Accounting & MIS
advertisement

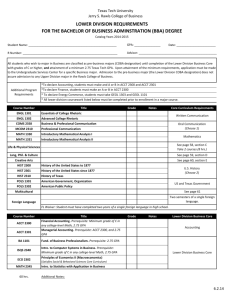
Accounting and Management Information Systems Course Descriptions Accounting Course Descriptions ACCT 110 Introduction to Financial Accounting (3-0-3) This introductory course to financial accounting aims to develop sufficient literacy for students to understand the uses, strengths, and weaknesses of financial reporting. The course develops students’ skills underlying the preparation and analysis of financial statements of a business enterprise. The course also provides an overview of generally accepted accounting principles as they relate to the recognition of revenues and expenses, and the valuation of assets and liabilities. Ethics in accounting incorporated in the presentation of financial statements. Prerequisite: None. ACCT 210 Introduction to Managerial Accounting (3-0-3) This Course covers uses of accounting information for managerial decision making to aid planning and control activities of managers in business enterprises. Topics include methods for determining the costs of products and services, cost behavior analysis, assessing product and project profitability, cost-volume-profit analysis, budgeting, cost control using standard costing and variance analysis. Prerequisite: ACCT 110 ACCT 300 Accounting Information Systems (2-2-3) This course teaches students the principles and concepts of providing information support for managerial activities in the functional areas of logistics, manufacturing, marketing, human resources, and finance. Students also learn to concepts related to internal control in manual and computerized accounting systems. Other concepts covered in the course include analysis, design, and implementation of accounting systems with emphasis on decision support systems, expert systems, and networked systems. The course also provides students with skills necessary for the utilization of basic accounting software packages and gives them with exposure to ERP systems. Prerequisites: ACCT 210 ACCT 301 Intermediate Accounting I (3-0-3) Objectives of financial statements, and their preparation. In-depth study of generally accepted accounting principles with concentration on the valuation techniques and procedures underlying the financial statements. The course also features several conceptual and theoretical issues that face the accounting profession. Accounting for current assets and current liabilities. Accounting for acquisition and disposition of plant assets including depreciation and depletion. Accounting for intangible assets. Study of ethics in accounting. Prerequisite: ACCT 210 ACCT 302 Intermediate Accounting II (3-0-3) Study of stockholders' equity including issuance and reacquisition of capital stock, dividends and retained earnings. Accounting for short-term and long-term investments in securities. Revenue recognition and long-term contracts. Study of cash flows, capital leases, and interpretation and analysis of financial statements. Use of cases and study of ethics in accounting. Computer applications in financial accounting. Prerequisite: ACCT 301 ACCT 304 International Accounting (3-0-3) Objectives of international accounting. International accounting standards and organizations. Transnational financial reporting and disclosure problems. Accounting information systems and control for multinational operations. Financial planning for multinational operations. Accounting for foreign currency translation and inflation. Multinational taxation and transfer pricing. Consolidated financial statements for multinational operations. Accounting and Economic Development. Accounting for multinational corporate responsibility. Prerequisite: ACCT 301 ACCT 305 Accounting for Governmental and Non-Profit Entities (3-0-3) Accounting concepts and techniques for governmental operations including fund accounting. Financial reporting and disclosure problems of governmental and non-profit organizations. Budgetary control procedures for governmental and non-profit entities such as universities, hospitals, and charities. Prerequisite: ACCT 210 ACCT 307: Islamic Financial Jurisprudence (3-0-3) Fundamentals of commercial law, the Islamic principles of property rights, contracts, capital, types of ownership, sale contracts, commercial papers and bankruptcy. Secured transactions, and concepts of agency, estate, and trust under Islamic Sharia Law. Prerequisite: None ACCT 311 Auditing (3-0-3) Generally accepted auditing standards and procedures used by the external auditor. Professional ethics, professional responsibility, and legal liability of the external auditor. Audit concepts such as auditor's independence, fair presentation, and due professional care. Internal control evaluation and design of audit programs; collection of audit evidence including statistical sampling and analytical review; evaluation of audit evidence; arriving at audit opinions. Development of working papers and audit reports. Assurance services. Uses of the computer as an audit tool. Utilization of generalized audit software packages. Information Technology and the audit process. Prerequisite: ACCT 300 ACCT 314: Computer Control and Audit (3-0-3) Auditing of computer-based information systems. Audit environment and information systems controls. Theory of internal control and the application of audit procedures in a computerized environment. Techniques for evaluating applications, data integrity, general operations, security, systems software and maintenance. Prerequisite: ACCT 300 ACCT 351: Accounting Cooperative Work (0-0-6) Comprehensive period for accounting practical training in a selected economic organization. The Department of Accounting and Management Information Systems approves the training program and monitors the student's progress during his co-op period. Under the supervision of an accounting faculty member or a faculty member in a related discipline, the student writes an analytical report about his co-op experience. Prerequisite: None ACCT 403 Advanced Accounting (3-0-3) Study of accounting principles and procedures related to business combinations. Methods and techniques for preparing consolidated financial statements. Receiverships and statement of affairs. Accounting for formation, operation, and liquidation of partnerships. Accounting for branches, consignments, and joint-ventures. Ethics in accounting. Prerequisite: ACCT 302 ACCT 405: Accounting Theory & Research (3-0-3) The development and structure of accounting theory, principles, and practices applicable to business organizations. Objectives of financial reporting and disclosure. Models of income determination and balance sheet valuations including historical cost, replacement cost, exit values, and discounted cash flows. Controversial accounting treatments and their effect of the usefulness and reliability of financial statements. The pronouncements of professional accounting bodies. Study of contemporary issues in financial accounting. Prerequisites: ACCT 301 ACCT 406 Internal Auditing (3-0-3) Development and evolution of the internal auditing profession; scope and objectives of internal auditing; standards of professional practice; control concepts; techniques of internal auditing; internal auditing and internal control; the internal audit process; reporting and communication of internal audit findings; administration of internal audit departments and quality assurance; internal auditor's independence; relationships between internal and external auditors and audit committees; ethics in internal auditing; financial audits; operational, efficiency, and management audits; compliance audits and computer applications in internal auditing. Prerequisites: ACCT 210 ACCT 407 Financial Statement Analysis (3-0-3) The basic skills required for a structured analysis of financial statements; forecasting of income and cash flows; pro-forma financial statements; firm valuation using discounted cash flows and discounted residual income methods; comparative valuation analysis; credit analysis. A study of the potential effects of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles financial statement analysis and valuation techniques and outcomes. Concepts of earnings quality and management of earnings. Prerequisites: ACCT 210 ACCT 408: Zakat and Business Tax Accounting (3-0-3) Study of the fundamentals, rules, and objectives of taxation under Saudi Arabian tax and zakat regulations. The course provides students with the skills necessary to compute and assess income tax and zakat base for business entities. In addition, students become familiar with the business income tax and zakat rates, and The Department of Zakat and Income Tax functions. Prerequisite: ACCT 210 ACCT 410: Cost Accounting (3-0-3) This course emphasizes contemporary topics in strategic cost management through and understanding of the underlying concepts and fundamental techniques involved in cost accounting for manufacturing and service companies. The emphasis is on how cost management systems, with their performance evaluation and reward systems, encourage efforts to achieve an organization’s strategic goals. Topics include activity-based costing; decision making; pricing; joint and common cost allocation; cost of quality and continuous improvement; responsibility accounting, performance measurement and reward systems; transfer pricing and capital investment decisions. Prerequisite: ACCT 210 ACCT 411: Cost Management & Cost Control (3-0-3) This course addresses advanced and contemporary issues in cost management and management control with emphasis on industrial and business practices. Behavioral and organizational foundations of managerial accounting. Cost and management accounting practices. Gap between management accounting theories and practices. The role of management accounting in inter-organizational relationships such as supply chain and outsourcing. Case studies in managerial accounting. Prerequisite: ACCT 410 ACCT 420: Petroleum Accounting (3-0-3) The objective of this course is to familiarize students with accounting practices in the petroleum industry. The course entails an overview of the industry with a detailed focus on certain aspects of the Successful Efforts the Full Cost Methods of accounting. Petroleum accounting issues specific to the industry are also discussed. Topics coved include oil and gas reserves, the standardized measure, supplemental disclosures, and depreciation, depletion, and amortization of exploration and development costs. Financial statement presentation issues will be analyzed to gain an appreciation for the unique impact of generally accepted accounting principles in the petroleum industry. Prerequisites: ACCT 302 ACCT 499 Special topics in Accounting (3-0-3) Topics and issues to be advised, covering contemporary developments in financial and managerial accounting, such as corporate financial reporting, strategic management accounting, management control systems and regulation of financial reporting. Prerequisites: ACCT 210 Management Information Systems Course Descriptions MIS 215: Principles of Management Information Systems (3-0-3) Information systems concepts and principles with managerial emphasis. Information systems for operational, tactical and top management. Strategic impact of technologies on organizations. Prerequisite: None MIS 300: Fundamentals of Electronic Commerce (2-2-3) E-Commerce fundamentals; E-Commerce business models; infrastructure; electronic payment systems and E-commerce security; Development, implementation, marketing and managing E-Commerce applications. Benefits and limitations, legal, ethical and global issues. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 301: Business Systems Analysis & Design (2-2-3) Examining the design of information systems from a problem-solving perspective. Providing a methodological approach to developing computer systems including feasibility studies, systems planning, analysis, design, testing, implementation, and maintenance. Emphasis is on the strategies and techniques of systems analysis and design for producing logical methodologies for dealing with complexity in the development of information systems. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 302: Business Applications Development (3-0-3) Programming process with emphasis on program design and quality assurance and control. End user systems versus traditional systems development issues. Advanced HCI concepts and principles. Common business topics: data validation, report taxonomy, files and database processing. RAD methodologies, techniques, and tools. RAD success and risk factors. User documentation development techniques and tools. Application deployment issues. Emphasis on the development of end-user-focused, high quality business applications with user-centered-design and using RAD methodologies, techniques, and tools. Prerequisite: ICS 102 MIS 311: Business Data Management (2-2-3) Data resource management concepts. Database support for various levels of management. Relational database model. Database life cycle. Conceptual data modeling. Database logical and physical design. Database integrity. Database languages and technologies. Data and database administration. Prerequisite: ICS 102 MIS 315: MIS Innovation and New Technologies (3-0-3) Introduction to MIS Innovation and New Technologies. Nurturing an Entrepreneurial Innovative Environment. Understand the Business Value of Innovation. Innovation with Online Communities; Social Web Networks. Re-engineer business processes with Innovations and New Technologies. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 320: Knowledge Management (3-0-3) Introduction to Knowledge Management (KM) – Knowledge Management (KM) to gain competitive advantage. KM for innovation, KM’s emerging systems (Enterprise 2.0, Semantic Web), E-Knowledge Management.KM Development Methods. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 325: Human Resources Information Systems (3-0-3) Introduction to Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS): Strategic role of Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) in the effective management of organizations, HRIS capabilities and limitations, Organizational needs for HRIS, Evaluation and selection factors of an appropriate HRIS, HRIS software application packages for management decision-making. Role of HRIS in current Information Technology topics (Internet, Privacy, Security). Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 345: Information Technology in Society (3-0-3) Impact of IT on individuals, organizations, society, and quality of life. Social and ethical considerations. Computer and Internet crimes. Intellectual property rights. Risks of IT. Human computer interaction. Data protection. National and international legal environment of IT.E-Government issues. Health and work hazards related to IT. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 351: MIS Cooperative Work (0-0-6) A 28 week industry-based learning for MIS students to get practical experience in the area of Management Information Systems with reputable business organizations as approved by the Department and guided by a coop advisor. Evaluation of performance through submission of progress reports, employer’s feedback, final report, and presentation. Student’s defense of his coop work by a panel of faculty members inclusive of the coop advisor. Prerequisite: None MIS 355: Enterprise Systems (3-0-3) Architecture, setup, configuration, operations and management of system that is of "enterprise class". Fundamentals of business process and business process re-engineering concepts. Selection, process mapping, GAP analysis, and implementation of enterprise systems. Enterprise modules and decision analysis tools. Use of project management techniques to emphasize team dynamics and management skills. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 365 : Enterprise Architecture (3-0-3) Introduction to Enterprise Architecture: Enterprise architecture frameworks, Systems integration, Infrastructure and content management, System administration, Data/information architecture and data integration, Risk management, Software as a service. Emerging technologies. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 375 : Human Computer Factors in Systems Design (3-0-3) Factors related to both people interaction with technology, and the ways of technology effects on humans’ performance. An introduction to human related to the design of information systems. Emphasis on the human component of human-computer interaction (HCI), and the process of usercentered design and evaluation. Develop knowledge and skills of creating enhanced human-computer interfaces and user-computer interaction designs. Prerequisite: MIS 215 MIS 405: IS Project Management (3-0-3) Project management fundamentals and strategies. Project management body of knowledge. Human aspect of project management. Project Management processes, methods, techniques, tools, and implementation issues. Systematic methodology for initiating, planning, executing, controlling, and closing projects in team based environment. Prerequisite: MIS 301 MIS 410: Management Support Systems (2-2-3) Introduction to Management Support Systems (MSS): Decision Support Systems, Collaborative Work Systems, Executive Support Systems, Expert Systems, and Neural Networks. Impact of MSS on decision making. Exposure to MSS tools and development methods. Integration of MSS. Team projects to develop MSS. Prerequisite: MIS 311 MIS 411: Database Applications Development (3-0-3) Multi-tier application architecture concepts and technologies. Advanced SQL including procedural, embedded SQL, client-side and server-side SQL. Transaction management, consider multi-user system including concurrency control and security. Advanced database concepts including distributed and object-oriented databases, and data warehouse. Database application implementation issues Special emphasis is on development of client/server database applications. Prerequisite: MIS 311 MIS 415: Computer Supported Collaborative Work (2-2-3) Comprehensive overview of Computer Supported Collaborative Work (CSCW),Group Dynamics, Collaboration Architectures, Groupware and Group Tools, Asynchronous and Synchronous Collaboration, Video in Collaboration, Web-based Collaboration, Collaborative Virtual Environments, Facilitation and leadership, Integration with other computerized systems, Exposure to literature and cases and Team-based projects. Prerequisite: MIS 311 MIS 490: Information Resources Management (3-0-3) Theories and practices in the management of organizational information systems resources. Frameworks for introduction, evolution and assimilation of information systems into an organization. Align IT strategy with business strategy. Roles of IT and people using, developing. Managing systems. Global concepts of IT. Societal and ethical issues. Pre-requisite: MIS 405 MIS 499: Special Topics in MIS (3-0-3) Coverage of the contemporary and advanced MIS topics such as data management, information processing, decision making, social implications of IT, and emerging technologies. Prerequisite: MIS 311