Terms: The Russian Revolution
advertisement

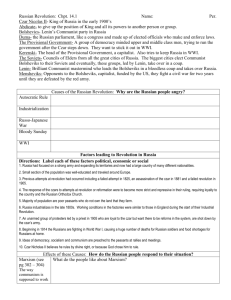
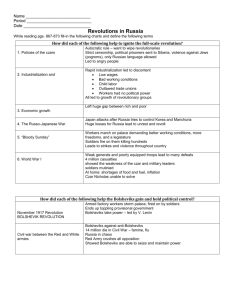
The Russian Revolution Notes 1. WW I – Russia poorly equipped to fight the war against the Germans; Russians soldiers had no guns, medical supplies etc… 2. Nicholas II – Czar of Russia; he went to the front to take personal charge of the war. 3. Alexandra – Czarina (queen) that was left in charge of domestic affairs when the Czar went to the front during WW I; she was German and many people did not trust her. 4. Rasputin – The corrupt monk that had influence over the Czar and Czarina because he could stop Alexis’ bleeding. 5. Alexis – Hemophiliac son of the Czar; Rasputin was the only person that could stop his bleeding. 6. Rasputin’s Death – Czar’s family (jealous of his influence) lure him to their palace; they poison and shoot him, then throw him in the river. He died of drowning. 7. St. Petersburg – The Czar abdicated and the Duma set up a provisional government that stayed in the war. The city was renamed Petrograd; people set up soviets which were councils of workers and soldiers. 8. Bolsheviks – (means majority) – Russian communists. 9. Lenin – Revolutionary leader of the Bolsheviks; he was in exile in Switzerland. The Germans transported him to Russia so he would lead a revolt against the provisional government. He became the first dictator of the U.S.S.R. 10. November 1917 – Led by Lenin, the Bolsheviks overthrew the provisional government. 11. Kremlin – The fortress in Moscow that became the headquarters for the Bolsheviks. 12. Moscow – The city that became the Russian capital under communist rule. 13. Hammer & Sickle – The communist flag; it symbolized the unity between factory workers and farmers. 14. Treaty of Brest-Litovsk – The Bolsheviks surrendered to the Germans ending WW I for Russia, but started a civil war in Russia between the Reds and the Whites. 15. Reds – The Bolsheviks led by Lenin. 16. Whites – Counter revolutionaries that supported the Czar; the allies sent soldiers to help the Whites. 17. Cheka – The Communist secret police; they used a reign of terror to squash all opposition. They also assassinated the Czar and his family. 18. Leon Trotsky – Lenin’s assistant, he was the ruthless leader of the Red Army during the Revolution. 19. Lenin 1924 –Lenin died; his body laid on display in Moscow for 65 years. 20. NEP – Lenin’s economic policy; it allowed farmers to sell their extra crops. 21. Stalin – Outmaneuvered Trotsky to become dictator after Lenin; his name means: “Man of Steel”. 22. Five Year Plans – Stalin’s economic policy. Based on quotas, it brought all economic activity under government control (including farms). 23. Collectives – Large state owned farms. 24. Kulaks – Wealthy Russian peasants who resisted Collectives; they were wiped out by Stalin. Angry farmers grew just enough for themselves. The government seized their crops and millions starved. 25. Great Purge – Stalin’s Reign of Terror. He and his secret police wiped out 90% of the army officers and old Bolsheviks he suspected of disloyalty. 26. Comintern – Means: Communist International. Lenin pledged to aid any communist revolution.