of the semi-permeable membrane. Water molecules will move back and forth across the membrane but the overall amount of water on both sides of the membrane remains the same. For every molecule that moves into the cell, another water molecule moves out. 3 2. Hypotonic Solutions The prefix “hypo-” means “less”. In this case there are fewer solute molecules outside the cell, and more solute inside the cell. Since water moves toward an area of high solute concentration, the water moves into the cell. The cell will swell. In plants, the cell wall prevents the cell from bursting when water enters. In animal cells, the cell may be in danger of bursting because it does not have a cell wall to limit its expansion. 3 <http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/isotonic.gif> Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Group: ________________________ 3. Hypertonic Solutions The prefix “hyper” means “more”. In hypertonic solutions, there are more solute molecules outside the cell, which causes the water to move out of the cell. In plants, this loss of water causes wilting. In animals, the cells also shrink. In both plants and animals, the cells may die.4 It is because of this movement of water out of the cells that drinking sea water increases the rate of dehydration, because adding the salt to your body causes water to move out of the cells instead of into them. 4 <http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/hypertonic.gif>