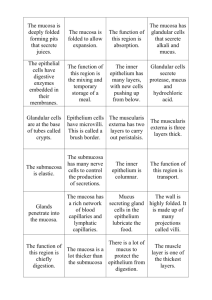
VERTEBRATE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Functions:
advertisement

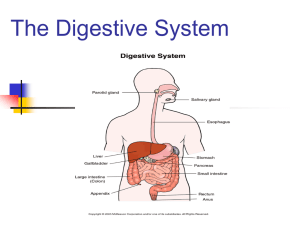
VERTEBRATE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Functions: - mechanical breakdown - big lumps of food to small - chemical breakdown - digestion → monomers - absorption of monomers - compact waste → feces, extract water → eliminate Common features: - longitudinal tube through body - regional specializations along length - basic wall plan common to all vertebrate groups Trends: - simple → complex as diet harder to digest - easily digested food: simple, short gut (filter-feeders, carnivores) - "tough" food: gut longer, more complex (herbivores) FISH DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Trends: no oral salivary glands - water lubricates food no separate stomach in some species intestine surface area for absorption increased: -long tube, folded/coiled in coelom -mucosa folded internally -spiral valve -villi HUMAN LIP (H108) ORAL EPITHELIUM TELEOST ESOPHAGUS CROSS-SECTION (CVH138) TELEOST ESOPHAGUS: SECRETORY AND NON-SECRTORY REGIONS (CVH138) mucus-secreting columnar cells non-secreting region stratified squamous/cuboidal epithelium ELASMOBRANCH ESOPHAGUS (CVH60) ELASMOBRANCH ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA - GLANDULAR REGION (CVH60) simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells GUT-ASSOCIATED LYMPHOID TISSUE IN ELASMOBRANCH ESOPHAGUS (CVH60) muscularis externa Leydig's organ large unencapsulated lymphocyte population DOGFISH STOMACH, FUNDUS REGION (CVH72) DOGFISH STOMACH WALL - FUNDUS (CVH72) SM ME mucosal glands GLANDULAR MUCOSA IN DOGFISH FUNDUS (CVH72) LP DOGFISH STOMACH, PYLORUS REGION (CVH71) mucosal glands SM ME DOGFISH STOMACH WALL, PYLORUS REGION (CVH71) lamina propria glandular epithelium MM SM ME GLANDULAR MUCOSA IN PYLORUS OF DOGFISH STOMACH (CVH71) LP MM SPIRAL VALVE IN DOGFISH INTESTINE (CVH133) wall of intestine leaflet of spiral valve TROUT INTESTINE CROSS-SECTION (CVH145) villi TROUT INTESTINE WALL (CVH145) LP ME TROUT VILLI (CVH145) columnar epithelium (absorptive) brush border goblet cells LP LP MUCOSA ON DOGFISH SPIRAL VALVE (CVH133) small villi on valve submucosal core of spiral valve DOGFISH LARGE INTESTINE (CVH66) DOGFISH LARGE INTESTINE WALL (CVH66) mucosa with goblet cells ME AMPHIBIAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Trends: ciliated oral epithelium esophagus short, wide, ciliated stomach regions: fundus, pylorus -glands short tubular small intestine coiled -large mucosal villi, no glands large intestine → cloaca FROG ORAL EPITHELIUM - CUBOIDAL SURFACE CELLS, CILATED (CVH21) FROG ESOPHAGUS WALL (CVH26) SM ME FROG ESOPHAGEAL GLANDS IN SUBMUCOSA MUCO-SEROSAL (CVH26) FROG ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA - GOBLET CELLS AND CILIATED COLUMNAR CELLS (CVH26) SALAMANDER ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA - GUT-ASSOCIATED LYMPHATIC TISSUE (CVH50) SALAMANDER STOMACH WALL - THICK MUSCULARIS EXTERNA (CVH55) SM ME SALAMANDER STOMACH MUCOSA - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM - SHORT TUBULAR GLANDS (CVH55) - SURFACE GOBLET CELLS LP MM VILLI IN FROG SMALL INTESTINE (CVH16) FROG INTESTINAL VILLI STRUCTURE (CVH16) ME FROG VILLI: COLUMNAR ENTEROCYTES - ABSORPTION GOBLET CELLS (CVH16) SALAMANDER GOBLET CELLS RELEASING MUCUS (CVH46) SALAMANDER LARGE INTESTINE CROSS-SECTION - MUCOSA FOLDED (CVH45) SALAMANDER LARGE INTESTINE MUCOSA - FOLDS → WIDE GLANDS (CVH45) SM ME REPTILIAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM -regional structure similar to amphibian gut Trends: gizzard: enlarged pylorus - grind food cecae: pouches off intestine -more time for digestion SNAKE TONGUE CROSS-SECTION (CVH174) oral epithelium CVH174 oral epithelium nerve skeletal muscle TURTLE ESOPHAGUS (CVH91) SM ME TURTLE ESOGPHAGUS MUCOSA - GOBLET CELLS (CVH91) WALL STRUCTURE IN TURTLE STOMACH (CVH94) glandular mucosa submucosa muscularis externa GLANDULAR MUCOSA OF TURTLE STOMACH (CVH94) mucous cells at surface simple tubular glands: HCl digestive enzymes lamina propria between glands TURTLE SMALL INTESTINE - TYPICAL REPTILIAN (CVH85) mucosa folded muscularis externa STRUCTURE OF FOLDS IN TURTLE SMALL INTESTINE (CVH85) simple columnar epithelium: - enterocytes - goblet cells lamina propria in core of fold BIRD DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Trends: keratinized beak - no teeth in modern birds keratinized tongue - aids mechanical breakdown crop: expanded esophagus food reservoir - regurgitation for young herbivores/seed eaters: gizzard - mechanical breakdown using stones, grit to grind food MAMMALIAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diet-related specializations: length of gut related to digestion time -carnivores - chemical digestion fast, gut short -herbivores - chemical digestion slow, gut longer keratinized esophagus - rodents, herbivores fermentation - extra chambers for bacterial action to break down plant cellulose -foregut fermenters -intestinal fermenters GUINEA PIG ESOPHAGUS (E) AND TRACHEA (T) CROSS-SECTION (CVH196) T E WALL OF GUINEA PIG ESOPHAGUS - KERATINIZED EPITHELIUM (CVH196) keratin EPI LP MM SM ME