18. Perfect Competition (3)
advertisement
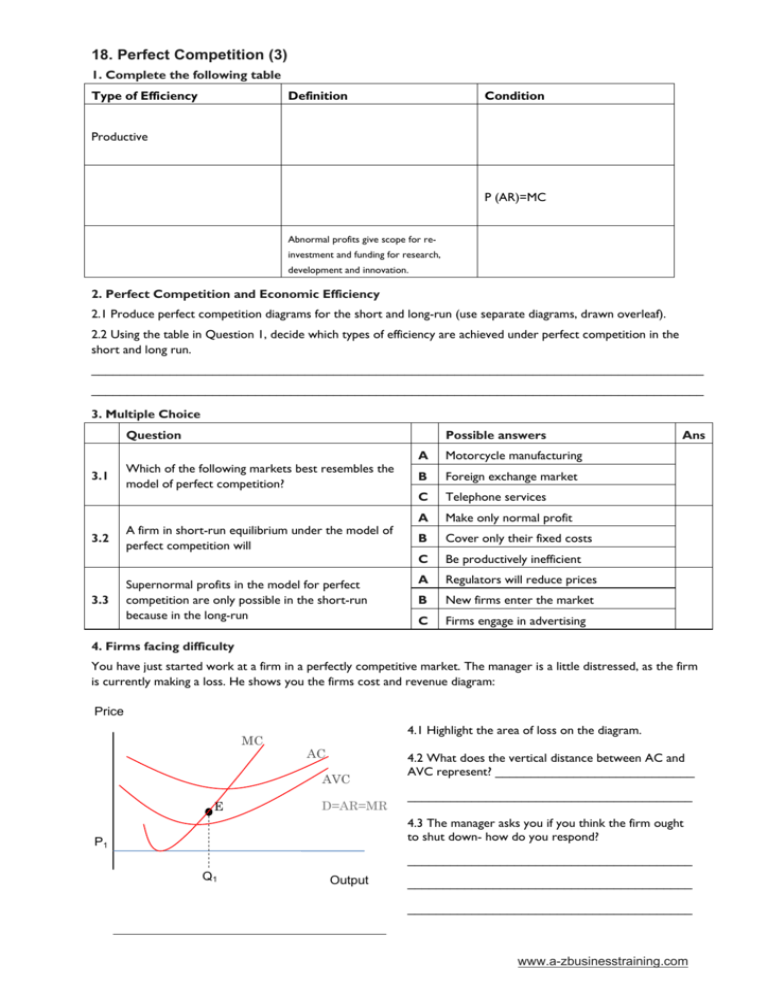
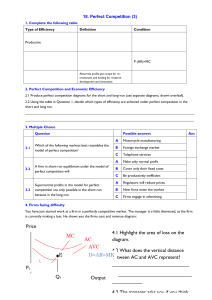
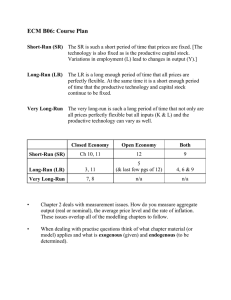
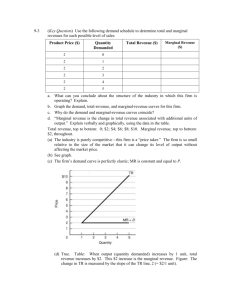
18. Perfect Competition (3) 1. Complete the following table Type of Efficiency Definition Condition Productive P (AR)=MC Abnormal profits give scope for reinvestment and funding for research, development and innovation. 2. Perfect Competition and Economic Efficiency 2.1 Produce perfect competition diagrams for the short and long-run (use separate diagrams, drawn overleaf). 2.2 Using the table in Question 1, decide which types of efficiency are achieved under perfect competition in the short and long run. ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Multiple Choice Question 3.1 3.2 3.3 Possible answers Which of the following markets best resembles the model of perfect competition? A firm in short-run equilibrium under the model of perfect competition will Supernormal profits in the model for perfect competition are only possible in the short-run because in the long-run A Motorcycle manufacturing B Foreign exchange market C Telephone services A Make only normal profit B Cover only their fixed costs C Be productively inefficient A Regulators will reduce prices B New firms enter the market C Firms engage in advertising Ans 4. Firms facing difficulty You have just started work at a firm in a perfectly competitive market. The manager is a little distressed, as the firm is currently making a loss. He shows you the firms cost and revenue diagram: Price MC 4.1 Highlight the area of loss on the diagram. AC AVC E D=AR=MR 4.2 What does the vertical distance between AC and AVC represent? ____________________________ ________________________________________ 4.3 The manager asks you if you think the firm ought to shut down- how do you respond? P1 ________________________________________ Q1 Output ________________________________________ ________________________________________ www.a-zbusinesstraining.com 18. ANSWERS: Perfect Competition (3) 1. Type of Efficiency Definition Where a firm produces at the lowest point on its average cost curve and thus minimises the use of resources per unit produced. Occurs when resources cannot be reallocated to produce a different combination of goods that will increase economic welfare. Abnormal profits give scope for reinvestment and funding for research, development and innovation. Productive Allocative Dynamic 2.1 Price Condition Short-run MC=AC P(AR)=MC AR > AC Long-run Price MC MC AC E P1 D=AR=MR E2 P2 Q1 Q2 Output AC D1=AR1=MR Output 2.2 Type of Efficiency Short-run Long-run 3.1 3.2 3.3 Productive X √ Allocative Dynamic √ √ X √ B C B 4.1 AC AVC LOSS P1 4.2 Average fixed cost (AFC=TFC/Q) MC Price D=AR=MR E Output Q1 4.3 You ought to suggest that the firm continue to operate at Q1, even at a loss in the short-run. This is because the firm is currently covering AVC, and therefore making a contribution towards their fixed costs. By shutting down immediately, the firm would still have to pay these fixed costs, and would incur a greater loss. The firm must also assume that other firms are in the same position, and if they begin to drop out of the market, market price will begin to rise, and the firm may return to normal profit. The shut-down point for a firm is when AR=AVC. www.a-zbusinesstraining.com