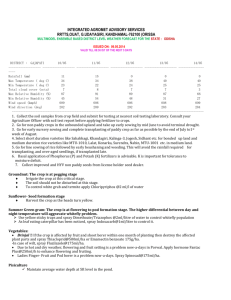
Central Telangana Zone-Package of Practices
advertisement

PACKAGE OF PRACTICES FOR THE CROPS GROWN IN Cenral Telangana Zone RICE 1. Early sowing (May last week to 20th June where as in Khammam upto the end of June) 2. Normal sowings (21st June to 10th July where as in Khammam upto 20th July) 3. Late sowings Upto July end : Long duration varieties Swarna, Samba Mashuri, Phalguna, Vajram, Improved samba Mahsuri, Pelala Vadlu and Chaitanya : Medium and short duration varieties Warangal samba, Warangal Sannalu, Polasa Prabha, Vijetha, Bhadrakali, Kavya, Shiva, Keshava, Varsha, Indur Samba, MTU 1010, Jagtial Sannalu, Tellahamsa, Pothana, Erramallelu, IR 64, Jagtial samba, Ramappa, Nelluri mahsuri, Maneru sona, Taramathi : Short duration varieties Jagtiyala Sannalu, Pothana, Erramallelu, Keshava, Varalu, IR-64, MTU-1010, Indur Samba, Rammappa, Taramathi, Nellure mahsuri, Jagtial samba 4. For precarious sources (Tank fed) : Erramallelu, Pothana, Varsha, Keshava, Varalu, Ramappa and Indur Samba, Taramathi, Jagtial samba 5. For rainfed upland : Varalu, Rudrama and Metta Sannalu I. Nursery management 1. For every 2.5 cents of nursery (100 m2) area, 1.0 kg N, 0.5 kg P2O5 and 1.0 kg K2O are to be applied in the last puddling. Another 0.5 kg N is to be applied 12 days after sowing. 2. Wherever zinc deficiency is observed 0.5 kg zinc sulphate per one cent (40 m2) of nursery field is to be applied in last puddling. 3. Sow the seed @ 5 kg for every one cent (40 m2). 50 kg seed is required for planting one ha of main field. 4. To protect nursery from insect pests, spray monocrotophos 1.6 ml/l ten (10) days before pulling and planting. 5. Plant seedlings of 25 to 30 days old. II. Main field 1 Manures and fertilizers 1. Apply 10 t of FYM/ha during land preparation. 2. Apply 100 kg N, 50 Kg P2O5, 40 kg K2O and 50 kg zinc sulphate/ha. 3. Apply nitrogen in 3 splits i.e. 1/3rd at planting and remaining in 2 equal splits at 25 and 50 days after planting to coincide with active tillering and panicle initiation stages. 4. Apply entire phosphorous, potash and zinc sulphate (without mixing zinc with phosphorous fertilizer) in the last puddling. In light soils, half of potash can be applied as basal and half at panicle initiation stage along with N. Land preparation 1. Ploughing followed by puddling to get fine tilth. 2. In order to reduce weed growth and for better water management good leveling is required. Planting, weed control and water management 1. Planting should be completed by August. 2. Plant two to three seedlings/hill. Maintain optimum plant population i.e., 44 hills/m2 (spacing 15 x 15 cm). 3. Alleys may be formed for every 3-4 m to facilitate field operations and to avoid BPH etc. in the later stages. 4. To control weeds, broadcast butachlor or benthiocarb @ 2.5 - 3.0 l/ha or anilophos @ 1.0-1.25 l/ha mixed in 25kg of dry sand 3-5 days after planting in a thin film of water. The water should be impounded for 3 to 4 days in the field. 5. Two weedings are required at 20 and 40 DAT to control weeds. 6. Thin film of water should be maintained up to maximum tillering stage. 7. Water level should be maintained to a depth of 5cm from panicle initiation onwards. Irrigation should be stopped 7-10 days before harvesting. Plant protection 2 a) Pests 1. Grow gallmidge resistant rice varieties particularly during kharif season. 2. Early sowing will enable the crop to escape the gallmidge and stemborer attack. 3. Apply recommended dose of nitrogen fertilizer at appropriate time. 4. Harvest the crop close to the ground to prevent carry over of stemborer to the next crop through stubbles. 5. Clipping of tips at nursery prevents carry over of the pests from nursery to main field. 6. Regularly monitor the crop and observe economic threshold levels as shown below. Stem borer Gallmidge BPH Leaf folder/whorl maggot Climbing cutworm - 5% Dead hearts 5% Silver shoots 10 insects/hill 3 damaged leaves/hill 1 larva/hill 7. Adopt need based application of insecticides based on economic threshold levels. 8. Against early stage insect pests like stemborer and gallmidge, apply carbofuran 3 G @ 25 kg/ha or cartap hydrochloride 4 G @ 20kg/ha. Alternatively, spray monocrotophos (1.6 ml/l) or chlorpyriphos (2.0 ml/l) or phosphamidon (1.0 ml/l). 9. To prevent stem borer at flowering, apply carbofuran 3G @ 25kg/ha or cartap hydrochloride 4G @ 20kg/ha between panicle initiation to booting which will also take care of BPH. 10. To control BPH and WBPH spray acephate 75 SP @ 1.5 g/l or monocrotophos @ 1.6 ml/l or imidacloprid 200 SL @ 0.2 ml or fenubocarb @ 2 ml/l on need basis. 11. Against BPH during grain hardening stage, apply carbary1 5% dust or endosulfan dust @ 25 kg/ha. Dusting should be directed to the base of the hills for effective control. 12. Avoid use of carbofuran 3G when leaf folder incidence is more. Spraying with monocrotophos (1.6 ml/l) or chlorpyriphos (2.0 ml/l) or quinalphos (2.0 ml/l) is more effective against leaf folder. 13. For control of climbing cutworm spray quinalphos (2.0 ml/l) or chlorpyriphos (2.0 ml/l) or monocrotophos (1.6 ml/l) or endosulfan (2.0 ml/l) mixed with dichlorophos (1.0 ml/l). Spraying in the evening is preferable. 3 14. For control of panicle mite, dicofol @ 5.0 ml/l or prophenophos 50 EC @ 2.0 ml/l should be sprayed when the initial symptoms of yellow patches on leaves/brown necrotic patches on leaf mid ribs/boot leaf sheath are noticed. Repeat spraying after 15 days. 1. To prevent/control blast, sheath blight etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Use disease free seed. Adopt dry seed treatment with carbendazim @ 1 g/kg seed or wet seed treatment with carbendazim solution @ 1 g/kg/l of water. Adopt clean cultivation. Crop should be weed free. Field should be cleaned by removing all weeds. N fertilizers should be applied in more splits. 2. To control rodents for kharif season: 1. 2. 3. Removal of garbage and observe sanitation. From puddling to panicle initiation, setting of local traps @ 50/ha. Installation of permanent bait stations throughout the crop period @ 5 stations/ha, four at corners of the field one meter inside from the bund and one at the centre. Bromadiolone bait @ 50 g per bait station should be replenished twice in a week. During crop period, action plan with bromadiolone 0.005% in baits from crop establishment till panicle initiation stage. From panicle initiation till harvest, smoking of burrows with burrow fumigators’ developed by APRRI, Maruteru. 4. 5. Action plan with bromadiolone 0.005% Day 1 : Identify live burrows and simultaneously place 15g freshly prepared bromadiolone loose bait in a packet inside the burrow. Day 12 : Repeat bromadilone loose baiting in the active/live burrows. Note: Control schedules should be executed on community basis to check cross infestation through migration. Unit requirement of bromadiolone 1. For 1st baiting to 50 burrows/ha @ 15 grams loose bait/burrow - 15 grams bromodiolone requirement/ha. 2. For 2nd baiting to 10 burrows/ha @ 15 grams loose bait per burrow (20% of 50 burrows) – 3 grams bromodiolone requirement per ha. 4 b) Diseases Stage Blast Threshold level Endemic areas Nursery Pre-tillering to mid-tillering Panicle initiation to booting Flowering and after Sheath blight Pre-tillering to mid tillering Light 2 - 5 % disease severity 2 - 5 % leaf area damaged Control measure Use tolerant varieties like IR 64, WGL 47970, MTU- 1001, MTU-1010. Adopt dry seed dressing with trycyclazole 75% WP or carbendazim @ 1.0 g/kg seed Spray carbendazim @ 1.0 g/l or ediphenphos @ 1.0 ml/l Apply ediphenphos @ 1.0 ml/l or trycyclazole @ 1.6 g/l Delay top dressing of N fertilizers Spray ediphenphos @ 1.0 ml/l or trycyclazole @ 1.6 g/l 5 % leaf area damaged or 1 - 2 % neck infection Spray ediphenphos @ 1.0 ml/l or trycyclazole 75 % WP @ 0.6 g/l. Repeat spray by changing chemical if required. 5% or more affected tillers per m2 Spray hexaconazole @ 2.0 ml/l or propiconazole @ 1.0 ml/l or validamycin @ 2 ml/l Reduce or delay top dressing of nitrogenous fertilizers & apply in 2 - 3 split doses. Control measure Spray hexaconazole @ 2.0 ml/l or propiconazole @ 1.0 ml/l or validamycin @ 2 ml/l Threshold level Stage Panicle 5% or more initiation to affected tillers booting per m2 Bacterial leaf blight Pre-tillering to 2-5% disease mid tillering severity Panicle Light to initiation to moderate booting Sheath rot/ Brown spot Flowering and Light after False smut Flowering and after Tungro Nursery Light Pre-tillering to mid-tillering One affected hill per m2 - Reduce nitrogen application and apply N in more split doses Skip top dressing of nitrogen fertilizer Apply mancozeb @ 2.5 g/l or carbendazim @ 1.0 g/l during early morning or afternoon hours. Spraying should be avoided during the period of flowering Apply copper oxychloride @ 2.5 g/l around flowering stage Apply carbofuran 3G @ 160 g/l /cent nursery. Remove and destroy infected seedlings before transplanting Remove and destroy infected plants and apply additional nitrogen for early recovery Apply carbofuran granules @ 25kg/ha or spray monocrotophos @ 2 ml/l to control insect vector 5 Stem rot 1. 2. 3. 4. Use disease free seed. Burn straw and stubbles in affected area. In endemic areas, spray validamycin or hexaconazole @ 2.0 ml/l or benomyl @ 1.0 g/l or carbendazim @ 1 g/l twice at 15 days interval after maximum tillering stage. Summer ploughing helps in reducing the inoculum. Management practices for high head rice recovery (HRR) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Balanced fertilization, avoid excessive nitrogenous fertilizers Avoid application of nitrogen at flowering/boot leaf stage Avoid water stress during panicle initiation to grain maturity Harvest in time at physiological maturity Allow the sheaves to dry in the field 1 or 2 or 3 days Adjust the sowing time in such a way that the grain filling time does not coincide with high temperature Dry the produce slowly and uniformely to maintain food grain quality Avoid cultivation of varieties having abdominal white or chalkiness Avoid varietal admixtures to over come poor milling recovery Storing for 3 to 4 months after harvest at a temperature above 15oC PUDDLE SEEDED RICE Farming situations : Well and tank fed areas FS-2, FS-5, FS-12 and FS-13 under late receipt of water in the season Varieties : Short duration (120 days), Jagtial Sannalu, Erramallelu, Pothana, Indur Samba, Varalu, Ramappa, Taramathi, Nelluri mahsuri, Jagtial samba Sowing time : July/August Seed rate : 50-75 kg/ha Fertilizers : 90 kg N in 3 splits at 10 DAS, 40 DAS, 65-70 DAS, 60 kg P2O5 and 40 kg K2O and 50 kg ZnSO4 per hectare as basal at sowing Weed control : Butachlor or pretilachlor 50 EC @ 2.5 or anilophos 1.0 - 1.25 l/ha Water management : Saturation to submergence i.e., 2-5 cm water level throughout the crop growth. Plant protection : Same as for transplanted rice 6 MAIZE Maize has gained importance among cereal crops in Andhra Pradesh during last 3-4 years. The following package of practices have to be adopted to achieve higher yields during kharif. Soils Deep or medium black soils with good drainage facilities are preferable. Maize does not come up well in saline, alkaline and waterlogged soils. The optimum pH range should be between 5.5 to 7.5. Sowings Time of sowing Middle of June to middle of July. In case of delayed monsoon, may be extended up to first week of August with short duration hybrids. Seed treatment : Seed treatment with Thiram or Captan @ 2 g/kg seed Seed rate : 7 kg/ac for normal hybrids, sweet corn 4 kg/ac, baby corn 10 kg/ac Spacing 75 cm between rows and 20 cm between plants or 60 cm between rows and 25 cm between plants. This gives a plant population of 26,000/ac approximately for all the hybrids Method of sowing Sowing on sides of ridges at a distance of 1/3rd from top facilitates irrigation as well as drainage. Excess seedlings should be thinned 10 days after emergence to have single seedling per hill. Fertilizers For Kharif crop 60-80 kg N, 24 kg P2O5, 20 kg K2O per acre is recommended. Nitrogen may be applied in three splits viz., at sowing, knee high stage and at flag leaf emergence. Zinc sulphate @ 20 kg per acre may be applied if soils are known to be deficient in available zinc. If symptoms appear later, the crop can be sprayed with 2 g/l solution of zinc sulphate. At the time of second dose of nitrogen, loosen the soil with cultivator and earthing up should be done with ridger. 7 Weeding Pre-emergence spraying of Atrazine (Atrataf) 50 W.P @ 800 g/ac in 200 litres of water will control most of the broad leaved weeds effectively. After 30-35 days, crop may be intercultivated and earthing up should be done. Atrazine is recommended when maize is grown as a pure crop. Irrigation Though the crop is grown under rainfed conditions, if drought occurs during flowering stage, irrigation helps to give good yields. When the crop is in initial stages, provide proper drainage facilities to drain out excess water in case of heavy down pour. Plant protection a) Pests The stem borer (Chilo partellus) infests the crop during kharif season. The borers cause dead hearts in early stage of corp. The pest incidence is recognized by the presence of shot holes in the leaf blades as well as exit holes on the stem. Generally hybrids are tolerant to these pests. In endemic areas prophylactic spraying of Endosulfan 35 EC @ 2 ml/lt or application of Endosulfan 4 G/Carbofuran 3 G in leaf whorls @ 3.0 kg/ac is recommended when the crop is 10-12 days old. b) Diseases The important diseases of maize are leafblight (Helminthosporium turcicum), late wilt (Cephalosporium maydis) and charcoal rot (Macrophomina phaseolina). Three sprayings of Mancozeb @ 2.5 g/l at 10 days interval starting from knee high stage of the crop controls the leaf blight. Banded leaf and sheath blight is observed in some of the district. As and when the sympotoms are noticed, stripping of the affected bottom 2-3 leaves along with their sheath and spraying of Propiconazole @ 1 ml/l at 40 DAS in endemic areas. For late wilt & charcoal rot, crop rotation, removing plant debris, summer ploughing, growing resistant hybrids and avoiding moisture stress after flowering stage should be followed. Recommended hybrids/varieties The following Hybrids/varieties can be recommended for kharif season Hybrids : DHM-103, DHM-105, DHM-111, DHM-113, DHM-115, DHM-117 Varieties : Ashwini, Harsha, Varun Specialty corn varieties Sweet corn : Madhuri, Priya and Win sweet corn, Sugar-75 8 Pop corn : Amber popcorn, Pearl popcorn Baby corn : Him-129 and DHM-115 Quality protein : Amber Shakti, HQPM-1 Critical interventions 1. 2. 3. 4. Spraying of Endosulfan @ 2 ml/l after 15 days of sowing Keeping the crop weed free upto 45 days Top dressing of Urea coinciding with the rains Irrigation at silking and dough stages MILLET CROPS GRAIN SORGHUM Varieties : Varieties: PSV-1, Palem-2, CSV-13, CSV-15 Hybrids : CSH-13, CSH-16, CSH-18, CSH-21 Sowing time : June-15th -July Seed rate : 8-10 kg/ha Seed treatment : Treat the seed with Thiram or Captan @ 3g/kg seed Manures & Fertilizers : FYM : (i) 10 t/ha Light soils with low rainfall Basal : Top dressing : (ii) 30 N + 30P + 30K kg/ha (30-40 days crop): 30 N kg/ha Fertile soils with assured rainfall Basal : Top dressing : 40 N + 40P + 40K kg/ha (30-40 days crop): 40 N kg/ha Spacing : 45 cm x 12 cm Inter cropping : Sorghum (2rows): Red gram (1 row) 9 Weed management 1. 2. Two manual weedings along with one or two intercultures with danti Pre emergence application of Atrazine @ 4g/litre with in 48 hrs of sowing coupled with one manual weeding and one interculture operation is also economical. Disease management i) Grain molds : Spray Propiconazole @ 1.0 ml/l twice at 50 % flowering and 10-15 days later. ii) Smuts : Seed dressing with Thiram @ 3g/kg seed. iii) Ergot 1. Mechanical removal of sclerotia from seeds by washing in 5% salt solution followed by rinsing with plain water before sowing. Spraying with Carbendazim @ 1 g/l or Propiconazole @ 1.0 ml/l at 50 % flowering and another spray at 15 days later. 2. iv) Witch seed (striga weed) 1. 2. Spray Ammonium sulphate @ 50 g/l or urea 200g/l on the striga plants. Destroy the parasite before flowering. Pest management 1. Shoot fly 1. 2. 3. Deep ploughing to expose larval and pupal stages present in the stubbles. Early sowings with the onset of monsoon. In the late sown crop use high seed rate of 10-12 kg/ha and thin out the affected and extra plants at 4 weeks after sowing. Seed treatment with Imidacloprid @ 14 ml/kg of seed /Furadan 50SP @ 100 g/kg seed / Carbofuran 50 WP @ 100 g / kg seed. In heavy infested areas soil application of carbofuran 3G 20 kg/ha in seed furrows Minimize damage by spraying Endosulfan @ 2 ml /l at 7 and 14 days after emergence. 4. 5. 6. 2. Stem borer 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Deep ploughing to expose larval and pupal stages present in the stubbles. Sowings with onset of monsoon Removal and destruction of dead hearts. Inter cropping with non cereal crop. Whorl application of Carbofuran 3 G / Endosulfan 4 G /Malathion 10D @ 7.5 kg/ha at 25 and 35 days after emergence. 10 3. Corn leaf aphid 1. 2. Lady bird beetles and horse flies devour aphids Spraying of Metasystox or Dimethoate @ 2 ml/l 4. Ear head bug 1. 2. Early sowing minimizes bug damage. Application of Endosulfan 4% dust/Malathion 5% dust @ 25 kg/ha at pre bloom and again at milk stages. 5. Panicle worm 1. 2. Dust application of Malathion 5% dust @ 25 kg/ha Spraying of Monocrotophos @ 1.6 ml/l or Endosulfan @ 2 ml/l 6. Red mite 7. Sorghum midge : : Spray Dicofol @ 5 ml/l Application of Endosulfan 4 G/Malathion 5 D @ 20 kg/ha at 90 % days after emergence. BAJRA Varieties Open pollinated varieties : (Composites & synthetics) ICMV 221, ICTP 8203 and Raj 171 Hybrids : HHB 67, RHB 121 and any other popular private hybrid from reputed companies. Sowing time : June-July Seed rate : 4 kg/ha Seed treatment : Treat the seed with Thiram or Captan @ 3g/kg seed. Manures & Fertilizers : FYM : Basal : Bio-fertilizers : Seed inoculum with local strains of bacterium Azospirillum brasillense increase yield markedly in the presence of 10-40 kg N/ha. Spacing : 45 cm x 10-12 cm thinning to one seedling/hill at 15-20 days age of the crop. Inter cropping : Bajra (2 rows): Red gram (1 row) 11 25 t/ha 30-40N + 20-40P + 20-30K kg/ha Weed management 1. 2. Two manual weedings along with one or two intercultures with danti. Pre emergence application of Atrazine @ 4g/litre with in 48 hrs of sowing coupled with one manual weeding and one interculture operation is also economical. Disease management i) Downy mildew 1. 2. 3. 4. Treat the seed with Apron 35% SD @ 6g/kg seed. Foliar spray of Ridomil 25 WP (100ppm) at 21 days after sowing if infection exceeds 5%. Uproot and burn the infected plants. Avoid monoculture of particulars cultivar. ii) Ergot 1. Dip the seeds in 20% brine solution, stir and remove the floating seeds and sclerotia. Dry the seeds lying at the bottom and sow. Need based spray of Ziram @ 2g/litre at boot leaf and flowering stages. Plough the field soon after harvest to bury the ergot inoculum deep. 2. 3. Pest management (i) White grub 1. Apply Phorate or Carbofuran granules @ 12 kg/ha in seed furrows at the time of sowing. (ii) Shoot fly 1. Two dustings of Malathion 5% @ 25 kg/ha or two sprayings of Endosulfan @ 2 ml/l after germination. (iii) Grey weevil and other leaf feeding and ear head pests 1. Dust Methyl parathion 2 % or Fenvalerate 0.4 % or Quinolphos 1.5 % @ 25 kg/ha. SUGARCANE 1. Varieties a. Early maturing : Co 6907, 83 A 30, 84 A 125, 85 A261, Co 8014, 81 A 99, 87 A 298, 86 V 96, 97 A 85, 2000 V 59, 91 V 83 2003 V 46, 93 A 145 and 83 R 23 12 b. Mid-late maturing : Co T 8201, Co A 7602, Co 7805, 83 V 15, 86 A 146, 88 A 162, 96 A 3and 99 A 5 c. Late maturing : Co 8011, Co 7219, Co 7706, 87 A 380 and Co R 8001 d. Moisture stress : Co 6907, 84 A 125, 81 A 99, 83 A 30, 87 A 298, 83 R 23 Co T 8201, 90 A 272, 97 A 85, Co 7219 and Co A 7602 e. Swamp conditions : 96 A 3, 99 A 5, 97 A 85, 84 A 125, Co 6907, Co T 8201, Co 7219, 85 A 261, 83 V 15, Co 7706, Co A 7602, 93 A 145 and Co R 8001 f. Saline – Alkaline soils : Co T 8201, 81 A 99, 93 A 145, 97 A 85 and Co 7219 2. Soils / Areas : Alluvial and red soils of rice deltas. Welldrained loamy soils 3. Land preparation : Soils to be worked to fine tilth to a depth of 20-25 cm. Open trenches of 30 cm width, 20 cm depth and 50 cm ridges have to be formed by manual labour or iron plough or ridgemar 4. Seed rate 5. Seed treatment : 40,000 three budded setts per hectare. Hot water treatment of seed material at 52o C for 30 minutes or treatment with aerated steam for smut and grassy shoot disease followed by dipping of setts in Carbendazim (0.05%) and Malathion (0.1%) to eliminate pineapple disease and scale insect 6. Short crop Primary seed nurseries of six to seven months age can be raised from treated seed material in the months of December-January. Secondary seed material should be planted in July-August months utilizing seed from primary seed nurseries. Commercial plantings can be done utilizing seed from secondary nurseries. 7. Spacing 8. Planting with cut off dates Early varieties Mid varieties : 80 cm between rows for early varieties and 90 cm for mid-late varieties : : December – January February 13 Late varieties 9. : March Manures and fertilizers including bio-fertilizers, micro nutrients etc Farm yard manure @ 25 tones per hectare or press mud cake @ 12 tones per hectare in the last ploughing. 112 kg nitrogen (pocket application) has to be applied in two equal split doses at 45 and 90 days after planting. Phosphorous @ 100 kg P2O5 and Potassium @ 120 kg K2O per hectare as basal application. Zinc sulphate (2 gm/lt) and Ferrous sulphate (10-20 gm/lt) as foliar spray at 4560 days after planting where zinc and iron deficiencies are observed. 10. Inter cultivation and other management practices, if any Weed management Application of Atrazine @ 5 kg/ha in 1125 lts of water to be sprayed on the third or fourth days after planting, depending on soil moisture. At 20 and 60 days of planting spraying of 2,4-D (4 ½ kg) + Gramoxone (2.5 lts) in 1125 lts/ha is recommended. Inter culture Earthing up at about four months after planting, propping the crop by trash twist, twice or thrice, depending on crop growth. 11. Irrigation Once in six days during summer and once in 15-21 days from November to harvest. During grand growth period, irrigation is to be provided when dry spell exceeds 15 days. If, only one irrigation is possible during formative phase, it has to be given at 30 days after planting and trash mulching has to be done three days after planting @ 3 t/ha. 12. Harvesting Crop has to be harvested at peak maturity depending upon variety, date of planting and juice quality. 13. Post harvest technology Sugarcane harvested in a field should be free from root material, soil etc., The immature top portion should be cut to the first visible top internode. Such dressed cane should be crushed within 24 hours either in a sugar factory or jaggery crusher to avoid loss in the weight of cane and recovery of end product. 14 Powdery and bucket shaped forms of jaggery were found to be better for storage and handling. Jaggery kept in painted earthern pots and gur drying cum storage bins was not subjected to any spoilage for longer period. Jaggery powder kept either in polythene bag or polythene bottles can be stored for periods longer than an year without any loss in quality or quantity. Normal areas and seasons : Ratoon crop 1. Varieties a. Early maturing : Co 6907, 83 A 30, 84 A 125, 85 A261, Co 8014, 81 A 99, 87 A 298, 86 V 96, 97 A 85, 91 V 83, 2003 V 46, 93 A 145 and 83 R 23 b. Mid-late maturing : Co T 8201, Co A 7602, Co 7805, 83 V 15, 86 A 146, 88 A 162, 96 A 3 and 99 A 5 c. Late maturing : Co 8011, Co 7219, Co 7706, 87 A 380 and Co R 8001 2. Soils/Areas : Alluvial, red and well drained loamy soils 3. Stubble shaving and interculture Plant crop has to be harvested to the ground level or just below ground level. Stubble shaving has to be done with spades without disturbing the stools. The interspaces have to be ploughed to 12 to 15 cm depth to break the crust and improve aeration for better ratooning. 4. Trash mulching Trash mulching @ 3 t/ha at 3rd-5th days after ratooning ensures conservation of soil moisture and suppression of early shoot borer and weed growth. 5. Manures and fertilizers including bio fertilizers, micro nutrients etc., 224 kg N/ha has to be applied in two split doses at ratooning and 45 days later. P 2O5 @ 100 kg / ha and K2O @ 120 kg / ha are to be applied at the time of ratooning. If deficiency of iron is noticed Ferrous sulphate (2%) is to be sprayed on foliage immediately. 6. Gap filling Gap filling has to be done with seedlings raised in polythene bags or in nursery from single budded setts within two weeks after ratooning. 7. Weed management 15 Weeding and hoeing at 1st, 4th and 7th weeks after ratooning or spraying Atrazine @ 2.0 kg / acre immediately after ratooning followed by one hand weeding at 45 days after ratooning or metribuzin @ 600 g/acre in 450 lit. of water within three days after ratooning followed by one hand weeding at 45 days after ratooning. 8. Harvesting Ratooning crop matures earlier than plant crop. Therefore crop has to be harvested earlier than plant crop at peak maturity. Saline/Alkaline soil conditions 1. Varieties : 81 A 99, 93 A 145, 97 A 85, Co T 8201 and Co 7219 2. Soils / Areas : Saline / Alkaline soils 3. Land preparation : Deep ploughing is not advisable but other aspects are similar to plant crop 4. Seed rate : 45,000 three budded setts per hectare. Seed material should be selected from matured crop 5. Planting / Sowing/ with cut off dates Early planting Late planning 6. : : December – January June Manures and fertilizers including bio fertilizers, micronutrients etc; Gypsum has to be applied @ 2-5 t/ha depending upon PH ranging from 8.5–9.2. Farm yard manure @ 25 t/ha or press mud cake @ 12 t/ha and Zinc sulphate @ 50 kg / ha are to be applied in the last ploughing. P2O5 @ 100 kg / ha and K2O @ 120 kg / ha for early planted crop and 50 kg / ha K2O for late planted crop at the time of formation of ridges and furrows. For early planting, Nitrogen @ 112 kg/ha in two splits at 60 and 120 days and for late planting 75 kg N/ha in two splits at 30 and 60 days after should be applied after planting. 7. Inter cultivation and other management practices if any i. ii. iii. Provision of drainage and leaching with good quality water. Earthing up at 4 months after planting and trash twist propping 2-3 times depending upon the growth of the crop. Trash mulching @ 3 t/ha three days after planting. 8. Irrigation 16 For early planted crop – once in six days during summer and once in 15-21 days from November to harvest. During rainy season if dry spells prevails one to two irrigations may be provided. Late planted crop is usually rainfed. 9. Harvesting Crop has to be harvested at peak maturity depending upon variety, date of planting and juice quality. Pests and diseases of sugarcane and their management Insect pests 1. Early shoot borer 1. 2. 3. Planting of setts in deep furrows. Application of Phorate 10 G granules @ 15 kg/ha at the time of planting. Trash mulching @ 3 t/ha at 3 days after planting in plant crop and immediately after stubble shaving in ratoon crop. Irrigation at frequent intervals during summer. Spraying Endosulfan 0.07% or Chlorpyriphos 0.05% at 4, 6 and 9 weeks after planting in 450, 675 and 900 lts of water, respectively. Early ratooning in the months of November and December coupled with closer irrigations in the formative phase of the crop. Use of synthetic pheromones in water traps @ 5 /acre commencing from 35 days after ratooning. Field release of egg parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis @ 50,000/ha at 30 days after ratooning and subsequent releases should be made at fortnightly intervals for four times. Internode borer 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 2. 1. 2. 8. Control of early shoot borer in early stages of the crop growth. Detrashing of the crop with a view to destroying the larvae and pupae attached with the leaf sheaths. Removal of water shoots at eighth/ ninth months. Avoid high dose of nitrogen Draining off water in low-lying areas. Use of synthetic pheromones in water traps @ 5 /acre commencing from the internode formation stage of the crop. Field release of egg parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis @ 50,000/ha at fortnightly intervals from 120 days after planting until a month before harvest. Spray endosulfan @ 0.07% twice at 15 days interval during June-July months. 3. Scale insect 1. Dipping three budded setts in Malathion 0.1% or Dimethoate 0.05% for 15 minutes before planting. Detrashing the cane in the first weeks of July, August and September months followed by spraying with dimethoate 0.05% or malathion 0.15%. Dimethoate is preferred for spraying during heavy rains. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 2. 3. 17 4. Plant crop once met with heavy infestation should not be ratooned. 4. Mealy bug 1. 2. The plant crop infested with mealy bugs should not be ratooned. Known alternative host plants (certain grasses like Cymbopogan) near sugarcane fields may be destroyed. Avoid over dosage of nitrogenous fertilisers. Repeated ratooning may be avoided in areas prone to mealy bug. Detrashing in grown-up crop is advocated followed by thorough spraying with dimethoate @ 1.7 ml/lt or malathion @ 3ml/lt. by using foot sprayer with long lance. 3. 4. 5. 5. White fly 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Providing of adequate drainage facilities Heavy rainfall washes out the pest. Application of ‘N’ fertilisers at recommended dose at stipulated time. Ratooning is to be avoided in low lying areas prone for water logging. Spraying with endosulfan 0.07% or malathion 0.1% or chlorpyriphos 0.05% using foot sprayer with long lance. 6. Termites 1. Systematic digging of termite mounds and destruction of queens. Application of lindane dust @ 200g/ mound followed by proper leveling. Application of Lindane 1.2% Dust in the furrows @ 25 kg/ha. On standing crop, spay chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 5ml/lt. on internodes. Cane fly 2. 3. 7. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Removal of lower leaves Judicious use of Nitrogenous fertilisers. Prevention of lodging. Spray endosulfan @ 2ml/lt or malathion @ 2 ml/lt with foot sprayer Release of Epiricania melanoleuca 4000-5000 cocoons/ha and 4-5 lakhs eggs per hectare. 8. Mites 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Removal and destruction of infested leaves Removal and destruction of grasses on the bunds. Spray the sugarcane crop and grasses with wettable sulphur @ 3g/lt at 15 days interval starting from the appearance of the pest. Adoption of balanced nutrition. Frequent irrigations in the pre-monsoon period reduce O. indicus infestation. 9. Woolly aphid 1. Harvesting of affected matured crop on priority basis. 18 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 10. Avoidance of transportation of infested leaves. Avoidance of ratooning, if the plant crop is heavily infested with woolly aphid. Adoption of paired/wider row planting. Removal and burning of affected leaves. Wrapping and propping of canes. Judicious use of nitrogenous fertilisers and irrigation water. Providing proper drainage. Collection and release of predators like Chrysoperla carnea @ 5000-7500 eggs/ha ; Syrphid fly, Brown lace wing, Micromus timidis ( Ord.Neuroptera) and Dipha aphidivora (Ord. Lepidoptera) in infested patches. Monitoring of the pest through yellow traps. Thorough spraying with malathion 50 EC @ 2ml/lt. or endosulfan 35 EC @ 2ml/lt or monocrotophos @ 1.6 ml/lt. or dimethoate 30 EC @ 1.7ml/lt or chlorpyriphos 20EC @ 2.5 ml/lt. or methyl demeton @ 2ml/lt. or Acephate @ 1g/lt. Root grub Damage due to root grub appears to be severe in light soils. Application of phorate 10 G granules @ 15 kg/ha to soil at planting reduces the damage. * In standing crop, flooding of fields for 2-3 days is effective in reducing the severity. Diseases * * 1. Smut * * * Systematic eradication of smutted clumps. Avoidance of second ratoon if incidence is severe. Treating three budded setts in hot water at 52o C for 30 minutes or aerated steam at 51o C for two hours followed by dipping setts in Carbendazim and raise special seed nurseries. Selecting seed material from disease free areas atleast 40 mt away from affected fields. Sett treatment with propiconazole (1 ml/lt) for 15 minutes before planting in susceptible varieties Spray propiconazole (0.5 ml/lt) twice, one at 35 days after ratooning and 30 days later if infection persists. * * 2. Red rot * * * Selection of healthy seed material from disease free localities. Systematic eradication of affected clumps. Uproot and destroy un-germinated setts of plant crop and un-sprouted clumps of ratoon crop. Affected plant crop should not be ratooned. Proper drainage should be maintained to avoid stagnation. After harvesting affected plots, all stubbles and debris should be burnt and further cane planting should not be taken up to four months. Diseased canes are to be harvested as early as possible and crop residues should be burnt. * * * * 19 * * Keep the crop erect without lodging by propping with bamboos or trash twist propping. Growing resistant varieties like Co 7706, Co A 7602, Co 8021,97 A 85, Co T 8201, Co R 8001, 85 A 261, 83 A 30, 87 A 298, 86 V 96, 83 V 15, 83 R 23, 90 A 272 and Co 7219. 3. Grassy shoot disease * * * * * Uproot and destroy affected clumps. Severely affected plots should not be ratooned. Select seed material from disease free plots. Treat setts in hot water at 52O C for 30 minutes of aerated steam at 50O C for one hour and raise special seed nursery. Spray malathion (2 ml/ lt) or dimethoate (2 ml/lt) to check vector population. 4. Pineapple disease * * The disease can be avoided by dipping the setts in 0.05 percent solution of carbendazim (150 g of carbendazim in 300 litres of water for 40,000 three budded setts sufficient to plant in one hectare). Fungicidal sett drip treatment is essential for heat treated setts 5. Wilt * * * * * Frequent irrigations during summer Avoid water logging Use of disease free seed material Effective control of diseases and pests Application of recommended dose of nitrogen 6. Leaf scald * * * Grow healthy short crop seed material for planting Sterilize harvesting knives with 5 % formaldehyde or on direct flame Hot water treatment at 52oc for 30 minutes then treats the setts with carbendazim (0.05 %) for 15 minutes to avoid pineapple. 7. Top rot * Two sprays of mancozeb (3 g/lt) at 2-3 weeks interval. 8. Ring spot * Spray either carbendazim (0.1 5) or mancozeb (0.3 %) or copper oxychloride (0.04 %) twice or thrice at three weeks interval starting from the first appearance of disease. 9. Rust 20 * Spray tridemorph 1 ml / lt. or mancozeb 3 g/ lt. bi-weekly intervals. PULSES GREENGRAM Varieties : LGG-450, LGG-407, LGG-460, WGG-2, WGG-37, MGG-295,MGG-347, MGG-348, TM-96-2, ML-267, Pusa-105 and PDM-54. Soils/Areas : All types of soils with good drainage facilities. Saline soils are not suitable. Land Preparation : Land should be prepared to fine tilth with 2 ploughings followed by a harrowing. Sowing time : June 15 - July 15 Seed rate : 15-16 kg/ha Seed treatment : Carbosulfan @ 30 g/kg or Imidacloprid @ 5 ml/kg or Thiomethoxam @ 5 g + Captan/ Thiram/Mancozeb Carbendazim @ 2.5 g per kg seed to protect the crop from all pests and diseases upto 20-25 days. Spacing : 30 x 10 cm Manures and fertilizers : 20 kg N + 50 Kg P2O5 per ha. Treat the seed with good quality Rhizobium inoculants. Intercultivation and other management practices, if any Keep fields weed free by giving 2-3 hoeings within 25-30 DAS. Application of Fluchloralin @ 2.5l/ha as pre-sowing incorporation checks weed growth or pre-emergence application of Pendimethalin @ 1.5 kg /ha for the first 20-25 days. Irrigation : Nil Stemfly : Seed treatment as above. Acephate @ 1 g/lt or Monocrotophos @ 1.6 ml/lt or Dimethoate @ 2 ml/lt twice at weekly intervals from 15 days after sowing (if seed treatment is not followed). Flea beetles : Seed treatment as above. Spray Endosulfan @ 2 ml/lt Pest management 21 or Quinalphos @ 2 ml/lt (if seed treatment is not given). Thrips, Whiteflies, Jassids, Aphids Seed treatment as above. Spray Monocrotophos @ 1.6 g/lt or Acephate @ 1 g/lt or Chlorpyriphos @ 2.5 ml/lt soon after pest appearance (if seed treatment is not given). Integrated Pest Management for pod borers like blue butterflies, spotted borers, tobacco caterpillar, gram caterpillar * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Deep ploughing in summer reduce the development of further generation. Practice crop rotation. Clean inter cultivation. Practice inter cropping with Jowar, Redgram. Sow guard crops such as Jowar Crop rotation with maize, soybean, sunhemp etc., Cultivate tolerant varieties. Monitoring of the pests through pheromone traps @ 10/ha during the crop season is very essential so as to time the spraying schedules at the appropriate period. Encouraging bird predation by keeping bird perches in the field @ 50 /ha Removal of egg masses and skeltonised leaves with early instar larvae was found advantageous particularly for Spodoptera. Spraying of biopesticides like NSKE 5% or Neem oil 5% inhibit the development of the pests. Foliar application of chlorpyriphos @ 2.5 ml/lt or Acephate @ 1 g/lt useful in controlling Spodoptera. Prepare as pellets and spread in the field during evening hours will keep the pest under check in severity for Spodoptera through poison baiting with rice bran 25 kg + jaggery 3.5 kg + Methomil 800 ml per hectare along with sufficient quantity of water. For spotted and pea pod borers apply Acephate 1 g/lt or Chlorpyriphos 2.5 ml/lt + DDVP 1 ml/lt from pre-flowering stage for checking the pod borers at weekly interval. In severe form use of Spinosad 0.25 ml/lt or Novaluron 1 ml/lt. Disease management Collar rot : Seed treatment as above Anthracnose, Cercospora leaf spot : Seed treatment as above. Spray Carbendazim 0.1% or Mancozeb (0.25%) twice at 10 days interval. Powdery mildew : Spray Carbendazim (0.1%) or Thiophanate methyl (0.1%) twice at 10 days interval soon after noticing the disease. 22 Angular black leaf spot Grow resistant varieties like LGG 407, LGG 450, WGG 2 and MGG 295. Spray Carbendazim (0.1%) twice at 10 days interval. Bacterial leaf spot Soak the seed in Paushamycin suspension 0.1 g in 1 lt. water per 1 kg seed for 30 minutes. Spray twice with Plantomycin 1.0 g + Copper oxychloride 30 g/ 10 lt water at 12 days interval. Yellow mosaic virus Grow resistant varieties like LGG 407, LGG 460, WGG 37, ML 267, PDM 54. Control whitefly as above, to check further spread. Leaf curl virus Seed treatment with Carbosulfan 30g/ or Imidacloprid 5 ml/ or Thiomethoxam 5g per kg seed. Post harvest technology Store properly dried seed in nylon bag or polythene bag or compactly knitted gunny bags. BLACKGRAM Varieties : LBG-752, LBG-20, LBG-623, T- 9, WBG-26, MBG-207,PBG-1, Pant U-31, TAU-1. Yellow mosaic virus resistant varieties : LBG-752, T-9, Pant U-31 Soils/Areas : Medium to deep black soils with good moisture retentive capacity. Avoid cultivation of blackgram on light soils and in areas of uncertain rainfall, as it is sensitive to moisture stress. Land preparation : Land should be prepared to fine tilth with 2 ploughings followed by a harrowing. Sowing time : June 15 - July 15 23 Seed rate : 18-20 kg/ha Seed treatment : Carbosulfan 30 g / Imidacloprid 5 ml/ Thiomethoxam 5g + Cap tan/ Thiram / Mancozeb / Carbendazim @ 2.5 g per kg seed. Spacing : 30 x 10 cm Manures and fertilizers including bio-fertilizers and micronutrients etc. 20 kg N+ 50 Kg P2O5 per ha. Treat the seed with good quality Rhizobium noculants. Apply FYM if available. Intercultivation and other management practices, if any One or two hoeings. Keep the field weed free upto 30 DAS. Apply Fluchloralin @ 2.5 l/ha as pre-sowing incorporation or apply Pendimethalin @ 1.5 kg /ha as pre-emergence. Irrigation : Rainfed Pest management : Same as in greengram : Seed treatment as above. Disease management Collar rot Anthracnose, Cercospora and alternaria leaf spots Spray twice Carbendazim (0.1%) or Thiophanate methyl (0.1%) or Mancozeb (0.25%) at 15 days interval. Corynespora leaf spot Spray twice Copper oxychloride (0.3%) or Mancozeb (0.25%) at 10 days interval. Powdery mildew Spray twice Carbendazim (0.1%) or Thiophanate methyl (0.1%) at 10 days interval soon after the appearance of the disease. Rust Spray twice Karathane (0.1%) + Mancozeb (0.25%) or Tridemorph (0.1%) twice at weekly intervals at 50-55 DAS. Yellow mosaic virus 24 Grow resistant varieties such as LBG 752,T9 and Pant U 31 for YMV and follow seed treatment with Carbosulphan 30 g/ or Imidacloprid 5 ml/ or Thiomethoxam 5g per kg of seed both for YMV and leaf curl. REDGRAM Varieties : LRG-41, LRG-30, LRG-38, ICP-8863, ICPL-332, ICPL-87119, (Medium duration) : MRG-66ICPL-85063, PRG-100, WRG-27, PRG-158, MRG-1004, WRG-53. Short duration : ICPL-84031 (Durga), ICPL-85010, CORG-9701 Wilt resistant varieties : ICP-8863, ICPL-87119. SMD resistant varieties : ICPL-87119, BSMR-736, BSMR-853. Soils/areas : All types of soils with good drainage. Saline soils not suitable. Land preparation : Land should be prepared to fine tilth by ploughing 2 to 3 times followed by a harrowing. Seed rate : Medium duration varieties Short duration varieties : : 5-10 kg/ha 15-18 kg/ha depending on type of soils. Medium duration varieties : Short duration varieties : 150 to 240 x 20 cm (depending on soil type) 90 x 20 cm (black soils) or 60 x 20 cm (light soils) Spacing Sowing/planting with cut off dates 15th June – August. : Manures and fertilizers including bio-fertilizers and micronutrients etc. Apply 20 N + 50 P2O5 kg/ha as basal dose. Treat the seed with Rhizobium cultures. Intercultivation and other management practices, if any 25 One or two hoeings to keep the crop free from weeds upto 60 DAS or application of Fluchloralin @ 2-5 l/ha as pre sowing incorporation checks weed growth. INTERGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT OF HELICOVERPA ON REDGRAM I. * * * * * * * Cultural Summer ploughing Avoid mono-cropping Follow crop rotation Adopt wider row spacing (more than 2 meters) Use recommended dose of fertilizers Cultivate tolerant/recouping varieties (LRG-41, ICPL-332, ICPL-84060, LRG-38 and LRG-30) Grow intercrops Kharif : Sorghum, Soybean, Gingelly, Greengram, Blackgram, Greengram, Dry paddy, Bajra) Rabi : Coriander, Cowpea, Greengram, Blackgram, Groundnut) * * * Grow single variety on large scale Sow rabi redgram during October first fortnight. Cultivate short duration varieties in Telangana II. Mechanical * * Monitor with Pheromone traps @ 10/ha Dislodge the larvae by shaking the plants III. Biological * * * Release Trichogramma twice at weekly intervals @ 65000/ha Keep bird perches @ 50/ha Spray NPV and B.T. (NPV @ 500 LE/ha or B.T. @ 1 kg/ha) IV. Plant products * Use Neem oil @ 5 ml/1 or Repelin @ 10 ml/1 or NSKE @ 50 g/1 V. Synthetic pesticides * * * Follow need based application Avoid cocktail mixtures. Aim the sprayings at early instars 26 * * * * * * Apply Endosulfan @ 2 ml/lt or Chlorpyriphos @ 2.5 ml/lt or Quinolphos @ 2 ml/lt or Acephate @ 1 g/lt alternatively during the flowering & pod formation stage. Ensure thorough coverage (900-1000 l/ha) Use Hydraulic/Pneumatic hand compression sprayers (900-1000 l/ha) Discourage synthetic pyrethroids Avoid sub-lethal dosage Adopt community approach Maruca Pod borer : Spray a combination of Chlorpyriphos 2.5 ml + Nuvan 1ml/lit of water. Pod fly : Monocrotophos 1.6 ml/lt or Acephate 1 g/lt at the time of seed development on need basis. Wilt : Grow resistant varieties, ICPL 87119 and ICPL 8863 Sterility mosaic virus : Grow resistant varieties, ICPL 85063, BSMR 853, BSMR 736, ICPL 87119. Macrophomina blight : Grow resistant variety, MRG 66, MRG 1004. Disease management Post harvest technology Properly dried produce can be stored in nylon bag, polythene lined gunny bag or compactly knitted gunny bag upto a period of 180 days. SOYBEAN Varieties : JS 335, PK 1029, MACS 58, MACS 201, MACS 124, MACS 450, PK 471, PK 472, LSb-1, JS 80-21. Soils/Areas : Medium clay soils, light soils under irrigation. Land preparation : Plough the field twice followed by harrowing to achieve fine tilth. Seed rate : 50-65 kg/ha Seed treatment : Seed treatment with Cap tan or Thiram @ 3 g and Carbosulfan @ 30g/kg seed. Treat the seed with Rhizobium japonicum bacteria before sowing. Spacing : Red soils - 30 x 7.5 cm Black soils - 45 x 5.0 cm 27 Sowing : June – July for Telengana Region End of July to 1st F.N. of August for coastal region Manures and fertilizers : 30 N + 60 P2O5 + 40 K20 kg/ha, if inoculated with Rhizobium. 60 to 90 N + 60 P2O5 + 40 K20 kg/ha, if not inoculated. Use of FYM and Sulphur containing fertilizers should be encouraged. Treat the seed with Rhizobium japonicum. Intercultivation and other management practices Keep the crop free from weeds upto 45 DAS. One to two Pendimethalin @ 3.3 l/ha as pre-emergence to check weed growth. hoeings. Use Irrigation Under I.D. conditions irrigate at critical stages i.e., at pre-flowering and pod filling stages. Pest Management Stemfly : Spray Monocrotophos 1.6 ml/lt or Acephate 1 g/lt. Leaf folder/Webber and Spodoptera exigua Methyl parathion 1 ml/lt or Quinalphos 2 ml/lt or Acephate 1 g/lt. Gram caterpillar : Quionolphos 2 ml/lt or Chlorpyriphos 2.5 ml/lt. Pod borers including Spodoptera : Collection and destruction of egg masses and skeletonized leaves. Need based spray with Quinalphos 2 ml/lt or Chlorpyriphos 2.5 ml/lt. Whitefly : Triazophos 0.75 ml/lt or Nictotine suphate 0.5 kg a.i/ha or Neem oil formulations 5 ml/lt . Jassids : Monocrotophos 1.6 ml/lt Thrips : Acephate 1 g/lt. Cercospora leaf spot : Spray Carbendazim 0.1%. Alternaria blight : Seed treatment with Cap tan or Thiram @ 3 g/kg of seed. Rust : Mancozeb @ 1.5 kg/ha Disease Management 28 Bacterial leaf spot : Chlormycitin 100 ppm Mosaic : Acephate 1 g/lt to check vector YMV : Triazophos 0.2 kg a.i/ha or Dimethoate 0.3 kg a.i/ha to check whitefly. Harvesting and Post Harvesting Technology The crop is harvested when the majority of leaves have become golden yellow and ready to fall and the lower pods are yellowish and dry. Seed is to be dried properly to a moisture level of 11-12% before storage. OILSEED CROPS GROUNDNUT 1. Introduction Groundnut is an important oilseed crop grown in India. Globally India ranks first in area and second in production. India, accounts for 31 % of the total groundnut area in the world (24.6 m. ha) and 22 % of the total production (35.7 mt.) . In Andhra Pradesh it is mainly cultivated in Rayalaseema districts viz., Anantapur, Cuddapah, Kurnool and Chittoor districts followed by Telangana and coastal districts. In Andhra Pradesh it is cultivated in an area of around 17.66 lakh ha in kharif with a production of about 9.73 lakh tonnes and a productivity of 551 kg/ha ( 2008-09) In kharif, this crop is mainly grown as rainfed crop. This can be cultivated in rice fallows after harvesting kharif rice. Well drained loose and friable sandy loams and red soils are preferable. Deep black and clay soils are not suitable for groundnut cultivation. 2. Varietal recommendations Season kharif Suitability For Scarce Rainfall areas For excess rainfall conditions Varieties Kadiri-9* Kadiri Harithandhra+ Greeshma* Vemana ,Kadiri-5, Kadiri-6, Tirupati-4, Narayani, Abhaya, ICGV-91114 Tirupati-3, Kadiri-7Bold*, Kadiri-8Bold*, Vemana, Kadiri-5,Abhaya, Kadiri-9 For assured rainfall areas with supplementary irrigations Kadiri-7 Bold, Kadiri-8Bold Vemana, Kadiri-5, kadiri-6 Kadiri-9 Kadiri Harithandra Greeshma Tirupati-4, Narayani, Abhaya, ICGV-91114 29 Duration (days ) 105-110 days 125–130 days 105–110 days 125–130 days 105–110 days Varieties having tolerance to leaf spot Nematode infected areas Kadiri-9 Kadiri Harithandra Greeshma Vemana, Kadiri-5,Abhaya Tirupati-3 Kalahasti , Prasuna For delayed Monsoons Kadiri-4, Kadiri-5, Greeshma, Varieties having drought tolerance For rice fallow conditions Kadiri-9, Greeshma, Vemana, Kadiri-5, Abhaya, ICGV-91114 Kadiri-4, Kadiri-5, Kadiri-6, Greeshma, Kadiri Harithandra TAG-24 Vemana, Kadiri-4, Kadiri-6, Tirupati-4, Greeshma TAG-24 & Narayani Coastal sands 105–110 days 125-130 days 100-105 days 90-100 days 105–110 days 95-100 days 105–110 days (Released in +2008 *2009) 3. Land preparation * * * Prepare the land till fine tilth is attained. It facilitates root growth, peg penetration and pod development. Weeds and clods are to be avoided. 4. Seed rate : Depends on variety and season Varieties 5. Kharif Vemana, Narayani, Kadiri-6, Tirupati-3, Tirupati – 4, ICGS 44, Kalahasti, JL-24 150 kg. Kernel/ha Kadiri-7Bold, Kadiri-8Bold, Kadiri-4, Kadiri-5, TAG-24, JCG-88, TMV-2, Abhaya , Kadiri-9 ICGV 91114, Kadiri Harithandra, Greeshma 125 kg. Kernel/ha Spacing Varieties Kharif Spanish Bunch Vemana,kadiri-5,kadiri-6, Tirupati-4, Narayani, ICGV-91114, JL-24, TMV-2, Kadiri Harithandra, Greeshma, Kadiri-9 30 30 x 10 cm Virginia Bunch ICGS-11, 44, Tirupati-3, Kadiri-7Bold, Kadiri-8Bold. 30 x 15 cm 6. Seed treatment * * * Seed should be treated with Imidachloprid @ 2 ml / kg seed followed by Mancozeb @ 3 gm / kg seed. If the seed is dormant, soak it in 0.05 % Ethrel solution for 12 hours followed by shade drying. Trichoderma viride seed treatment @ 4 g/kg seed rot prone areas Rhizobium inoculation is necessary for groundnut in non-traditional areas. 7. Sowing time * North Telangana 8. Fertilizer recommendations * * * Application of farm yard manure/ compost @ 10 tonnes /ha once in 2–3 seasons NPK recommendations should be on soil test basis Apply 20N + 40 P2O5 + 50 K2O kg/ha as basal . Phosphorus should be applied through single super phosphate. Apply Gypsum @ 500 kg /ha at flowering stage by placement. Wherever Zinc deficiency is observed, apply Zinc sulphate 50 kg/ha. Once in 3 seasons. * * * * * * - First week of June to last week of July Wherever Iron deficiency is noticed on crop, spray 0.5 % ferrous sulphate along with 0. 1 % citric acid two times with one week intervel . In Nagarjunasagar ayacut, where groundnut is grown, application of 60 kg P 2O5 is necessary. Seed treatment with Rhizobium and soil application of Phosphorous Solubulising Bacteria will reduce the chemical fertilizers requirement. 9. Weed management * * * * * Crop must be weed free up to 45 days after sowing. Intercultivation at 20 and 40 DAS followed by one hand weeding. The crop should not be disturbed by weeding or inter cultivation after 45 DAS. Preplanting application of Fluchloralin @ 2.5 to 3 l./ ha. Pre-emergence application of Butachlor /Metalachlore/ Pendimethalin @ 2.5 to 3 l./ ha. or Oxyflourfen 1.5 to 2.0 l./ha followed by one intercultivation and one hand weeding will effectively control the weeds. 31 * * Wherever, pre-emergence herbicides could not apply, weeds can be controlled by post-emergence herbicides by spraying Imazethaphyr @ 750 ml/ha or Quizalofop ethyl @ 1.0 l/ha at 20 DAS. In heavy soils higher dose of chemical should be used. . 10. Irrigation management * * Groundnut crop requires on average 400 to 450 mm depth of water. Good crop of groundnut requires 8 to 9 irrigations at 10 day interval starting from 25 DAS. After the crop is established, it is necessary to with held irrigation for about 25 days to create stress which helps in synchronization of flowering. The last irrigation is to be at 90 days after sowing. 24-30 % irrigation water can be saved due to sprinklers with water productivity of 5.13 kg/ha/mm. * * * Soil moisture conservation practices should be followed in rainfed crop viz., * Apply 5 tonnes of groundnut shells per acre at 15-20 DAS as mulch to reduce evaporation losses of soil moisture. To reduce transpiration losses from crop canopy, spray calcium sulphate solution (50 g/l ). Spray urea solution (20 g/l) during dry spell period in order to make recover the crop from stress. * * Critical stages for water requirement: Flowering, peg penetration and pod development, 11. Crop management A. Pest management 1. Red hairy caterpillar Identification * * * * Young larvae feed gregariously on the undersurface of leaves. Grown up larvae feed individually by devouring leaves, flowers and growing points. When the pest is severe only the bare stem points remain resulting in heavy yield loss. Early instar larvae are ash brown in color, but when fully grown assume reddish color with hairs on the body. Problem areas : Srikakulam, Visakhapatnam, Kadapa, Kurnool, Anantapur and Chittoor districts. 32 Remedies * * * * * * * * * 2. Pre-monsoon deep ploughing (two/three times) will expose the hibernating pupae to sunlight and predatory birds. Removal and destruction of alternate wild hosts which harbour the hairy caterpillars. Use trap crops around main crop Eg. Cowpea. Monitor the emergence of adult moths through light trap. Organize bonfires on community basis from 7.30 PM to 11.0 PM to attract the newly emerging moths for 3 or 4 succeeding days when good showers are received. Collect and destroy egg masses and early instars larvae. Dust Quinolphos or Carbaryl @ 25 kg /ha to control early instars of the caterpillar. To control grown up larvae, spray Dimethoate @ 2.0 ml or Monocrotophos1.6 ml/l of water. Trap and kill the migrating larvae in deep cut straight trenches by dusting Methyl parathion 2% in the trench around the field. Root grub Identification * * * * * Young grubs feed on rootlets and nodules. Old grubs devour the entire taproot. Affected plants wither and die. Such plants when pulled from the soil, the devoured taproot can be clearly seen. Damage usually occurs in patches. Pest usually occurs in August and September months. Distribution : In localized parts of A.P. Remedies * * * 3. Pre-monsoon deep ploughing (two/three times) will expose the hibernating pupae to sunlight and predatory birds Apply 10 G Phorate granules @ 1.5 kg a.i. /ha at the time of sowing. Seed treatment with chlorpyriphos @ 6 ml /kg in root grub problem fields or Imidachloprid 2ml/kg seed. Leaf miner Identification * * * Small blister like mines appear initially on the upper surface of the leaf. At severe stages entire leaflet becomes brown and it rolls, shrivels and dries up. Severely infected crop may die and give burnt appearance in the field when we see from distance. Problem areas : Presently it is a major pest in all parts of the state. 33 Remedies * * * * * 4. Rotation of groundnut with non-leguminous crops should be followed to reduce the pest incidence. Rotation of groundnut with soybean should be avoided. Collection and destruction of moths by setting light traps early in the season. Keeping pheromone traps in the field. Spraying of Quinolphos 2.0 ml or Monocrotophos 1.6 ml/l of water should be followed. Tobacco caterpillar (Spodoptera litura) Identification * * * * * * * Larvae long, Stout, pale green (or) brown with black spots on the body During daytime it hides in cracks and crevices. Eggs are small and in masses, covered with yellow anal hairs In initial stages larvae congregate and scrapes and skeletonises on the leaves. Leaves become white papery. In severe cases it defoliates. Grown up larvae disburses and make irregular holes Problem Areas All groundnut areas (Anantapur, Cuddapah, Chittoor, Karimnagar). Severe in the months of September, October and November. Remedies * * * * * * * * Monitor the pest from September last week onwards by Pheromone traps @ 10 per ha. Collection and destruction of eggs masses and damaged leaves along with gregarious larvae. For early stages spray neem oil 5ml or Chlorpyriphos 2.5 ml or Monocrotophos 1.6 ml per liter of water. Arrange bird perches @ 25 per ha. Spray N.P.V 500 LE/ha. from third instar larvae Make deep plough furrow around the field and dust with methyl parathion or Endosulfan dust to control migratory caterpillars For late instar (3rd onwards) larvae spray Thiodicarb 1.0 g or Novaluron 1.0 ml or Chlorfenpyr 2.0 ml/l. of water Use poison bait to attract and to control late instar larvae per hectare Rice bran Jaggery Carbaryl - 12.5 kg 1.25 kg 1.25 kg (or) 34 Monocrotophos Methomyl Water - 1.25 litres (or) 0.75 kg 10-12 litres * Mix the above and make small pellets and apply them in one hectare, during evening hours near base of plants. 5. Sucking pests (Jassids, Aphids and Thrips) Identification * * * * Jassid infestation results in yellowing of the leaves. Thrips infestation results in curling of leaves and stunting of the crop. Aphid infestation results in chlorotic plants and curling of leaves. Aphids and thrips transmit Rosette and Bud necrosis diseases of groundnut. Distribution Present in all groundnut growing areas. Remedies Spraying of Monocrotophos 1.6 ml or dimethoate 2.0 ml or Imidacloprid 0.4 ml per liter of water 6. Storage Pests * * * * Groundnut bruchid which occurs in storage. Spray 5% Malathion on pod and gunny bags. Fumigation with aluminium phosphide tablets 3-5 tablets /tonne of groundnut pods. Mixing neem oil 5 ml/kg of pods protect from bruchid. B. Disease management 1. Tikka leaf spot Identification * * * In case of early leaf spot, the lesions are sub circular and 1-10 mm diameter and dark brown on the upper surface of the leaf In case of late leaf spot, the lesions on the leaf are small, more nearly circular and darker than those of early leaf spot. Both the lesions may also appear on the stem, petiole and pegs Problem areas Both the leaf spots are commonly present in all groundnut-growing areas, but, the incidence as relatively more in North coastal and heavy rainfall areas. Remedies 35 * * * * * 2. Removal of infected plant debris Crop rotation should be followed Seed treatment with mancozeb @ 3 g/kg of seed Growing tolerant varieties viz., Vemana, Kadiri Harithandra, JCG-88, Abhaya and Kadiri 7 bold Spraying of mancozeb 1000 g + Carbendazim 500 g /ha or Hexaconazole @ 1000 ml or Chlorothalonil @ 1000 g or Tebuconazole @ 500 ml/ha in 500 liter of water at fortnightly intervals from first disease appearance. Rust Identification * * Orange coloured pustules appear on the lower surface of the leaflets In severe cases, lesions also appear on other plant parts expect flowers Problem areas : Occurs in all groundnut-growing areas Remedies * * * * Removal of infected free areas Collect seed from disease free areas Seed treatment with 3 g of mancozeb/kg of seed Spraying of mancozeb 1000 g or Chlorothalonil 1000 g or Tridemorph 1000 g /ha in 500 liter of water at 15 days interval starting from disease appearance. 3. Collar rot Identification * * * * Rapid desiccation of the affected plant Affected tissue is covered with black mass of spores In mature plants, lesions develop on the stem just below the soil surface and then spread upward along the branches. In mature plants, symptoms generally do not appear until the wilting of the entire plant is apparent Problem areas : More prevalent in light sandy soils Remedies * * * Select healthy seed Seed treatment with mancozeb 3 g/kg or Captan 2 g/kg of seed Deep sowing of seed should be avoided 36 * * Deep ploughing of fields and destruction of plant debris Crop rotation with chickpea reduces the disease 4. Stem rot Identification * * * * Appears generally after 70 days of sowing Yellowing and wilting of branches just above the soil White mycelium of the fungus develops around the affected stem above the soil level Infection of pegs and pods occurs in severe cases and seeds turn to bluish colour\ Problem areas : Occurs in areas where the soils are heavy Remedies * * * * Deep ploughing in summer Selection of healthy seed Seed treatment with mancozeb @ 3 g/kg of seed Soil application before sowing with Trichoderma viride developed by mixing 225 kg farm yard manure +25 kg neem cake + 5 kg Trichoderma viride/ha and allow to grow for 15 days under shade * * Gypsum application @ 500 kg/ ha Timely management of foliar diseases leads to reduction of incidence of stem rot 4. Peanut Stem Necrosis Disease (PSND) Identification * * * Necrotic lesions on terminal leaf lets, death of top growing bud on main stem followed by necrosis of all top buds on primaries. Complete stem necrosis and oftentotal necrosis of entire plant in early infection Infected plants become stunted and showed auxiliary shoot proliferation with small sized and chlorotic leaflets Necrotic spots on pods. Testa are not discolored or mottled Problem Areas : Anantapur, Mahaboobnagar, Kurnool and Chittoor districts of A.P. Remedies * * Seed treatment with Imidachloprid @ 2 ml/Kg of seed Weds such as Parthenium hysterophorus, Tridax procumbence, Ageratum conyzoides, Cleome viscose, Commelina benghalensis, Vernonia cineraria, 37 * * * 5. Achyranthus aspera, Acanthospermum hispidum. Acalypha sp. should be removed before flowering in and around the field Barrier crops namely bajra, maize and sorghum should be planted in 4-8 rows around the groundnut field. These will prevent thrips and wind borne weed pollen carrying virus Grow inter crop with bajra/ sorghum/ maize in the ratio of 7:1 or 11:1 Spraying of monocrotophos @ 800 ml or Dimethoate @ 1000 ml or Imidachloprid @ 200 ml/ha in 500 liters of water at 25-30 days after sowing Peanut bud necrosis disease Identification * * * * Initial symptoms appear on young leaflets as chlorotic spots and develope in to chlorotic or necrotic ring spots Terminal bud necrosis on main stem followed by death of top buds on all primaries Stunting growth with reduced size of leaflets and petioles Leaflets produced on auxiliary shoot showed reduction in size, distortion of lamina and mosaic Remedies * * * * Use of tolerent varieties viz., R-8808, ICGS-11, 44 Intercropping with bajra (7:1) Spraying of monocrotophos @ 800 ml or Dimethoate @ 1000 ml or Imidachloprid @ 200 ml/ha in 500 liters of water at 25-30 days after sowing Maintenance of recommended plant population 12. Harvesting * * * * Should be done at right stage of maturity At the time of 70-80% leaves and stems turn yellow When the inner side of the shell turn black When sufficient moisture is available in the root zone 13. Storage * * * Seed should not contain more than 9% moisture for storage Prefer poly ethylene/gunny bags for storage Spray Malathion 5 ml / liter of water once in 2-3 weeks on storage bags against storage pests. 14. Tips for increasing production * * * * * * * Deep summer ploughing Adoption of quality seed of HYVs Use small seed with out shrivelling of improved varieties Seed treatment Adoption of recommended seed rate Adoption of Ferti-cum- seed drill to ensure right placement of seed and fertilizer Ensure optimum population 38 * * * * * * Adopt recommended fertilizer dose Apply Gypsum and SSP to provide calcium and Sulphur Avoid inter cultivation/weeding after 45 DAS, but earthing up should be done. Adopt IPM Package Practice crop rotation and intercropping Use mechanization for sowing, inter cultivation ,harvesting and stripping to reduce cost of cultivation SESAME Soils : Low lying soils with water stagnation, acidic and saline soils are not suitable. Recommended varieties/hybrids S. No. Variety 1. Rajeswari 2. Swetha thil 3. Chandana Duration Yield Oil (Days) (Kg/ac) Content (%) 90 200 50 Seed colour Special Characters White Tolerant to stem rot and powdery mildew Tolerant to stem rot Tolerant to phyllody 85-90 250 51-52 ,, 85 ,, 50-51 Dark brown 3. Sowing Season : July second fortnight to August first fortnight. 4. Seed Rate and Sowing : Treat one-kilogram seed with 3 g capton/ thiram/ mancozeb. Sow 2-4 kg/ac after 2-4 ploughings and leveling with 2 harrowings adopting 30x15cm spacing. 5. Nutritional Management : Basal application of 4 t of FYM, 16-8-8 Kg N:P2O5 K2O/ha and top dress 6 kg N 30-35 DAS and 60-65 DAS. For hybrids additional dose of 6 kg N as at 90-95 DAS can be given. 6. Intercultivation : Thinning should be done 15 DAS and harrowing at 20-25 DAS. 7. Plant protection 7.1 Insects 7.1.1. Sucking pests: Spray Dimethoate (2ml) or monocrotophos (1.6 ml)/l. 39 7.1.2. Semilooper and pod borer: Spray monocrotophos (1.6 ml)/ endosulphon (2 ml) Chloropyriphos (2.5 ml)/l or Acephate 1.5 g/lit or Thiodicarb 1.5g/lit. 7.1.3. Gallfly: Spray monocrotophos (1.6 ml) or endosulphon/ dimethoate (2 ml)/l. 7.1.4. Bihary hairy caterpiller: * Spray endosulphon (2 ml) or Chloripiriphos (2.5 ml)/acephate(1.5g) per L. 7.2. Diseases 7.2.1. Root and stem rot * Treat the seed with Thiram or capton or Carbendazim @ 3 g/kg. * Spray copper oxy chloride or mancozeb3g/l. * Removal and destruction of affected plants. 7.2.2. Alternaria * Remove infected parts and destroy. * Spray 1g Carbendazim/ Mancozeb 2.5 g/l 2-3 times with 15 days interval. 7.2.3. Phyllody * Remove infected parts and destroy. * Spray 1ml Methyl dematon or Dimethoate 3 ml/l. 7.2.4. Powdery Mildew 8. : Spray wettable Sulphur 3 g/l. Harvesting and storage Harvest when 75% pods turn yellow in a spike. Thresh after drying for 5-6 days and store the seed with 8% moisture. SUNFLOWER 1. Soils : Low lying and coastal soils with water stagnation and acidic soils are not suitable. (pH 6.5-8.0 is ideal). 2. Recommended varieties/hybrids S. No. Variety/ Hybrid Duration (Days) 1 Morden 80-85 Yield (Kg/ac) under rainfed conditions 400 2 3 4 DRSF-108 KBSH-1 NDSH-1 90-95 ,, 80-85 500 600 ,, 40 Oil Content (%) Plant Height (Cm) Special Characters 35-38 90-120 Suitable for intercropping 40 40-42 40-42 150-160 ,, 120-130 Resistant to downy mildew, tolerant to 5 DRSH-1 90-95 600 42-44 150-160 rust and moisture stress Resistant to Downy mildew, tolerant to alternaria. 3. Time of sowing In light soils sowing is done from second fortnight of June to first fortnight of July, while in heavy soils second fortnight of August is recommended. Sowing on ridges after four/five ploughings and leveling will be convenient for topdressing. 4. Seed rate and spacing Rain fed crop requires more seed (3-4 kg /ac for varieties and 2-2.5 Kg for hybrids) than Irrigated (2.5-3.5 and 2 kg/ac, respectively, for varieties and hybrids). Seed should be soaked for 14 hrs and shade dried prior to seed treatment with 2-3 g thiram/capton/ metalaxil or 5g imidacloprid. Spacing of 45 x 20 cm in light soil, 45 x 30 cm in medium soil & 60 x 30 cm in heavy soils is recommended. 5. Nutritional Management Basal application of 3 t of FYM, 12-24-12 Kg N: P2O5 K2O/ha and top-dress 6 kg N 30 DAS and 50 DAS for rainfed crop. For hybrids in black soils with irrigation, 30-36-12 dose is recommended. 6. Water management : During Kharif irrigations can be given based on soil type i.e. 1-2, 2-3 and 3-4 for heavy, medium and light soils, respectively. 7. Intercultivation : Thinning should be done 10-15 DAS and harrowing at 20-25 DAS. 8. Plant protection 8.1. Insects 8.1.1. Sucking pests Spray Dimethoate/ methyl dematon (2ml) or monocrotophos (1.6 ml)/l for Jassids. For white fly, spray trizophos(2.5 ml)/ monocrotophos (1.6ml)/ acephate(1.5 g)/l. To control mites which transmit necrosis, spray imidacloprid (6 ml/ 15 l)/ monocrotophos (1.6 ml/l). 8.1.2. Spodoptera * * Deep summer ploughing Collection and destruction of egg masses and larvae. 41 * In early stages spray Neem oil (5 ml/l) or monocrotophos (2.0 ml/l) or Chloripyriphos (2.5 ml/l). Poison baits (5 kg rice bran + 500 g jaggery + 500ml monocrotophos/500 g carbaryl/500 ml chloropyriphos). * 8.1.3. Bihary hairy caterpillar * Spray neem oil (5ml)/Chloripyriphos (2 ml)/Dichlorovos/ methyl parathion (1ml) per L. 8.1.4. Helicoverpa: Spray HNPV (200LE) or Chloripyriphos/endosulphon/quinalphos (2 ml) or monocrotophos (1.6 ml) or cypermethrin/deltamethrin/fenvalrate/methyl parathion (1ml)/l or Novaluron 1ml/lit or Spinosad 0.3ml/lit or Indoxacarb 1 ml/lit. 8.2. Diseases 8.2.1. Alternaria/rust * * * * Use tolerant varieties like BSH-1. Treat the seed with Thiram or Capton @ 3 g/kg. Spray Mancozeb or zeneb 2g/l. Removal and destruction of affected plants. 8.2.2. Head Rot : Spray metalaxyl (1g) + 3g wettable Sulphur/l twice with 10days interval. 8.2.3. Downy mildew * * Remove infected spikes and destroy. Spray metalaxyl MZ (2g) or Copper oxy chloride (3g)/l. 8.3. Parrots: Bird scaring with reflecting ribbons. 9. Harvesting and storage : Harvest when back side of the head turns yellow. Thresh after drying for 2-3 days and store the seed with 9-10% moisture. CASTOR 1. Soils 2. Recommended varieties/hybrids S. No. 1. Variety / Hybrid Kranthi : Castor can be cultivated on almost all types of well-drained soils. Saline soils and soils with water stagnation are not suitable. Duration (Days) 90-150 Yield (q/ac) 8-10 42 Special Characters Bold seed, early maturing 2. 3. Haritha Kiran 90-180 90-150 8-10 6-8 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Jyothi Jwala GCH-4 DCH-32 DCH-177 DCH- 519 ,, 90-180 ,, ,, ,, ,, 6-8 8-10 10-12 9-11 10-13 10-13 3. Sowing Season : 4. Seed Rate and Sowing Resistant to wilt Tolerant to drought and to grey rot due to non spiny capsules Wilt resistant Tolerant to wilt and grey rot Tolerant to wilt and root rot Resistant to wilt Resistant to wilt 15th June to end of July. Situation Seed rate Spacing (cm)* (kg/ac)* Heavy soils, irrigated 2.0 90 x 90 cm Light soils, irrigated 3.0 90 x 60 cm Treat one-kilogram seed with 3 g capton/ thiram or 1 g carbendazim. 5. Nutritional Management : Basal application of 2 t of FYM, 12-16-12 Kg N:P2O5 K2O/ha and top dress 6 kg N 30-35 DAS and 60-65 DAS. For hybrids additional dose of 6 kg N as at 90-95 DAS can be given. 6. Intercultivation 7. Plant protection 7.1. Insects : Thinning should be done 15-20 DAS and harrowing at 20 and 40 DAS. 7.1.1. Red hairy caterpillar * * * * Arrange bon-fires between 7-10 p.m. one day after the receipt of soaking monsoon rain. Repeat 2, 3 times after each rain. Apply kg of 2% Methyl parathion/endosulphon or 4% quinolphos per 70 m furrow around the field to prevent migration. Spray monocrotophos (1.6 ml/l of water) or chloropyriphos 2ml/lit. For the control of adults use poison bait with 5 kg Rice bran + 500 gm Jaggery + 500 lit Quinolphos 7.1.2. Semilooper * In early stages spray neem oil (5 ml/l) or NSKE (5%) twice with an interval of 43 * 10-15 days. Collection and destruction of larvae. * * * Release 50, 000Trichogramma parasitoids/ac. Arrange 10 bird perches /ac. Spray monocrotophos (1.5 ml)/ carbaryl (3 g)/l or Acephate 1.5 g/lit. 7.1.3. Spodoptera * * * * Deep summer ploughing Collection and destruction of egg masses and larvae. In early stages spray Neem oil (5 ml/l) or monocrotophos (2.0 ml/l) or Chloripyriphos (2.5 ml/l) or acephate 1.5 g/lit or thiodicarb 1.5 g/lit. Poison baits (5 kg rice bran + 500 g jaggery + 500ml monocrotophos or 500 g carbaryl or Chlorpyriphos 500ml). 7.1.4. Shoot and capsule borer: * Spray Dimethoate/ Methyl-o-dematon/monocrotophos (2ml/l) or Acephate 1.5g/lit or Indoxacarb 1ml/lit at flowering stage and 20 days later. 7.1.5. Bihar hairy caterpillar * Spray neem oil (5ml)/Chloripyriphos (2ml)/Dichlorovos(1ml) per L. 7.1.6. Jassids * Spray Dimethoate (2ml)/ monocrotophos (1.5ml/l) per L. 7.2. Diseases 7.2.1. Fusarium Wilt: * * * * * Use tolerant varieties like Haritha, 48-1, GCH-4, and Jyothi. Treat the seed with Thiram or Carbendazim @ 3 g/kg. Intercropping with Redgram and crop rotation with bajra. Spray Carbendazim 1g/l. Removal and destruction of affected plants. 7.2.2. Botrytis Grey Rot * * * * Soon after cyclone warning is given in Radio/T.V., spray carbendazim (1.0 g/l). Remove infected spikes and destroy. Spray carbendazim after the rains. Apply 20 kg urea and 10 kg potash/ac. 44 8. Harvesting and storage Harvest when 80% capsules turn yellow in a spike. Thresh after drying and store the seed with 9-10% moisture. COTTON Farming situations : FS 2, FS 5, Fs 8, FS10, FS11, FS12 and FS14 Varieties (hirsutum) : MCU-5, LRA-5l66, - Kanchana (LPS-141), L-389, L-603, L-604 & Narasimha (NA-1325) Hybrids : H 6, JKHy l, H 8, LAHH 4, NHH 44, Savitha & NSPHH 5 Bt Hybrids : Private hybrids found suitable during past 3 years in a specific location may be selected Sowing time Sow the crop after the receipt of an accumulated rainfall of 60 mm or more after monsoon sets in. Generally by June third/fourth week cotton can be sown. Early sowing of cotton (May 20) under wells/borewells is advantageous. Don’t sow cotton beyond July 20. Soils Deep black soils and red loamy soils with irrigation and good drainage. Cotton comes up well in neutral non calcareous soils. Can be grown as rainfed crop in clay loams under medium rainfall of 500-750 mm. Land preparation Deep ploughing once in 3 to 4 years with disc or mould board plough facilitates deep infiltration of water and charging of soil profile with large quantities of water. The land has to be ploughed 2 to 3 times and worked with harrow to bring the soil to good tilth. Seeds can be dibbled by maintaining spacing in between plants after running a marker in both the directions. For irrigated crop, ridges and furrows are to be formed at recommended spacings after deep ploughing. Seed rate and spacing Bt cotton Hybrids Seed rate depends on the spacing adopted Spacing (cm) 90 x 90 Plant population/ha 12345 45 Seed rate (kg/ha) 1.20 90 x 60 120 x 45 90 x 30 18518 18518 37037 1.80 1.80 3.60 Sow single seed/hill. Research results that Bt cotton hybrids give higher yields t closer spacing of 90 x 60 or 90 x 45 cm. Varieties Seed rate : 8-10 kg/ha Spacing : 90 x 30 cm Seed treatment For acid delinting, the seed should be treated with 80-l00 ml concentrated sulphuric acid/kg of seed for 2-3 minutes followed by thorough washing with water 2-3 times. To remove the acid traces it should be washed with lime water to neutralize. Seed dressing with appropriate insecticide, imidachloprid 70 WS @ 5 g/kg or thiomethoxam 70 WS @ 4g/kg is recommended. To control seed borne diseases. Soak the seed in water containing panshamycin/plantamycin @ 100 mg + carboxin 1 g/l of water, for 6-8 hours and shade dry. Inter cropping Suggested inter crops in non Bt cotton are black gram / green gram / soybean in 1:2 ratio. At closer spacing inter cropping is not advisable. Thinning and gap filling Gap filling should be done with in 10 days after sowing. Excess seedlings should be removed within three weeks, retaining 2 plants per hill in case of varieties and one plant per hill in case of hybrids. Fertilizers Varieties : Apply FYM @ 10 t/ha in the final ploughing. Apply 90 kg N + 45 kg P2O5 + 45 kg K2O/ha. Entire P as basal, N and K in three splits 30, 60 and 90 DAS by pocketing. Hybrids : Apply FYM @ 10 t/ha in the final ploughing. Apply 120 kg N + 60 kg P2O5 + 60 kg K2O/ha. Entire P as basal, or within 15 days after sowing. N and K in four equal splits at 20, 40, 60, and 80 DAS by pocketing. 46 * * Band placement of fertilizers at 5 cm depth is recommended for efficient utilization. Use of organic manures and growing of green manure crops like sunhemp is recommended. Foliar application of borax or boric acid @ 1.5 g/l is recommended at 60 and 75 days after sowing to correct boron deficiency. * * * Soil application of 50 kg ZnSO4/ha is recommended to prevent zinc deficiency. Foliar spray of ZnSO4 @ 2.0 g/l at 50 and 70 DAS is recommended for correction of zinc deficiency, if soil application could not be done. Foliar spray of MgSO4 @ 10 g/l during the period of low temperature is recommended for correction of Mg deficiency. If the crop is waterlogged for a week or more, immediately spray urea or KNO 3 @ 10 g/l for rejuvenation. Foliar spraying of urea @ 20 g/l three to four times at weekly intervals at flowering and boll development enhances seed cotton yield. Terminate Bt cotton by 150/160 days and sow maize, groundnut, white sesamum, sunflower, greengram, melons or vegetables as sequence crop to Bt cotton * * * * Chemical weed management Pre-emergence application of pendimethalin @ 3.0 l/ha or alachlor @ 2.0 l/ha. Post emergence directed spray of paraquat or glyphosate @ 5 ml/litre of water in between cotton rows can be practiced to control weeds. Intercultivation and other management practices Rainfed crop must be kept weed free by harrowing 2-3 times within the first 30-60 days of crop growth. In case of irrigated cotton crop, earthing up should be done with the help of a plough or blade harrow after fertilizer application and irrigation. Topping (i.e.,nipping the terminal bud) should be done after emergence of 15 to 16 sympodial branches at the age of 90-100 days. Irrigation : Three to four irrigations are necessary at critical stages of crop growth depending upon soil moisture. The field should not be over flooded. Plant protection: Sucking pests viz., jassids, thrips, aphids, whitefly and red spider mite and bollworms viz., spotted, Heliothis, Spodoptera and pink bollworm occur on cotton crop. Threshold level for major pests Insect Aphids Age of Threshold level crop (days) 1-50 15-20% infected leaves Jassids 1-50 Thrips 1-50 50-100 nymph/adult/50 random terminal leaves 10 thrips/leaf 47 Nature of treatment Avoid persistant insecticide. Foliar application of systemic insecticide at sparse level of predators. - do - do - Spotted bollworm American bollworm Whitefly 35-110 65-110 35-110 10% damaged Mechanical + contact insecticides reproductive parts 10% damaged flowers - do with larvae 8-10 adults/20 nymphs per Grow resistant variety. Use neem leaf products and contact insecticides. Pest Management in Cotton 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Growing intercrop for increasing the effectiveness of natural enemies Growing fodder Jowar or maize as barrier crops around cotton and castor and marigold as trap crop in between cotton rows. Seed dressing with imidacloprid @5g/kg seed or thiomethoxam 4g/kg seed. Stem application with monocrotophos or imidacloprid at 1:4 or 1:20 dilution at 20, 40 and 60 DAS for controlling aphids and leafhoppers in initial stages of crop growth. Monitoring pests by using sticky, pheromone and light traps. The adult monitoring should be supported by egg and larval monitoring. Bird perches @ 10 to 20 per acre for encouraging bird predation on bollworm larvae. Release of Trichogramma egg parasite @ 1,50,000/ha and chrysopa egg larval predator @ 10000/ha, as soon as the first brood of bollworms are noticed. Use of biopesticides Helio NPV @ 500 LE/ha or Bt formulation @1 lt/ha or neem seed kernel extract (5%) in synchrony with incidence of young larva of Helicoverpa. Neem oil formulation to manage whitefly initially. Hand collection and destruction of egg masses and skeletonised leaves in respect of Spodoptera. Removal of top leaves by topping of cotton plants when maximum egg laying of Helicoverpa armigera is noticed (October-November months) Need based application of recommended insecticides. Recommended insecticides Aphids/Jassid /Thrips - Monocrotophos Imidacloprid200SL Acetamiprid Thiomethoxam Acephate Whitefly Triazophos Profenophos NSKE Neem oil Red mite Wettable sulphur Dicofol Boll Worms Endosulfan Quinalphos Chlorpyriphos Acephate Triazophos Thiodicarb 48 - 1.5 ml/l 0.4 ml/l 0.2 g/l 0.2 g/l 1.5 g/l 2.0 ml/l 2.0 ml/l 5% 5 ml/l 3 g/l 5.0 ml/l 2 ml/l 2.5 ml/l 3.0 ml/l 1.5 g/l 2.0 ml/l 1.5 g/l Profenophos Indoxacarb Spinosad Emamectin benzoateNovaluron Lufenuron - 2.0 ml/l 1.0 ml/l 0.3 ml/l 0.5 g/l 1 ml/l 1 ml/l 12. Use of poison bait for Spodoptera @ 10 kg rice bran +1 kg jaggery + 1 liter chlorpyriphos or 250g thiodicarb per acre 13. Removal of cotton stubbles after last picking without prolonging the crop duration to break the perpetuation of pests. Management strategy for Mealy bug Mealy bug has emerged as a major pest of cotton in Andhra Pradesh occurring sporadically. It is therefore, important to understand this pest and the management options available, so as to take up timely measures to avert any impending losses in cotton crop. Three species of mealy bugs are found on cotton in our country. Phenacoccus solenopsis is the most predominant in the north and central India, whereas Maconellicoccus hirsutus (also known as pink mealy bug) is seen in the south. Phenacoccas solani is the third species less commonly encountered. Life cycle Males are not necessary for reproduction in mealy bugs. In the two commonly seen species (F.solenopsis and M. hirsutus). Female adult produces 150-160 parthenogenetic eggs in a thin bag called ovisac and within 3-9 days the young mealy bugs, called ‘crawlers’, come out from such ovisac. Crawlers actively move and spread from plant to plant or even field to field and settle down for food on plant parts. They are initially without a waxy coating, but gradually develop. One generation takes 25-30 days. In warm weather, the insect is very active and in cold weather it is able to survive as eggs in ovisac or other stages both on the host plant and in soil. Nature of damage Mealy bugs suck sap from leaves, twigs, stems, and sometimes from the roots and also from fruiting bodies. The entire plant may be stunted and shoot tips develop a bushy appearance. In affected plants bolls are deformed, fewer, and smaller in size. The pest secretes sweet honey dew which encourages the development of black sooty mould, adversely affecting photosynthetic activity. The honey dew also attracts ants which in turn help in the dispersion of mealy bugs from plant to plant. Ants also provide protection to mealy bugs from predatory ladybird beetle, parasites and other natural enemies. Integrated management Before planting 1. 2. 3. Alternate host plants like parthenium and other weeds in and around the fields should be removed Do not throw uprooted weeds in water channel Locate ant colonies and destroy them by drenching of chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2.5 49 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. ml/l or by application of 5% malathion dust. This operation can be carried out 2 or 3 times during the season. Severely affected cotton plants at early stage of infestation should be uprooted and destroyed. Equipments should be washed with a jet of water or sprayed with chemical insecticides before moving to uninfected portions in a field. Regular monitoring of field should be done and spot application of recommended insecticides should be given so as to avoid further spread of mealy bugs from infested plants. Stem application with monocrotophos @ 1:4 is highly effective during early stages of crop growth. In case of severe infestation, spray recommended insecticides such as profenophos 3 ml or Acephate 1.5 g along with detergent powder @ 0.5 g per litre of water. Thorough coverage of the crop is necessary. Management strategy for pink bollworm Pink boll worm is a late season pest and reduces the yield and quality of fiber. Life cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. Female lays small, flattish and white eggs on tender parts of the plant, terminal bunds, squares and young bolls. Single female can lay about 125 eggs. Incubation period ranges from 3-7 days. Larvae are minute and whitish in colour with small dark head. Grown up larvae are pink in colour. Larval period lasts for 8-41 days through three instars depending upon weather conditions. Pupation takes place on shredded leaves, inside flowers and lint. Pupal period lasts for 6-20 days. Nine generations per year are possible. Female adults can live upto 56 days while male adults live upto 20 days. Nature of damage 1. 2. 3. 4. First brood develops mainly on bunds and flowers. Larvae feed upon developing anthers and style and occasionally on the ovary. The attacked small buds shed while larger buds develop with poor quality kapas. The lint in one or several locules of the boll is spoiled and seeds eaten away. Seeds are completely or partially destroyed and results in pre-mature ripening of bolls, which do not open. As a result of the above, the oil content in seeds and spinning quality of the lint are adversely affected. Management strategies: Since the eggs are mostly protected by calyx and the newly hatched larvae born into the bolls immediately, it is difficult to manage this pest with insecticides. Therefore, hygienic methods are more important than chemical control. However, the following integrated methods are suggested to control this insect pest. 50 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) Grow early maturing varieties so that the cotton bolls mature before the heavy population of pink bollworm builds up. Avoid staggered sowings in an area and take up timely sowings. Use acid delinted seed. Adopt efficient and timely agronomic practices such as use of organic manures and recommended doses of N fertilizers. Keep the crop free from weeds. Monitor regularly for pest build up with field scouting and pheromone traps. Destroy pink bollworm larvae in rosette flowers and also through periodical removal of dropped squares, dried flowers and pre-mature bolls, to suppress pest population in the initial stage. Avoid ratooning and summer cotton. Allow cattle, sheep and goats to graze upon immature green bolls and attacked bolls after final picking to prevent carry-over of the pest to the next season. Remove and destroy cotton stubbles promptly to prevent carry over of the pest to next season. Restrict the movement of cotton seed from other areas / states. Use insecticides on need basis. Fumigation of the seed with methyl bromide @ 0.4 kg/1000 cu.ft. or phostoxin 50 tablets/1000 cu. ft. for 24 hours. Spray persistent insecticides like quinalphos/chlorpyriphos @ 2.5 ml/l at 15 days interval on the crop. Finally, advise even the ginning mills to burn the stained kapas regularly. Disease management a) Black arm 1) 2) 3) 4) Seed treatment with 80-100 ml concentrated sulphuric acid. Use of resistant varieties like L 389. Removal and destruction of infected seedlings. Seed soaking in antibiotics (Agrimycin 100 mg/l) solution along with vitavax @ 1.0 g/l for 6-8 hours will eliminate seed borne diseases. Spray agrimycin @ 0.1 g/l + copper oxychloride @ 3.0 g/l thrice at fortnightly intervals. 5) b) Root-rot: Trichoderma application @ 5 kg/ha along with FYM at sowing seed treatment with carbendazim @ 2.0 g/kg seed. Drench the soil around base of affected plants with copper oxychloride @ 3.0 g/l. c) Leaf spots: Spray mancozeb @ 2.5 g or copper oxychloride @ 3.0 g/l for 4-5 times at 15 days interval. d) Grey mildew: Spray wettable sulphur @ 3.0 g/l, carbendazim @ 1.0 g/l for 2-3 times at 10 days interval on lower leaves. e) Boll rots: Spray paushamycin @ 1.0 g/l + copper oxychloride @ 30 g/10 l of water for 2-3 times at 15 days interval. 51 Harvesting and post harvest technology: Kapas from fully opened bolls should be collected during cooler periods of the day. Kapas picked should be free from dried leaves, dried bracts etc., Kapas from the first and last pickings should not be mixed with middle pickings, which are of better quality. Kapas damaged by bollworms should be picked separately. The cleaned kapas is to be graded and stored in heaps or in gunny bags in dry and well ventilated godowns. DESI COTTON (G. arboreum) Farming situations: FS 10, FS 11, FS 12 and FS 14 Varieties: Saraswathi, Raghavendra, Aravinda and Veena. Preparatory cultivation: Deep ploughing once in three years and regular ploughings and harrowing two times every year is essential. Marking of rows at 45 cm is advised. Seeds and sowing Seed rate Spacing - 10 kg/ha 60 X 15 or 45 X 45 cm To ensure optimum plant population gap filling should be taken up within ten days after germination. Sowing should not be delayed beyond 30th June. Intercultivation: The plot must be kept weed free by giving one or two hand weedings. Preemergence spraying of weedicide alachlor @ 5 ml/l will help in controlling weeds. Fertilizes: A fertilizer dose of 60:40:30 kg NPK should be applied per hectare. The entire dose of phosphorous should be given as basal application. Nitrogen and potash fertilizers may be applied as top dressing in 2 split doses at an interval of 30 days depending on the soil moisture. Plant protection: Though desi cottons are tolerant to pests and diseases, it still attracts some of the pests and diseases. However, plant protection is necessary only when the infestation crosses ETL, which is generally a rare phenomenon. Plant protection Semilooper: Spray monocrotophos @ 1.6 ml/l or endosulfan @ 2.0 ml/l. Aphids, jassids, thrips & mites: Apply phorate 10 G granules @ 10 kg/ha 10 days after germination. This is to be applied 5 cm away from the seedling by removing 1-2 cm layer of soil. Alternately, spray dimethoate @ 2.0 ml/l or methyl demeton @ 2.0 ml/l or phosphamidon @ 1.0 ml/l. If the intensity of pest attack is more spray may be alternated with the above chemicals. 52 Bollworms: (a) Spotted bollworm; (b) American bollworm; (c) Pink bollworm. The following insecticides may be used for the control of bollworms. Endosulfan @ 2.0 ml/l or quinalphos @ 3.0 ml/l, or chlorpyriphos @ 2.5 ml/l or dimethoate @ 2.0 ml/l Since the boll worms attack the crop from square initiation stage to boll development stage i.e., from 45 to 120 days sufficient spray fluid (about 600 liters) may be prepared depending on the crop canopy to ensure proper drenching. Diseases Bacterial blight: Depending on the severity of disease spray 3-4 times with paushamycin (100 mg) or plantomycin (100 mg) + copper oxychloride (3.0 g/l) at an interval of 15 days. Grey Mildew: Spray wettable sulphur @ 3.0 g/l at least twice at an interval of 10-15 days. The lower canopy must be covered thoroughly. Cultural practices a) b) c) Collect and destroy fallen squares, flowers and bolls. Collect skeletonized leaves with larvae and destroy Reduce the dose of nitrogen if the pest attack is severe. Harvesting: Clean picking from well opened bolls, free from dried leaf bits, bracts etc., fetches better price. The produce is to be picked periodically as and when bolls burst and stored. 53