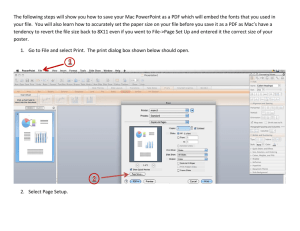
Dialog boxes
advertisement

15 Dialog boxes
CE00859-1:
Object-Oriented Programming Techniques
Week 8 Lecture 1
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
1
Objectives
In this lecture, we will:
• introduce dialog boxes
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
2
Input via dialog boxes
• in a Graphical User Interface (GUI), the console
window is generally not used for input and output
• for input we sometimes use input fields (such as text
boxes) embedded directly in the main window of the
GUI
• at other times, we display another window containing
the input fields
• this is called a dialog box
• we close it when input is complete
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
3
JOptionPane
• the JOptionPane class is one way of using dialog
boxes in Java
• it has several kinds of dialog box, which we invoke by
the methods:
•
•
•
•
December 11
showInputDialog()
showMessageDialog()
showConfirmDialog()
showOptionDialog()
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
4
Input Dialog
• the showInputDialog() method has several
combinations of parameters; we shall use:
• parentComponent
• in an applet: use null
• in an application: use this
• message
• a prompt to the user asking for the input
• title
• a string to be displayed as the box’s title
• messageType
• use JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
5
Input Dialog example
String nameMsg = "Please enter your name";
String nameTitle = "What is your name?";
String name =
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,
nameMsg,
nameTitle,
JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE);
• What value will name have if the
user clicks the cancel button?
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
6
Message Dialog
• the showMessageDialog() method has several
combinations of parameters; we shall use:
•
•
•
•
December 11
parentComponent
message
title
messageType
• use JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE
• or JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE
• or JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE
• or JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE
• or JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
7
Message Dialog example
String msg = "You have not typed your name";
String title = "Name error";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
msg,
title,
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
8
Confirm Dialog
• the showConfirmDialog() method has several
combinations of parameters; we shall use:
•
•
•
•
parentComponent
message
title
optionType
• use JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION
• or JOptionPane.YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION
• or JOptionPane.OK_CANCEL_OPTION
• messageType
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
9
Confirm Dialog example
String msg = “Do you wish to continue?";
String title = “Confirm continuation";
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(
null,
msg,
title,
JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION,
JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE);
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
10
Option Dialog
• the showOptionDialog() method has only one
combination of parameters:
•
•
•
•
•
•
parentComponent
message
title
optionType
messageType
icon
• use null unless you have an image to display
• options
• an array of objects that provides the option list
• initialValue
• The default selection; can be null
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
11
Option Dialog example
String msg = "Please pick an item";
String title = "Item selection";
String[] items = {"Apple", "Orange", "Pear"};
int index = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(
null,
msg,
title,
JOptionPane.OK_CANCEL_OPTION,
JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE,
null,
items,
items[1]);
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
12
Creating our own dialog boxes
• we can write sub-classes of the JDialog class to
create our own, customised dialog boxes
• essentially, a JDialog dialog box is a window, so we
are responsible for the components and layout of its
content
• the following example creates a custom dialog box
that mimics JOptionPane’s input dialog box (without
the image)
• this is not for the faint-hearted!
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
13
Custom Dialog example
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class CustomDialog extends JDialog
implements ActionListener
{
private JTextField username;
private String prompt;
private JButton OK, cancel;
private boolean cancelled;
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
14
Custom Dialog example
public CustomDialog(Frame owner,
String title, String prompt)
{
super(owner, title, true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
this.prompt = prompt;
cancelled = false;
setupGUI();
}
setSize(300, 100);
setVisible(true);
private void setupGUI()
{
//set up prompt, input box, buttons and layout
}
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
15
Custom Dialog example
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
cancelled = e.getSource() == cancel;
dispatchEvent(
new WindowEvent(this,
WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSING));
}
public String getUsername()
{
return username.getText();
}
}
public boolean wasCancelled()
{
return cancelled;
}
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
16
To use the CustomDialog
private String inputName()
{
String nameMsg = "Please enter your name";
String nameTitle = "What is your name?";
CustomDialog dialog =
new CustomDialog(null, nameTitle, nameMsg);
return dialog.wasCancelled() ?
“” : dialog.getUsername();
}
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
17
Summary
In this lecture we have:
• introduced dialog boxes
•
•
•
•
•
InputDialog
MessageDialog
ConfirmDialog
OptionDialog
JDialog
In the next lecture we will:
• see a worked example of the GUI concepts we have met so
far
December 11
OOPT Week 8 Lecture 1
18