Photosynthesis: the Calvin Cycle
advertisement

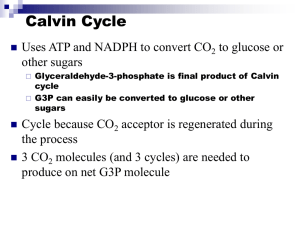
Photosynthesis: the Calvin Cycle • Light Independent Reactions – Can occur in the absence of light – Energy that was stored in ATP and NADPH during the light reactions is used to produce organic compounds in the form of sugars • Carbon fixation – Calvin cycle- series of enzyme- assisted chemical reactions that produces a three-carbon sugar – Carbon fixation- incorporation of CO2 into organic compounds – https://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/486/49 8596/CDA7_1/CDA7_1j/CDA7_1j.htm • Carbon fixation – Steps of the calvin cycle 1. each of the three CO2 molecules combines with a molecule of ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). Each resulting six-carbon molecule immediately splits into two molecules of 3-phophoglycerate (3-PGA) 2. ATP and NADPH are used to convert each molecule of 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) 3. One molecule of G3P is used to make organic compounds like glucose • 4 the rest of the G3P is converted back into RuBP– C3 plants- species that fix carbon exclusively through the Calvin cycle • Alternative pathways – C4 pathway • Found in plants that grow in hot climates and need to keep stomata closed to conserve water; low CO2 • Enzyme used to fix CO2 into four-carbon compounds, which are used for the Calvin cycle when needed • Such plants lose only about half as much water as C3 plants when producing the same amount of carbohydrates • Alternative pathway – CAM pathway 1. CAM = crassulacean acid metabolism 2. Plants open stomata at night to absorb CO2 and close them during the day 3. CO2 converted into other molecules and stored until needed 4. Grow slowly, but they lose less water than either C3 or C4 plants