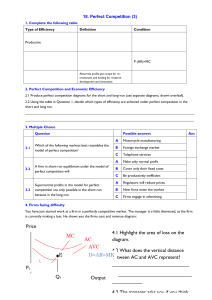
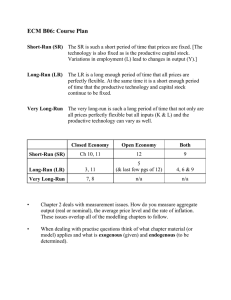
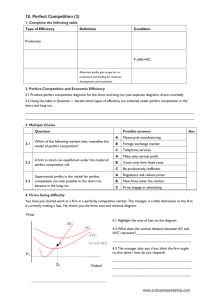
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, ROURKELA END SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2021 SESSION: 2021-22 (Autumn) Subject Code: HS-1340 Dept. Code: HS Subject Name: Principles of Economics Full Marks: 50 Duration of Examination: 2 hours Figures at the right hand margin indicate marks All parts of a question should be answered at one place Q. N. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Section A Marks Answer any FIVE 5x7=35 In the long run, all of firm's inputs are variable. Explain. How do firms use the long run average cost curve in their planning? Consider a perfectly competitive, constant cost industry. All firms in this industry have an identical long-run total cost function TC(q) = 4q2 + 100q + 100 and the long-run marginal cost function MC (q) = 8q + 100. What is the long-run equilibrium price for this industry? At an output of 9, MC = 20 and AVC = $25. At an output of 10, MC = $32 and AVC = $26. What is the lowest price the firm can accept in the short run? Explain. What actions might a firm take to stay in operation in the long-run? In a perfectly competitive industry, each producer has a long run total cost function given by LTC=q3−24q2+200q, where q denotes the output of the individual firm. The market demand for the product is q=1480−5p, where q and p denote the market output and price respectively. Calculate the optimal output produced by each firm at the long run competitive equilibrium. Because products are typically differentiated in some way, there tends to be significant advertising in monopolistically competitive industries. How will advertising affect a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive industry? Assume that two companies (C and D) are duopolies that produce identical products. Demand for the products is given by the following linear demand function: P=500−Qc−Qd where Qc and Qd are the quantities sold by the respective firms and P is the selling price. Total cost functions for the two companies are: TCc=25,000+100Qc and TCd=20,000+125Qd. Assume that the firms act independently as in the Cournot model (i.e., each firm assumes that the other firm's output will not change). Determine the long-run equilibrium output and selling price for each firm. Calculate Gross value added at factor cost from the following: (i) Gross value of output at market price 10500 (ii) Depreciation 1000 (iii) Indirect taxes 750 (iv) Economic subsidies 200 (v) Intermediate consumption 4000 (vi) Compensation of employees 200. Explain input, labour and land market and also define the firm’s profit-maximizing condition in input markets. The demand for land is a derived demand. Think of a popular location near your college. What determines the demand for land in that area? What outputs are sold by businesses located there? Discuss the relationship between land prices and the prices of those products. Section B Marks Answer any FIVE 5x3=15 1. Does the lowest price acceptable by firms for operation differ between monopoly versus a perfectly competitive firm? Explain 2. Suppose Bernard owns an ice cream shop. The ice cream industry is perfectly competitive, and the price of ice cream is $4. The minimum point of Bernard's average total cost curve is at $5. The minimum of his average variable cost is $3. Should Bernard stay in business in the short-run? Explain 3. What are sticky prices? Explain why prices are sticky in an oligopoly market. 4. Elucidate the types of short-run cost and explain each cost with a suitable diagram also explain the shape of the Marginal Cost Curve in the short-run. 5. Explain the circular flow of income in an economy. 6. Explain the product and expenditure methods of computing national income. 7. Which of the following are included in National Income and why as per Income Method? (a) The Income of dentist (b) Rent received on a two-bedroom apartment. (c) monthly pocket money received by student from his father.