Three Major Organs: Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Organization: I) The
advertisement

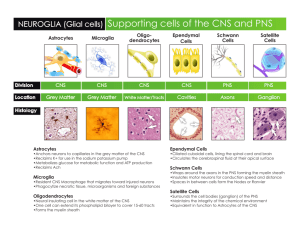
Three Major Organs: Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Organization: I) The Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and Spinal Cord II) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): The Cranial and Spinal Nerves A) Sensory (afferent division) B) Motor (efferent division) 1) Somatic Nervous System (Voluntary) 2) Autonomic Nervous System (Involuntary) a) Sympathetic Division b) Parasympathetic Division Histology: I) Two cell types form nerve tissue: A) The Neuron 1) transmits electrical signals called impulses 2) live a long time---a lifetime 3) amitotic (cannot divide) 4) high metabolic rate; need more glucose and oxygen than other cells 5) live only for a few minutes without oxygen 6) At rest the brain (3.1 lb) uses as much oxygen as 61.6 lb of skeletal muscle 7) Basic structure of a neuron include the cel body (soma), axons, dendrites, telodendrites,the synapse B) The Neuroglia (glial cells) supporting cells of the nervous system, they outnumber neurons 10 to 1; 50% of the brain consists of glial cells; found primarily in the CNS. There are four types found in the CNS and two types found in the PNS: CNS: -------Astrocytes: The largest and most numerous; secrete chemicals for the blood brain barrier; form the structural framework for the CNS; repairs damaged nerve tissue; star shaped; wrap around neurons and capillaries so they function in the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide and glucose; mops up leaked K+ ; recycles neurotransmitters.----------Microglia: The smallest rarest neuroglia which contain thorny processes that touch and monitor the health of neurons; migrate toward injured cells and turn into macrophages as they phagocytize neruonal debris and microorganisms (they have an immunological function; cells of the immune system are denied access to the CNS).----------Ependymal Cells: They form the ependyma, which lines the central canal and ventricles of the brain; range in shape from squamous to columnar and many are ciliated; ciliated forms circulate the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); formed into the choroid plexus in the ventricles of the brain which produces CSF------------Oligodendrites: Cells containing cytoplasmic extensions form the myelin sheaths around axons in the CNS (forming nodes and internodes). Myelin is fatty material surrounding axons. PNS: -----Schwann cells surround and form myelin sheaths around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS;--------Satellite cells surround neuron cell bodies within ganglia and their function is unknown----- Structural Classification of Neurons 1) Multipolar neurons are the most common(99%) and is the major nueron in the CNS; Three or more processes extend from the cell body; all dendrites except for a single axon 2) Bipolar neurons contain two processes that extend from the cell body; one is a fused dendrite and the other is an axon; found only in the sense organs (receptor cells in the retina, and nasal passages) 3) Unipolar neurons contain a single axon emerging from the cell body; begin as bipolar neurons in the embryo; axon consists of a central (proximal) process and a peripheral (distal) process receiving impulses from a sensory receptor. Found only in the PNS in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, and the sensory ganglia of cranial nerves. Structural Variations of Neurons(table 11.1) 1) Sensory (afferent) neurons; carry impulses toward the CNS; unipolar in that the cell bodies are found in the ganglia close to the spinal cord 2) Motor (efferent) neurons; carry impulses away from the CNS; multipolar cell bodies are located primarily in the CNS (cell bodies form the grey matter of the brain and spinal cord; axons form the white matter). 3) Interneurons (association neurons); most are multipolar; 99% of all neurons in the body are interneurons; transfer impulses between sensory and motor neurons in the CNS