Unit 3 and 4 Study Guide
2015-2016
Unit 3 & 4 Exam Study Guide
1.
Write the equation for photosynthesis.
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + light energy C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
2.
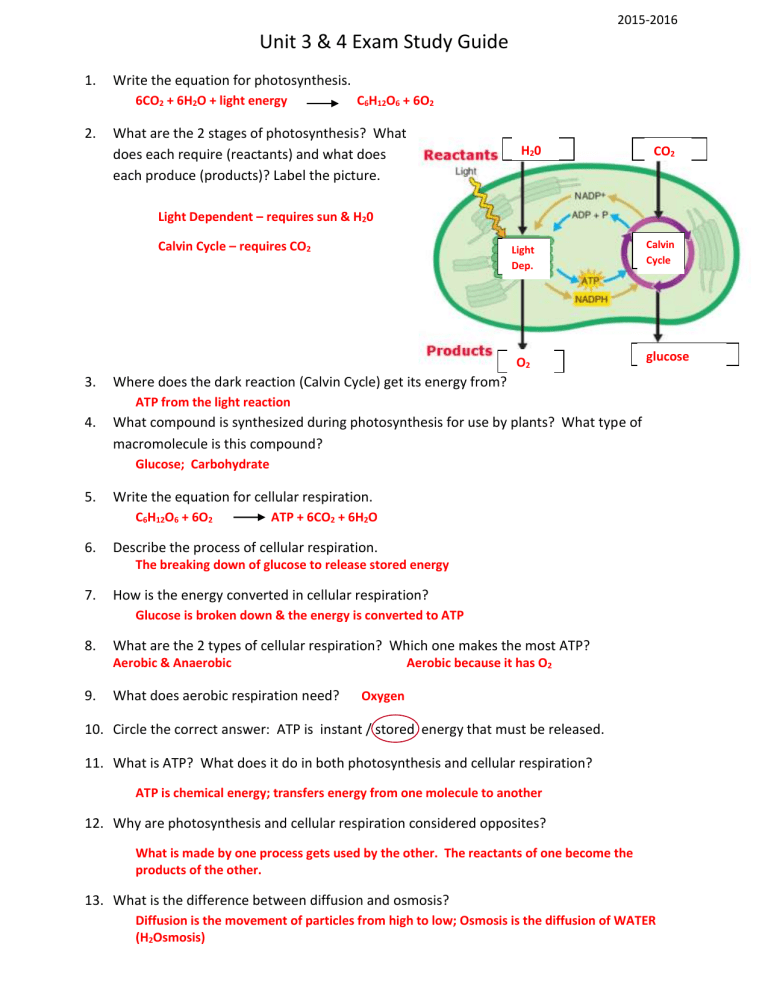
What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis? What does each require (reactants) and what does each produce (products)? Label the picture.
Light Dependent – requires sun & H
2
0
H
2
0 CO
2
Calvin Cycle – requires CO
2 Light
Dep.
Calvin
Cycle
3.
Where does the dark reaction (Calvin Cycle) get its energy from?
ATP from the light reaction
O
2
4.
What compound is synthesized during photosynthesis for use by plants? What type of macromolecule is this compound?
Glucose; Carbohydrate glucose
5.
Write the equation for cellular respiration.
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
ATP + 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O
6.
Describe the process of cellular respiration.
The breaking down of glucose to release stored energy
7.
How is the energy converted in cellular respiration?
Glucose is broken down & the energy is converted to ATP
8.
What are the 2 types of cellular respiration? Which one makes the most ATP?
Aerobic & Anaerobic Aerobic because it has O
2
9.
What does aerobic respiration need? Oxygen
10.
Circle the correct answer: ATP is instant / stored energy that must be released.
11.
What is ATP? What does it do in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
ATP is chemical energy; transfers energy from one molecule to another
12.
Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration considered opposites?
What is made by one process gets used by the other. The reactants of one become the products of the other.
13.
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low; Osmosis is the diffusion of WATER
(H
2
Osmosis)
2015-2016
14.
A cell with 60% sugar is placed in a solution of distilled water. What process is going to occur and which way will the water move? What kind of solution is this? Draw a picture.
Osmosis will cause the water to move into the cell making it a hypOtonic solution
15.
Describe what happens in each of the solutions below: a.
Hypotonic water moves in; cell will swell b.
Hypertonic water moves out; cell will get smaller c.
Isotonic no net movement
16.
Which type of passive transport uses carrier proteins to move molecules across the cell membrane?
Facilitated diffusion – proteins make it facil (easy!)
17.
What does active transport require? Why?
Energy because it is moving AGAINST the concentration gradient
18.
Define semi-permeable:
Only diffuses selected molecules and will block others
19.
What are the 4 components of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids, carbohydrates, proteins, cholesterol
20.
What are the characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
Have a nucleus, can be unicellular or multicellular, has membrane bound organelles, larger than prokaryotic cells
21.
What do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common?
DNA, cytoplasm,
22.
True or False: Eukaryotic cells can be unicellular.
23.
What are the functions of the following organelles: a.
Nucleus controls the cell b.
Mitochondria energy c.
Chloroplast makes glucose & O2 d.
Cell Membrane regulates transport e.
Ribosome makes proteins f.
ER transports proteins & makes lipids g.
Lysosome break down h.
Vacuole stores water i.
Golgi Body (apparatus) packages proteins