Lecture 9 - Photosynthesis 2
advertisement

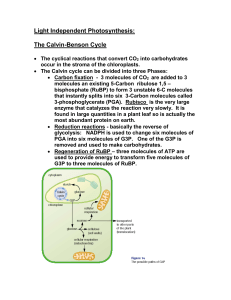
___________________________________ Photosynthesis: The Reactions, Carbon Fixation and the Environment Lecture 9 ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photosynthesis: The Details ___________________________________ Photosynthesis is divided into two processes: The light reactions begin when ___________________________________ Carbon fixation occurs only when ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Light Reactions The light reactions of photosynthesis are divided into three parts: ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 1. Photoexcitation: 2. Electron transport: ___________________________________ 3. Chemiosmosis: ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photoexcitation Chlorophyll is a molecule that will behave like any other molecule Its electrons are existing at a potential energy level know as its When a photon of light hits a chlorophyll molecule, ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photoexcitation The excitation of an electron results in an Normally, the electron will This process is known as ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photoexcitation In molecules of chlorophyll, the excited electron is “captured” by a This results in a REDOX reaction, The primary electron acceptor ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photosystems (Fig 3, p. 157) The photons that hit a chloroplast are always absorbed by a Photosystems have an The antenna complex transfers the energy of a photon to the reaction centre where it is ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Photosystems (Fig. 5 & 6 p. 160) Photosystem I and Photosystem II both occur in a chloroplast In both photosystems, a chlorophyll a molecule Photosystem I and II are both used to generate ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Cyclic and Non-cyclic Electron Flow In NON-CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW, electrons flow from In CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW, electrons flow from The electron passes through a series of ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ The Calvin Cycle (Fig. 9, p. 161) The CALVIN CYCLE is The Calvin Cycle has three phases 1. Carbon Fixation – 2. Reduction Reactions 3. Regeneration of RuBP These reactions are catalyzed by ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Carbon Fixation (C3 Photosynthesis) In carbon fixation, CO2 molecules bond with RuBP (5carbon molecule) to form This 6-carbon intermediate is then split into 2 3-carbon intermediates called These two 3-carbon molecules are the basis of The Calvin Cycle of most plants involves these 3-carbon intermediates and is known as ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Reduction Reactions The reduction reactions are as follows: 1. 2. 3. A 3-carbon PGA molecule is phosphorylated by ATP – becomes 1,3bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG) NADPH reduces BPG to G3P Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) is the final product of the Calvin Cycle – 1 molecule of G3P leaves This is a description of what happens to one molecule of PGA…more than one molecule enters this cycle ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Reduction Reactions – The Numbers Three molecules of CO2 will enter the Calvin Cycle at once Each molecule of CO2 will form 2 PGA molecules (6 total) Therefore, there are 6 PGA molecules being reduced to G3P…Why? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Regeneration of RuBP Remember that RuBP is the molecule that drives the Calvin Cycle ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ The remaining 5 G3P molecules that have been formed are ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ G3P – The Key Intermediate Plants will generally construct more sugars than they need G3P is needed to regenerate RuBP to drive the Calvin Cycle and ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Typically, G3P will be used to make ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation: C4 Photosynthesis and CAM Plants Rubisco is the enzyme that catalyzes the addition of carbon to RuBP (carboxylation) It can also add an If oxygen is more plentiful than CO2, PGA will not be produced and This process is known as ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation: C4 Photosynthesis (Fig. 2, p. 169) In C4 plants, the lack of PGA production has been remedied by an enzyme called PEP carboxylase fixes CO2 to a molecule of This creates a stable 4carbon molecule that can ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation: CAM Plants Plants that store water (cacti, pineapples – succulents) are members of the These plants ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ This action helps to conserve water, ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation: CAM Plants The CO2 that is taken in is converted into a The C4 molecule is actually an organic acid and the process is called ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________