Earth Dynamics Study Guide: Plate Tectonics & Landforms
advertisement

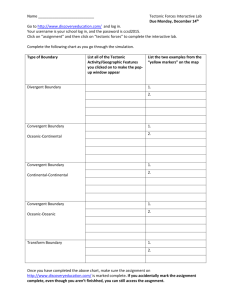
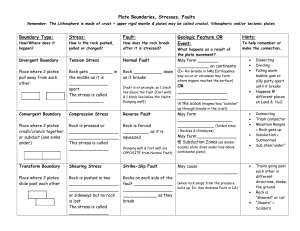
Chapter 8 Earth Dynamics Study Guide 1. List all types of Boundaries and Stress that apply for each Landform Continental Rift Tension Divergent Boundary Transform Fault Shear Transform Boundary Mountain Ranges Compression Uplift Convergent Boundary Ocean Trenches Subduction Convergent Boundary Compression Mid-Ocean Ridges Tension Seafloor Spreading Divergent Boundary Volcanic Arch Compression Subduction Convergent Boundary 2. Draw and label 3 different types of stress 3. Process that cause continents to grow 1. Erupting volcanoes add new land 2. Plate movements adds fragments 4. Understand the following terms Volcanic Arc form about 100km away from where plates converge and one plate sub-ducts under another Subside the downward vertical motion of Earth’s surface, like the formation of a glacier Isostasy the equilibrium between continental crust and the denser mantle below that causes continents to float on mantle Plain large area of nearly flat land at low elevations Uplift the process that moves large bodies of Earth materials to higher elevations Fault Zone area of many fractured pieces of crust along a large fault Strain change in a rock’s shape that is due to stress Volcanism is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth Basin area of subsidence or region of low elevation that can collect sediment as mountains erode Plateau flat land at a high elevation Transform Fault plates slide horizontally past each other 5. Characteristics of the following rocks within the rock cycle. a. igneous-rock experiences high pressure that causes minerals to align themselves in bands b. metamorphic-rock pushed further underground and completely melts, then erupts from a volcano and hardens c. sedimentary- rock is broken down by wind and water into small particles, which flow into a river and get compressed into rock