the Organic Regents Review Worksheet with answers.
advertisement
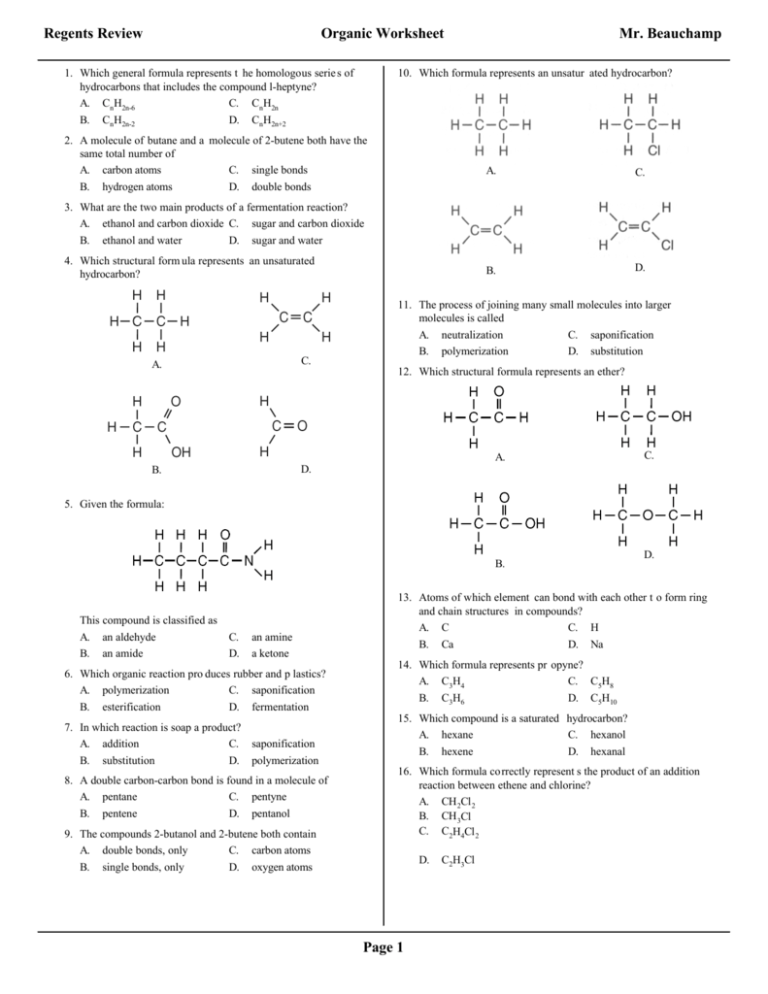
Regents Review Organic Worksheet 1. Which general formula represents t he homologous serie s of hydrocarbons that includes the compound l-heptyne? A. CnH2n-6 C. CnH2n B. CnH2n-2 D. CnH2n+2 Mr. Beauchamp 10. Which formula represents an unsatur ated hydrocarbon? 2. A molecule of butane and a molecule of 2-butene both have the same total number of A. carbon atoms C. single bonds B. hydrogen atoms D. double bonds A. C. B. D. 3. What are the two main products of a fermentation reaction? A. ethanol and carbon dioxide C. sugar and carbon dioxide B. ethanol and water D. sugar and water 4. Which structural form ula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon? A. C. B. D. 11. The process of joining many small molecules into larger molecules is called A. neutralization C. saponification B. polymerization D. substitution 12. Which structural formula represents an ether? A. C. 5. Given the formula: B. This compound is classified as A. an aldehyde B. an amide C. D. an amine a ketone 6. Which organic reaction pro duces rubber and p lastics? A. polymerization C. saponification B. esterification D. fermentation 7. In which reaction is soap a product? A. addition C. saponification B. substitution D. polymerization 8. A double carbon-carbon bond is found in a molecule of A. pentane C. pentyne B. pentene D. pentanol 9. The compounds 2-butanol and 2-butene both contain A. double bonds, only C. carbon atoms B. single bonds, only D. oxygen atoms D. 13. Atoms of which element can bond with each other t o form ring and chain structures in compounds? A. C C. H B. Ca D. Na 14. Which formula represents pr opyne? A. C3H4 C. C5H8 B. C3H6 D. C5H10 15. Which compound is a saturated hydrocarbon? A. hexane C. hexanol B. hexene D. hexanal 16. Which formula correctly represent s the product of an addition reaction between ethene and chlorine? A. CH 2Cl 2 B. CH 3Cl C. C2H4Cl 2 D. Page 1 C2H3Cl Organic Worksheet 17. Which structural formula represents an a lcohol? A. 24. Given the formulas for two compounds: B. C. These compounds differ in A. gram-formula mass B. molecular formula C. percent composition by mass D. physical properties at STP D. 25. Which organic com pounds are often used t o create fragrances for the perfume industry? A. ethers C. alkanes B. esters D. alkynes 26. Given the equation: 18. Given the structural formula: C 2H6+ Cl 2 → C2H5Cl + HCl This reaction is best described as A. B. C. D. What is t he IUPAC name of this compound? A. pentanal C. methyl pentanoate B. pentanol D. pentanoic acid 19. Which formula represents an unsatu rated hydrocarbon? A. CH 2CHCl C. CH 3CH 2CH 3 B. CH 3CH 2Cl D. CH 3CHCH 2 20. The compound CH 3COOCH 3 is classified as A. an acid C. a hydrocarbon B. an ester D. an alcohol additi on involving a saturated hydrocarbon additi on involving an unsaturated hydrocarbon substit ution involving a saturated hydrocarbon substit ution involving an unsaturated hydrocarbon 27. The principal products of saponification, a reaction between a fat and a base, are soap and A. water C. carbon dioxide B. glycerol D. ethyl alcohol 28. The organic compound represent ed by the condensed structural formula CH 3CH 2CH 2CHO is classified as an A. alcohol C. ester B. aldehyde D. ether 29. Given the structural formula: 21. When butane burns in an excess of oxygen, the principal products are A. CO 2 and H 2O C. CO and H 2O B. CO 2 and H 2 D. CO and H 2 22. What is the t otal number of carbon atoms in a molecule of ethanoic acid? A. 1 C. 3 B. 2 D. 4 The compound represented by this formula can be classified as an A. organic acid C. ester B. ether D. aldehyde 23. Which formula represents a ketone? A. HCOOH C. CH 3COCH 3 B. HCHO D. CH 3CH 2OH Page 2 Organic Worksheet 30. Two substances have different physical and chemical properties. Both substances have molecules that contain two carbon atoms, one oxyg en atom, and six hydrogen atoms. These two substances must be A. isomers of each other C. the same compound B. isotopes of each other D. the same h ydrocarbon 36. Which structural formula is correct for 2-methyl-3- pentanol? A. 31. Which formula represents an ether? A. B. B. C. C. D. 32. What is t he IUPAC name of the compound with th e following structural formula? D. A. B. propanone propanal C. D. butanone butanal 33. Which two compounds are isomers of each other? A. CH 3CH 2COOH and CH 3COOCH 2CH 3 B. CH 3CH 2CHO and CH 3COCH 3 C. CH 3CHBrCH 3 and CH 2BrCHBrCH 3 D. CH 3CHOHCH 3 and CH 3CHOHCH 2OH 37. Which structural formula represents 1,1-dibromopropane? 34. Given the balanced equati on for an organic reaction: C 2H2 + 2Cl 2 → C2H2Cl 4 This reaction is best classified as A. B. addition esterification C. D. A. C. B. D. fermentation substitution 35. Given the structural formula: What is the total number of electrons shared in the bond between the t wo carbon atoms? A. B. 6 2 C. D. 3 4 Page 3 Organic Worksheet 38. Given the structural formula: Base your answers to questions 42 and 43 on the information below. Many esters have distinctive odors, which lead to their widespread use as ar tificial flavorings and fragrances. For example, methyl butanoate has an odor like pineapple and ethyl methanoate has an odor like raspberry. 42. What is a chemical name for the alcohol that reacts with methanoic acid to produc e the ester that has an odor like raspberry? 43. Draw a structural formula for the ester that has an odor like pineapple. This structural formula represents a molecule of A. B. an aldehyde an ester C. D. a ketone an amino acid 44. 39. Which functional group, when attached t o a chain of carbon atoms, will produce an organic mo lecule with t he characteristic properties of an aldehyde? C. A. A gasoline engine burns gasoline in the pr esence of excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. The main components of gasoline are isomers of octane. A structural formula of octane is shown below. D. B. 40. Given the incomplete equation representi ng an organic addition reaction: X(g) + Cl 2(g) - XCl 2(g) Which compound could be repre sent ed by X? A. CH 4 B. C2H4 C. C3H8 D. C4H10 41. Given the balanced equation representing a reaction: CH 3CH 2CH 3 + Br 2 → CH 3CH 2CH 2Br + HBr This organic reaction is best classified as A. B. an addition reaction an esterification reaction C. D. a polymerization reaction a substitution reaction Page 4 Draw a structural formula for 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. Organic Worksheet 45. Which type of reaction is represe nted by the equati on below? A. esterification B. fermentation C. saponification D. polymerization 46. Given the three organic structural formulas shown below: Which organic compound classes are repres ented by these structural formulas, as shown from left to right? A. ester, organic acid, ketone B. ester, aldehyde, organic acid C. ketone, ald ehyde, alcohol D. ketone, organic acid, al cohol 47. Given the reaction: This reaction is an example of A. fermentation B. saponification C. hydrogenation Base your answers to questions 48 and 49 on the information below. The incomplete equation below represents an este rification reaction. The alcohol reactant is represented by X. 48. Write an IUPAC name for the reactant represent ed by its structural formula in this equati on. 49. Draw the structural formula for the alcohol represented by X. Page 5 D. esterification Organic Worksheet 50. Base your answer to the following question on the information below Ozone gas, O 3, can be used to kill adult inse cts in storage bins for grain without damaging the grain. The ozo ne is produced from oxygen gas, O 2, in portab le ozone generators located near the storage bins. The concentrations of ozone used are so low that t hey do not cause any environmental damage. This use of ozone is safer a nd more environmentally friendly than a method that used bromomethane, CH 3Br. However, bromomethane was more effective than ozone because CH 3Br killed immature insects as well as adult insects. Adapted From: The Sunday Gazette (Schenectady, NY) 3/9/03 Given the balanced equat ion for producing bromo methane. Br 2 + CH 4 -CH 3Br + HBr Identify the type of org anic reacti on shown. Page 6 Organic Worksheet Answer Key 1. B 31. C 47. D 2. A 32. C 48. Examples: – ethanoic acid – acetic acid 3. A 33. B 4. C 34. A 5. B 35. A 6. A 36. B 7. C 37. D 8. B 38. D 9. C 39. B 49. 10. B 40. B 11. B 41. D 12. D 42. Examples: – ethanol – ethyl alcohol 13. A 14. A 15. A 16. C 17. B 18. D 19. D 20. B 21. A 22. B 23. C 24. D 25. B 26. C 27. B 28. B 29. B 30. A 43. 44. 45. D 46. D 50. Examples: – substitution – bromination – halogentation