Digestive system powerpoint continued
advertisement

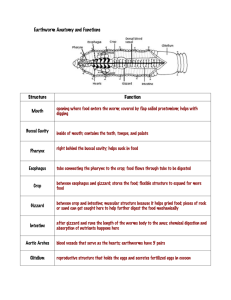
Bellwork – name and state the function of each organ Digestion and Evolutionary Adaptions Suspension Feeders Many aquatic animals are suspension feeders, which sift small food particles from the water Substrate Feeders Substrate feeders are animals that live in or on their food source Fluid Feeders Fluid feeders suck nutrient-rich fluid from a living host Bulk Feeders Bulk feeders eat relatively large pieces of food Animals with simple body plans have a gastrovascular cavity that functions in both digestion and distribution of nutrients Video: Hydra Eating Daphnia Fig. 41-9 More complex animals have a digestive tube with two openings, a mouth and an anus Crop Gizzard Intestine Esophagus Pharynx Anus Mouth Typhlosole Lumen of intestine (a) Earthworm Foregut Midgut Hindgut Esophagus Rectum Anus Crop Mouth Gastric cecae (b) Grasshopper Stomach Gizzard Intestine Mouth Esophagus Crop Anus (c) Bird This digestive tube is called an alimentary canal Some Dental Adaptations Dentition, an animal’s assortment of teeth, is one example of structural variation reflecting diet dentition is adapted to their usual diet Why might this have evolved? Hint: the cecum has bacteria that breaks down plant material Fig. 41-20 1 Rumen 2 Reticulum Intestine Esophagus 4 Abomasum 3 Omasum