Back
Print
Name
Class
Date
Skills Worksheet
Concept Mapping
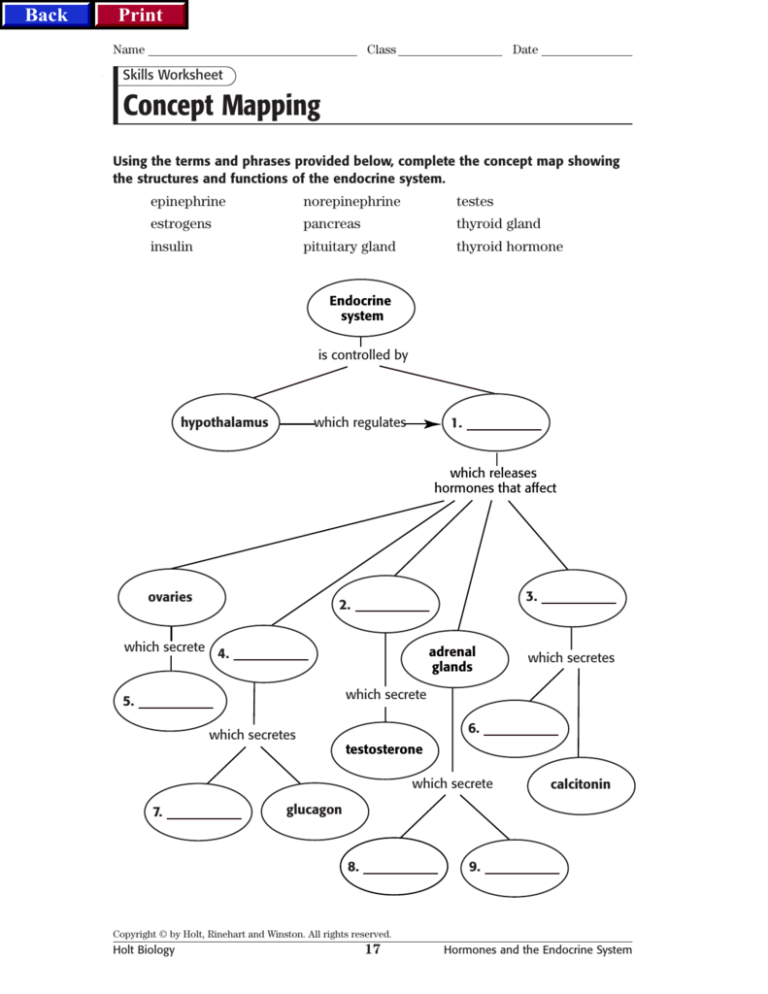
Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing
the structures and functions of the endocrine system.
epinephrine
norepinephrine
testes
estrogens
pancreas
thyroid gland
insulin
pituitary gland
thyroid hormone
Endocrine
system
is controlled by
hypothalamus
which regulates
1.
which releases
hormones that affect
ovaries
3.
2.
which secrete 4.
adrenal
glands
which secretes
which secrete
5.
6.
which secretes
testosterone
which secrete
7.
calcitonin
glucagon
8.
9.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
17
Hormones and the Endocrine System
Back
Print
TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE
3. extracellular fluid
4. The brain, stomach, small intestine,
Releasing hormones cause the front
part of the pituitary gland to make and
then release a corresponding pituitary
hormone, while inhibiting hormones
signal the anterior pituitary gland to
stop secreting one of its hormones.
8. c
kidney, liver, and heart contain cells
that secrete hormones.
5. The exocrine part of the pancreas produces digestive enzymes and delivers
them to the small intestine through
ducts. The endocrine part of the pancreas secretes two hormones into the
bloodstream which regulate blood glucose levels.
6. a
Vocabulary Review
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
SECTION: HOW HORMONES WORK
1. The hormones are not fat soluble.
2. The shape of the receptor protein
changes.
3. an amino-acid-based hormone made in
6.
7.
8.
1. In Situation 1, the receptors of Cell M
2.
1. Together they serve as a major control
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
l
n
j
o
b
h
c
INTERPRETING SCIENTIFIC
ILLUSTRATIONS
the first messenger, or hormone, to the
cell
a change in the shape of a receptor
protein
An enzyme is activated that converts
ATP to a second messenger called
cyclic AMP.
activates or deactivates certain
enzymes in a cascading fashion
b
SECTION: THE MAJOR ENDOCRINE
GLANDS
2.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Science Skills
the pancreas
4. a molecule that passes a message from
5.
f
i
d
m
k
g
e
a
center for the rest of the endocrine
system.
the area of the brain that coordinates
the activities of the nervous and
endocrine systems
temperature, blood pressure, and
emotions
through signals sent from the nervous
system as well as from blood concentrations of circulating hormones
by producing hormones that provide
response instructions to the pituitary
gland
suspended from the hypothalamus by
a short stalk
Both releasing and inhibiting hormones
are produced by nerve cells in the
hypothalamus and released into a special network of blood vessels between
the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
3.
4.
5.
6.
are defective. Cell M does not secrete
any Hormone B because the cell cannot be stimulated to do so. Cell D’s
secretion of Hormone A increases
because of the lack of release of
Hormone B.
In Situation 2, the receptors of Cell D
are defective. Cell D’s secretion of
Hormone A is increased because it is
unable to detect Hormone B secreted
by Cell M. In response to the increased
levels of Hormone A, Cell M’s secretion of Hormone B increases.
If Cell D could not produce Hormone
A, Cell M would not be stimulated to
release Hormone B. The concentrations of both hormones would be zero.
Liver cells release glucose.
Pancreas releases insulin.
Blood-glucose levels decrease.
Concept Mapping
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
pituitary gland
testes
thyroid gland
pancreas
estrogens
thyroid hormone
insulin
epinephrine or norepinephrine
norepinephrine or epinephrine
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
64
Hormones and the Endocrine System









