CHE 1010 Lecture Notes: Alkanes, Alkenes, Reaction Mechanisms
advertisement

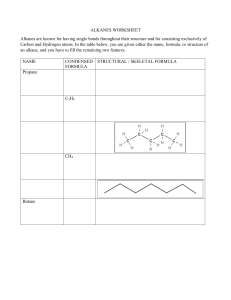
CHE 1010 Lecture Notes By Peter Mubanga Cheuka University of Zambia, Department of Chemistry, P.O Box 32379 Lusaka Zambia Adapted from Sarah Wilson, PhD, UCT Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms Reactions of Alkanes Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2 They are obtained from crude oil by fractional distillation, cracking and reformation. Alkanes are used as fuels. Alkanes as Fuels A fuel releases heat energy when burnt. Complete Combustion (In excess oxygen) Incomplete Combustion (In limited oxygen) Compared to complete combustion, incomplete combustion produces less energy per mole. The carbon (soot) from incomplete combustion can cause respiratory problems and global dimming which is a reflection of the sun’s light. Carbon monoxide is an odourless but highly toxic gas. If it builds up in an enclosed space due to faulty heating appliances, CO an cause death. The toxicity of CO is due to the strong bonds it forms with haemoglobin in the red blood cells. Because this bond is stronger than the one between oxygen and haemoglobin, CO prevents oxygen from attaching to haemoglobin. Pollution from Combustion Petroleum fractions also harbour sulfur-containing impurities which produce SO2 when burnt. Because coal contains large amounts of sulfur, its use in power stations results in the emission of large amounts of SO2. Once in the atmosphere, SO2 dissolves in atmospheric water to produce acid rain. The reaction between N2 and O2 inside the car engine produces nitrogen oxides (NOx). NO can form smog and is toxic. NO2 is toxic and forms acid rain. CO2 contributes towards global warming. Unburnt hydrocarbons also contribute to formation of smog. Global Warming CO2, CH4, and water vapour (H2O) are all green house gases. They trap the infra-red energy irradiated from the earth in the atmosphere. Water is the main greenhouse gas (but is natural), followed by carbon dioxide and methane. In recent years, CO2 levels have risen substantially due to increased burning of fossil fuels. CO2 is a particularly effective green house gas and its increase is thought to be largely responsible for global warming. The Earth is thought to be getting warmer, and many scientists believe it is due to increasing amounts of green house gases in the atmosphere. Sustainable energy sources need to be developed. These could include hydrogen-burning battery- and solar-powered cars. Other alternatives include cars run on methane, ethanol (produced by the fermentation of sugar cane). In all these alternative fuels, one should consider the overall carbon economy. • What carbon emissions are released in the production of the alternative fuel? • How much carbon dioxide is released as it is burnt? • How easy is it to refuel the vehicle? • Is the process really carbon neutral? For instance, the fermentation of plant and animal waste produces methane. CO2 is absorbed during the growth of the plants. The fermentation of plants such as maize can produce ethanol too. Therefore, the plants act as a carbon sink. But the energy needed for producing these biofuels mean these alternatives may not be really carbon neutral. Additionally, using too much land for fuel rather than food production is not very attractive. Free Radical Substitution Reaction of Alkanes Generally, because the C-C and C-H bonds in alkanes are relatively strong, alkanes do not react with many reagents. In the presence of UV light, alkanes react with chlorine to form a mixture of products with the halogens substituting hydrogen atoms. Mechanism: Free Radical Subtsitution Substitution reactions of Halogenoalkanes Alkenes Stereoisomerism in alkenes (Geometric isomerism) Stereoisomers have the same molecular and structural formula but have a different spatial arrangement of atoms. Alkenes can exhibit a type of isomerism called E-Z stereoisomerism. E-Z stereoisomers can exist when: • There is restricted rotation around the C=C double bond. • There are two different groups/atoms attached at both double bond carbons.