Film Elements/Notes
advertisement

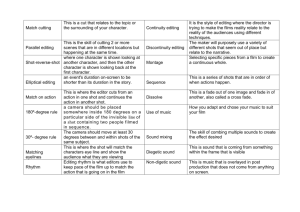
Film and Literature Elements of Film Contents…. n Traditional Elements ­Character ­Point of View ­Plot ­Setting Ø Elements of Cinematography ­Positioning and Composition of the Image ­Editing of Image and Sound Character ü External Appearance / Internal thoughts 1. 2. 3. Dependent upon medium ( ex: realistic or cartoonish) Images cancel out reader’s imagination. This can be confusing or dissatisfying. Interpretations of character are NO longer based on the exact word choices and details of the original author making it possible for meanings to change. Important Questions about Character 1. What are different ways that certain linguistic or narrative strategies produce literary characters? Ex: Does the author use a lot of adjectives? 2. How are movie characters a product of film materials? 3. What advantages/drawbacks do words and images have over written descriptions of characters? Visa Versa? 4. Which characters are added, omitted, or changed in an adaptation? Point of View v Remember First and Third­Person v Camera allows multiple points of view to interact v The role of the lens as the narrator v Existence of a Narrative Voice v Language and Image work together Questions about Point of View 1. How does the imagistic point of view used in a movie expand or limit the power of linguistic point of view? 2. At what rate is the audience presented with information and how is the audience allowed to process that information? (ex: short stories or books vs. 2hr movies) Plot § Film and Literature often part ways in terms of plot § Order of events often changes § Events, places, and times might actually change § Often becomes a function of character’s needs and desires rather than from dramatic conflict. (Ex: Dorothy just wants to go home in the Wizard of Oz). Questions about Plot 1. How has the narrative structure changed or not 2. 3. 4. 5. changed in the conversion to a movie? Do the same causal motives drive the narrative in both versions or have those motives changed? To what extent does the ending determine the meaning of the story, and, if an adaptation changes that ending, how does that change the meaning of the story? How have the many adaptations of one story altered the theme? Are different themes connected to the time and place when the different works were produced? Setting Like short stories, film settings can reflect realistic, historical, cultural, and symbolic meanings. In films, setting includes everything put in front of the camera before filming begins. This includes; props, lighting, costumes, etc. What do these different Settings tell you? Questions about Setting 1. Do film viewers take for granted a “natural” setting whose meanings they might be more aware of in writing? (Ex: storms and weather) 2. Do film makers use the same care in selecting locations, props, and backgrounds as do authors? What are the underlying meanings? Cinematography: Positioning and Composition of the Image The Shot: A single uncut segment of film. Shot Techniques… • Shape of Frame – Widescreen or Normal • Perspective of Image – Deep focus showing backgrounds, middlegrounds and foregrounds or a flat, shallow focus • Film Speed – Creates slow, fast, or normal motion Shot (continued) • Distance – Between the camera and the figure being filmed i.e. close­ups, long shots, and other relations • Angle – Is the camera at a high angle, low angle, or straight­on with its subject? • Camera Movements – i.e. sweeping pans of the horizon or tracks that follow the action on a cart • Color or Black and White – Both of these have a wide range of tones Editing of Image and Sound Scene When one or more shots are linked or edited together to describe a single space or place it is called a scene. Sequence A number of edited shots and scenes that are connected by a specific action or idea. Both scene and sequence are a result of editing Editing n The linking together of two or more shots n Continuity Editing – The editing of shots and sequences so that the editing is unnoticeable or invisible n Discontinuous Editing – When editing calls attention to itself and to actions and perspectives that do not fit smoothly together Questions about Editing 1. If comparable sections are significantly different, ask how and why the editing reshapes the material of the literature. 2. Might a modern adaptation update a classic literary work by simply transforming a continuous narrative style into a discontinuous one? Final Thoughts About Film • Consider the pacing of the film. This is established through long takes (holding a shot for a long time) and short takes (cut quickly between shots) • Consider how emotions and moods are set through shot/reverse shot • Think about the role of establishing shots in the narration of a film and in giving its setting • How do sounds such as dialogue, music, special effects and background noise affect your interpretation of a film through sound editing?