Light Independent Photosynthesis
Light Independent Photosynthesis:
The Calvin-Benson Cycle
The cyclical reactions that convert CO
2
into carbohydrates occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
The Calvin cycle can be divided into three Phases:
Carbon fixation - 3 molecules of CO
2
are added to 3 molecules an existing 5-Carbon ribulose 1,5 – bisphosphate (RuBP) to form 3 unstable 6-C molecules that instantly splits into six 3-Carbon molecules called
3-phosphoglycerate (PGA). Rubisco is the very large enzyme that catalyzes the reaction very slowly. It is found in large quantities in a plant leaf so is actually the most abundant protein on earth.
Reduction reactions - basically the reverse of glycolysis: NADPH is used to change six molecules of
PGA into six molecules of G3P. One of the G3P is removed and used to make carbohydrates.
Regeneration of RuBP – three molecules of ATP are used to provide energy to transform five molecules of
G3P to three molecules of RuBP.
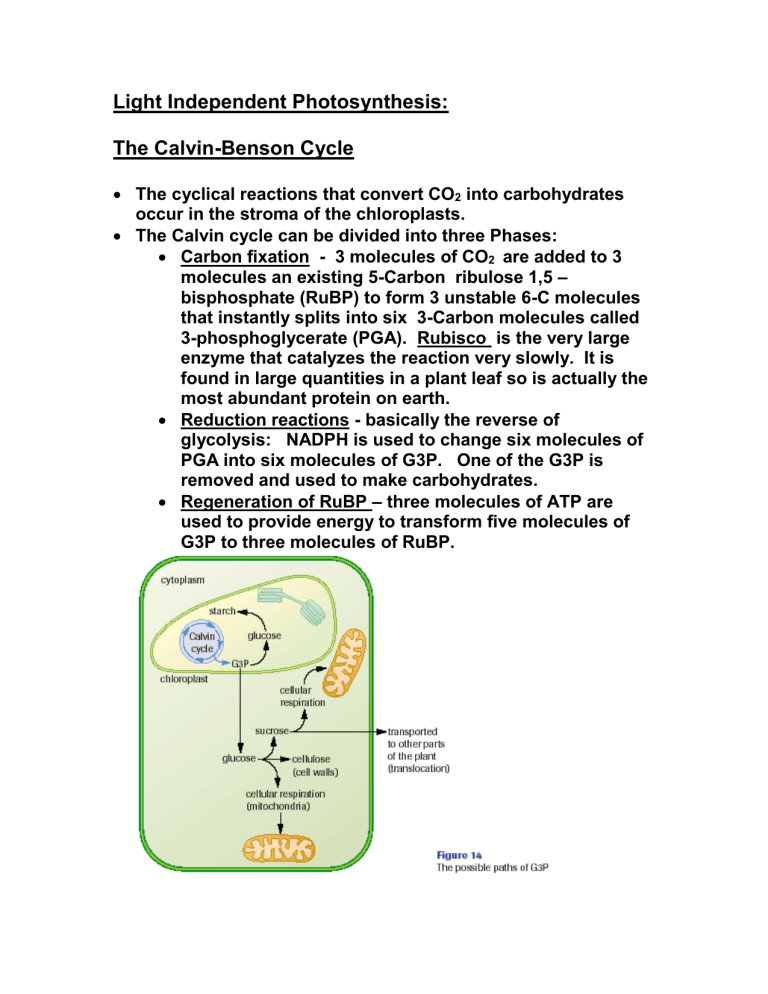
The role of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate G3P
1. Where and at what stage of photosynthesis is G3P made?
2. What products are made with G3P?
3. What is the extra G3P is for and where is it stored?
4. How is the Excess G3P transported around the plant and what is it used for?
Alternate ways of Carbon Fixation
1. What does C
3
metabolism mean? What types of plants perform it?
2. What enzyme is used to fix CO
2
during the Calvin cycle?
3. What is photorespiration? Why is it hazardous for plants?
4. Describe C
4
plants and C
4
photosynthesis in detail including a good diagram.
5. What does CAM stand for?
6. Describe CAM plants and the CAM form of carbon fixation.
The role of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate G3P
5. Where and at what stage of photosynthesis is G3P made?
6. What products are made with G3P?
7. What is the extra G3P is for and where is it stored?
8. How is the Excess G3P transported around the plant and what is it used for?
Alternate ways of Carbon Fixation
7. What does C
3
metabolism mean? What types of plants perform it?
8. What enzyme is used to fix CO
2
during the Calvin cycle?
9. What is photorespiration? Why is it hazardous for plants?
10. Describe C
4
plants and C
4
photosynthesis in detail including a good diagram.
11. What does CAM stand for?
12. Describe CAM plants and the CAM form of carbon fixation.











