answer key
advertisement
IIADRID (!to!!
Name
~~~~~==========~
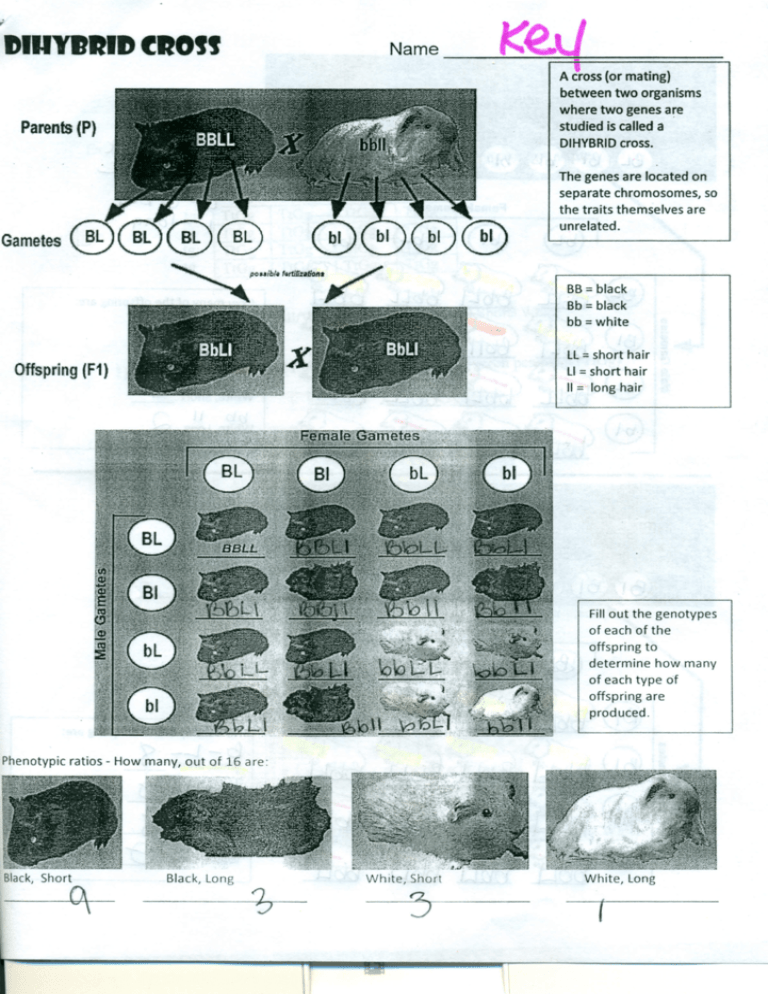
A cross (or mating)
between two organisms
where two genes are
Parents (P)
studied is called
a
DIHYBRID cross.
The genes are located on
separate chromosomes, so
the traits themselves are
Gametes
®®®® ®
~"
unrelated.
...-.~
BB
Bb
bb
= black
= black
= white
LL = short hair
Offspring (F1)
LI = short hair
II = long hair
Fill out the genotypes
of each of the
offspring to
determine how many
of each type of
offspring are
produced.
Phenotypic ratios - How many, out of 16 are:
.~
Black, Short
Ox
'"
Black, Long
White, Short
3
White, Long
\6\ v>t£t
~ z:
V ::
L0Y\lt-L
L :: SrY:>f t
Female Gametes
I@ ®
@~/~/~/~/~ ..~.~
®
@I
..~ ..
How many of the offspring
1@q;J!~~~
..•
~-
\...-
I
Black, Short
~-
~~/~/~~~
\\
White,
~M~··~(~··
/--~~/~.~
Q
--
'0'0
\\
Long
( -
_\....1/
__
Short
White,
are:
/I
_\.J/~
\Db L. -
~~~~'~.~'
~\
\ -:: \ DVtj
f\
.ss.:
Female Gametes
® @ ®I
®~~
~.~..~ ..- .~.
~~;i(~
I@
/--../0 -~O I--~~
<II
--./(~
J(@~~~-~~
~ tC7\ /~
~
/~
~
/'~
/~
t~. ~,.~~
... :.'(-~.'" (-~
'bW. 'rllll
!b- L-Black, Short
~~'~.~"~'-
fb\'
How many of the offspring
britt ~
~-
B'ta ck,
\\
Lo n g
d
_\>_
ex.
-L''/u---=-_
~~,k';-L
'0'10
White,
\\
Long
~
_KJ-=-_
are:
/
Dihybrid cross worksheet
Name
_
Ex) A tall green pea plant (ITGG) is crossed with a short white pea plant (ttgg).
IT or Tt = tall
tt = short
GG or Gg = green
gg = white
tg
tg
tg
tg
TG
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TG
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TG
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TG
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
TtGg
16 TalVGreen: 0 TalVWhite: 0 Short!Green: 0 Short! White
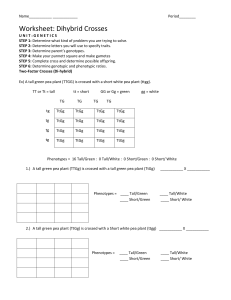
1) A tall green pea plant (TTGg) is crossed with a tall green pea plant (TtGg)
TG
T~
t~ ~~~~~~~~~~~
t (y LL.-"<..~t---'--'--'~\----,--,-~I"f-'--'--~p
~ - LJ "'- ~~
(J\ tt ~- ty( H:
r~<tr
Tall/Green: -=t... Tall/White: JL..L Short/Green: U- Short! Wtlite
I~'") \~
2) A tall green pea plant (TtGg) is crossed with a Short yellow pea plant (ttgg).
tt
'3"
Short! White
3) A Heterozygous tall red flowered plant is crossed with a
H£.mozygous short white flowered plant.
T:=
-\) =-
a.:;
-\-oJ \
8V'\0 rt
yeJ
x
----
T~
'( =- wr¥~
tv' Tt'iv
To(
-r~,~v
~
TalllRed :
±
tQ
t{
Tt ("( t,tYL ( ttvv
t:{ \t;~( Tt,({
'ft .(1
tv
tv Tet<
tt ((
\'V(/
TalllWhite : ~
t:t~( t tft!'
t,t (l. ('
ttrY
ttt( tt((
ShortlRed : ~
Short/White
4) Two Het~ozygous Tall, Green pea plants are crossed.
T taU
t ~6r\Oft
=:;
():; ~(en1
6'~~~
~
Tall/Green:
3 TalllWhite: 3 Short/Green:
\ Short/ White
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet
1. Set
•
•
•
•
•
up a pun nett square using the following information:
Dominate allele for tall plants D
Recessive allele for dwarf plants = d
Dominate allele for purple flowers = W
Recessive allele for white flowers = w
Cross a homozygous dominate parent
(DDWtN) with a homozygous recessive parent
(ddww)
=
\J0 '1)\)0 j)
~U)
to
2.
Using the punnett square in question #1:
a. What is the probability of producing tall plants.with
purple flowers? \ OO~I
D
. -:D~~§lb~~P~S)?~
b.
1)\j:)
What is the probability of producing dwarf plants
with white flowers?
-e-
c.
-e
What is the probability of producing tall plants with
white flowers?
Possible genotype(s)?n
~w
d.
o\~
.
d.e! co c0
Possible genotype(s)?
'1)c\~----1r--
'OJ \JJw 1)PV0\U
'1)'\) ~ve::>
c\ u:>w
What is the probability of producing dwarf plants
with purple flowers?
.-e-
Possible genotype(s)?
ddW~
4.
3. Set up a punnett square using the following
information:
•
Dominate allele for black fur in guinea pigs B
•
Recessive allele for white fur in guinea pigs =b
•
Dominate allele for rough fur in guinea pigs
=
=
R
•
•
Recessive allele for smooth fur in guinea pigs
r
Cross a heterozygous parent (Bbfcr) with a
heterozygous parent (BbRr)
=
~'((
€:>
btQ.e
b~(V '6'oa~'6'0'1..(
fJ~~(
'bfJ(( tJbQ1
if
'v(L
'of
'b\?\h
b?ff
~b~f
'o'p y {
wl0
Using the punnett square in question #3:
a. What is the probability of producing guinea
pigs with black, rough fur?
lltJ
ct (
VL Possiblegenotype(s)?
./).1)
Q
/)
o~e.(2. 't)£> 'l2J 't>~'L~ 0'0,,-(
b.
What is the probability of producing guinea
S1 I LP
P~s.
with, black, smooth fur?
Possible genotype(s)?
'b'o({
c.
p~s
'fJb ((
bb~Qb'oll{ I~bea'o'oQ(
clet
~€:>y(
What is the probability of producing guinea
with white, rough fur?
Possible gbb'tYe.e;s)?
d.
p~s
I
'2:>ll.()
\0'0 {Le.
What is the probability of producing guinea
with white, smooth fur?
Possible genotype(s)?
'10'0((
\1
I (p
5. Set up a pun nett square using the following
information:
•
Dominate allele for purple corn kernels
R
•
Recessive allele for yellow corn kernels
r
•
Dominate allele for starchy kernels = T
•
Recessive allele for sweet kernals = t
•
Cross a homozygous dominate parent with a
homozygous recessive parent
7.
=
=
-
~;rt
Set up a pun nett square using the following
information:
•
Dominate allele for normal coat color in wolves =
N
•
Recessive allele for black coat color in wolves =
n
•
•
•
=
Dominant allele for brown eyes B
Recessive allele for blue eyes b
Cross a heterozygous parent with a
heterozygous 'parent
=
N
F7
'0
'(\
(b
Y'\
\0
<,
I~
<,
rt
6.
.~
J
~
Using the punnett square in question #5:
a. What is the probability of producing purple,
starchy
.
corn kernels?
\
8.
Using the punnett square in question #7:
a. What is the probability of producing a wolf with a
normal coat color with brrwn eyes?
at l{.o
00 Of 0
Possible genotype(s)?
ReJt
p~~nnot(l~(~1
b.
b.
What is the probability of producing yellow,
starchy corn kernels?
,0
Possible genotype(s)?
c.
(Z.(·Tt
NN\36
.
'(,'f
--r.l\"
«« n
d. What is the probability of producing yellow, sweet
corn kernels?
():J'"
c.
·t\.H\) b '0
~
f(tt
10\\
\
Ph"' 1:>\0
What is the probability of producing a wolf with
a black coat with brown eyes?
3/1~
d.
("\ (\ <b b
.12....
'"
V"I
6w
What is the probability of produclnq a wolf with
a black coat with blue eyes?
Ill(::>
q
Possible genotype(s)?
Possible genotype(s)?
'D L
()DO
What is the probability of producing a wolf with a
normal coat color with blUEteyes?
Possible genotype(s)?
fLt-tt
N
3/1&1
0"
e.< bt
~\
~€> Niv(b~
Possible genotype(s)?
What is the probability of producing purple, sweet
corn kernels?
tl>
Possible genotype(s)?
f\}()