Lecture 4
advertisement

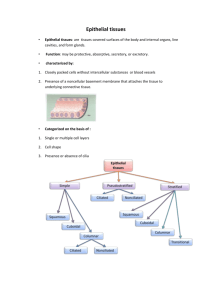
ZOO 117 1.0 Histology Glandular Tissues 1 Glandular Epithelium & Glands Glands develop during fetal life from epithelia by cells proliferation & invasion of subjacent of connective tissue 2 Exocrine Glands Description – Ducts or tubes carry exocrine products to epithelium. Retains their contact with the epithelium surface. They have a secretory potion & ducts 2 Types • Exocrine glands • Endocrine glands 3 4 1 Exocrine Glands Exocrine Glands 2 Types Include the following diverse glands • Mucous secreting glands • Sweat & oil glands • Salivary glands • Liver & pancreas 1. Unicellular: One cell 2. Multicellular: Many cells 5 Unicellular Exocrine Glands These are the Goblet cells 6 Multicellular Exocrine Glands Posses two basic parts • Produce mucin • Mucin + H2O Mucus • Protects & lubricate many internal body surfaces (small intestine & respiratory tract) • Epithelium walled duct • Secretory unit • Classified in two ways Classified by structure (branching & shape) of duct • Simple • Compound 7 8 2 Exocrine Glands Exocrine Glands Secretory portion : Can be simple Secretory portion : Can be branched i.e. Compound glands 1. Tubular : short or long 2. Coiled: 1. Tubular 3. Acinar: round or globular 2. Acinar 3. Tubuloacinar 9 Multicellular Exocrine Glands 10 Multicellular Exocrine Glands Characterized by Secretory unit (mode or type) • Merocrine secretion: Secretory vesicles released via exocytosis. Mainly proteins or glycoprotein s • Holocrine secretion: Entire cell is destroyed during secretion 11 12 3 Multicellular Exocrine Glands Characterized by Secretory unit (mode or type) Multicellular Exocrine Glands Exocrine glands with merocirne secretion can be further divided in to: 3 types depending on the nature of proteins or glycoproteins. • Apocrine secretion: Apical portion of the cell is lost. (only cytoplasm + excretory product). • Product is typically a large lipid droplet. • Serous: Mostly water but may contain some enzymes. Acinar cell of the Parotid salivary gland & Pancreas 13 14 Multicellular Exocrine Glands • Mucous : Contains strongly hydrophilic glycoproteins called mucin. When they are released become hydrated to mucus, a viscous elastic, protective lubricant material. Sublingual gland, Goblet cells Thyroid Gland • Mixes: Serous and mucus. Submandibular gland 15 16 4 Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland • Located in the cervical region anterior to lanrynx • Butterfly shaped 2 lobes • Lobes united by an Isthmus • Largest endocrine gland • Straddles the trachea 17 Thyroid Gland 18 Thyroid Gland • The thyroid gland contains numerous follicles, composed of epithelial follicle cells and colloid. • Also, between follicles are clear parafollicular cells, which produce calcitonin. 19 Function: • Synthesize thyroid hormones • Thyroxin (tetra-iodothyronine –T4) • Tri-iodothyronine (T3) • Important for growth, cell differentiation • Control of basal metabolic rate & oxygen consumption in the cells 20 5 Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland • Paranchyma composed of millions of thyroid follicles. • Each follicle consists of • Simple epithelium • Central lumen: filled with gelatinous substance; colloid. 21 Thyroid Gland 22 Thyroid Gland • Only endocrine glad with large quantities of secretory products are stored. • Densely packed separated by sparse reticular connective tissue T.S. of thyroid gland 23 24 6 Follicular Cells Parafollicular Cells / C. Cells • Range in shape from squamous to low • Found inside the basal columnar • Variable in diameter • How to identify an active gland? . More follicles with low columnar epithelial cells & more squamous cells lamina of the follicular epithelium or • Isolated clusters between follicular cells • Synthesis & secrete calcitonin 25 26 T4 and T3: Actions • increase synthesis of enzymes involved in cellular respiration --> increase basal metabolic rate Control • Major regulator is TSH • Release of TSH stimulated by TRH from hypothalamus – results in increased heat production. 28 7 T4 and T3: Control Release of TRH is stimulated by cold, pregnancy, low thyroxin 8