Chemical Bonding - Tactical Hazmat
advertisement

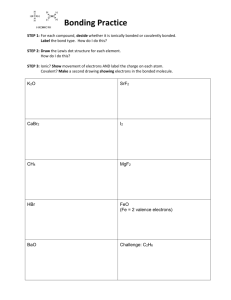
Chemical Bonding Chemical bonding is the start of all things great atom is now ‘feeling’ more positive without that and small. The ways in which atoms and electron. molecules bond together can determine how they behave in different environments. Take table salt and methane, for example. If we consider these materials at a basic level Chlorine, on the other hand, likes to take on other electrons, having a ‘desire’ to do so. When sodium donates its electron to chlorine, they form an attraction force. their bonding is very different. Sodium chloride consists of positively charged Na+ ions and negatively charged Cl- ions held together. This attraction is known as ionic bonding and describes the force in which opposite charges attract, like magnets. Magnets have no literal bond holding them together. In the same way ionically bonded materials are not literally bonded together but are held together by this attractive force. The diagram above shows how sodium gives its electron to chlorine and forms the bonding force between them. You may be familiar that table salt is a crystal. This crystal character is a result of the ionic bonding (attractive force) between the Na and Cl over a larger lattice structure. Methane is a covalently bonded material. This bonding involves atoms sharing the electrons they hold between them. We’ll discuss this concept later on. If it was possible to see the individual Na and Cl atoms you’d see they look like the diagram Back to table salt. Sodium (Na), being a metal, above. This lattice is a large and heavy structure likes to bond in a certain way. It feels a need to which means that it is relatively heavy. This lose an electron in order to bond. If you don’t heavy nature of the substance prevents it from know what an electron is have a look at “Atoms, melting (going from solid to liquid) and elements and isotopes”. evaporating (liquid to gas) at lower temperatures. The electron is given to chlorine to create the Ionic and covalent bonding are very different. As ionic bond. As electrons are negatively charged, mentioned, covalent bonds share the electrons when they are lost from the atom, they imbalance directly between the respective atoms. Whereas, the charge on the atom. This means that the in ionic bonding, one of the atoms has gained an electron V2 05/2015 FOR MORE INFORMATION AND TRAINING ON THIS TOPIC GO TO: WWW.TACTICALHAZMAT.COM and the other has lost one. Creating the attractive You’ll probably recognise methane as a gas. We force. tend to find covalently bonded materials in all Metals are bonded in a similar way to ionically three states (solids, liquids and gases). bonded materials. The difference being that the attraction isn’t just felt between neighbouring atoms but is felt over a larger number of atoms. This delocalisation of bonding allows the electrons to flow over the larger bonding area. The conductive character of metals is created by this delocalisation of electrons. Conversely we typically see ionically bonded materials as solids. This is because they form materials which are large and heavy at a molecular level. This means that they typically have lower vapour pressures. Definition: Vapour pressure: the pressure exerted by a vapour directly above its liquid as a result of evaporation. Covalent bonding, on the other hand, is more Substances with lower vapour pressures don’t common in non-metals, like methane. The atoms tend to evaporate quickly. In the context of a in methane, if you’re not familiar are carbon and hazmat response, this means that a leak/ spill, of hydrogen. You can see in the diagram below the an ionically bonded substance, won’t spread sharing of electron character of covalent bonding. through lots of vapours being created- without Each electron (blue and red) is shared by both input from external factors. Conversely, the hydrogen and the carbon. covalently bonded substances are more likely to evaporate; typically having a higher vapour pressure. V2 05/2015 FOR MORE INFORMATION AND TRAINING ON THIS TOPIC GO TO: WWW.TACTICALHAZMAT.COM