Glandular Epithelia/ Glands Helpful Vocab Epithelia Glands
advertisement

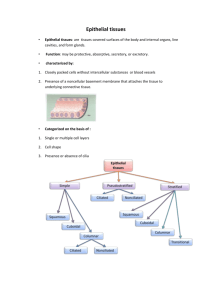
10/8/2008 Glandular Epithelia/ Glands Helpful Vocab • Gland- consists of one or more cells that make and secrete (export) a particular product. • Secretion- the passage of material formed by a cell to its exterior • Ducts- a canal passageway; a tubular structure that provides an exit for the secretions of a gland, or for conducting any fluid Epithelia Glands • Epithelial cells are specialized cells. They protect cells below them and may also carry out special functions. (Not found in book) • Epithelia Glands are a membranous tissue composed of one or more layers of cells separated by very little intercellular substance and forming the covering of most internal and external surfaces of the body and its organs.(Not found in book) • Glandular Epithelia contains two different types of glands. - Endocrine Gland and - Exocrine Gland 1 10/8/2008 Endocrine Glands • Also called ductless Glands - Which means glands eventually lose their ducts • The Endocrine Glands internally secrete their products. • This gland produces hormones - The hormones enter into the blood or lymphatic fluid and travel to specific target organs. • The Gland is structurally diverse, so one description doesn’t fit all. - Most Endocrine glands are compact Multicellular organs. - Some individual hormone-producing cells are scattered in the digestive tract mucosa and in the brain. Exocrine Glands • This gland is far more numerous than Endocrine Glands, many of their products are familiar. • This gland secrete their products onto the body surface or into body cavities • These glands are very diverse. - They include the mucous, sweat glands, oil, the salivary glands, the liver, the pancreas, and many others. • The Exocrine Glands include: - Unicellular Exocrine Gland and - Multicellular Exocrine Gland Unicellular Exocrine Glands • The only important example of unicellular gland is the goblet cell. • Goblet Cells are sprinkled in the epithelial linings of the intestinal and respiratory tracts amid columnar cells with other functions. • In humans, all such glands produce Mucin. -Mucin is a complex glycoprotein that dissolves in water when secreted. *Mucin forms mucus. 2 10/8/2008 Multicellular Exocrine Glands • • • • • Multicellular Exocrine are more complex than Unicellular Exocrine The Multicellular Exocrine contain two basic parts - Epithelium-derived duct and - Secretory Unit Structural Classification - Simple Glands- have an unbranched duct - Compound Glands- have a branched duct * From there the glands are categorized by their Secretory Units 1.) Tubular- means that the secretory cells form tubes 2.) Alveolar (or Acinar) - means if the secretory cells form small, flask-like sacs 3.) Tubuloalveolar- means that if they have both types of secretory units Multicellular Glands have two different modes of secretion -Merocrine Glands- secrete their products by exocytosis as they are produced * Most Multicellular Glands are Merocrine Glands - Holocrine Glands- accumulate their products within them until they rupture Simple and Compound Exocrine Glands Websites Used • http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/glandular+e pithelium • http://www.thefreedictionary.com/glandular +epithelium • http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/histology/wor d/2003/glandularepithelium03.htm 3