Back
Print
Name
Class
Date
Skills Worksheet
Concept Mapping
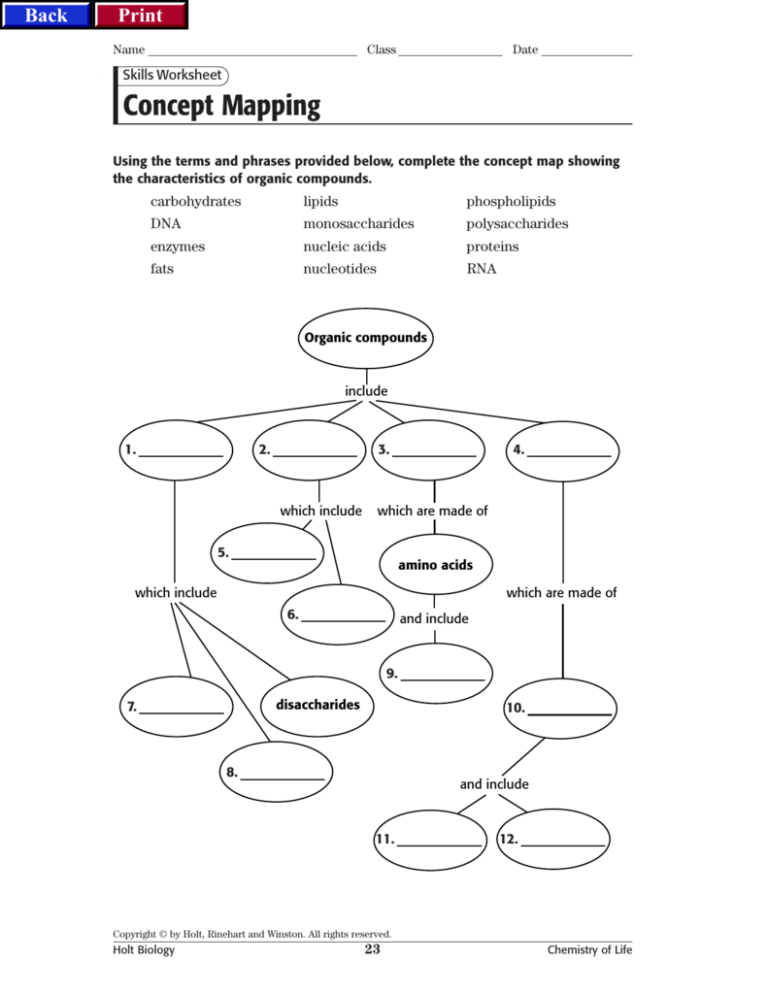
Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing
the characteristics of organic compounds.
carbohydrates
lipids
phospholipids
DNA
monosaccharides
polysaccharides
enzymes
nucleic acids
proteins
fats
nucleotides
RNA
Organic compounds
include
1.
2.
3.
which include
4.
which are made of
5.
amino acids
which are made of
which include
6.
and include
9.
disaccharides
7.
10.
8.
and include
11.
12.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
23
Chemistry of Life
Back
Print
TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Critical Thinking
water and soap molecules and
becomes separated from the dirt.
The dirt is released and can be rinsed
away. The oil molecules can also be
rinsed away.
The hydrogen bonds between water
molecules cause surface tension. This
prevents the surface of the water from
stretching or breaking easily. The needle is light enough that it does not
overcome the surface tension.
The polar ends of the soap molecules
point downward in the water because
of their attraction to the polar water
molecules. The nonpolar ends point
upward and disrupt the surface of the
water. This disruption frees water
molecules to adhere to the needle,
which becomes wet and sinks.
pepsin
trypsin
Something must be added to the liquid
to raise its pH close to 7 so trypsin can
be activated.
Enzymes typically function within a
range of pH values, although enzymes
are most efficient at a specific pH.
Yes, both pepsin and trypsin can function in a liquid with a pH value
between 4 and 5, but neither enzyme
will function optimally.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
b
d
a
g, b
i, a
h, d
j, e
l, k
f, c
d
c
b
d
a
Test Prep Pretest
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
Concept Mapping
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
b
d
a
f
c
e
d
a
f
b
e
c
e
c
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
fats or phospholipids
phospholipids or fats
monosaccharides or disaccharides
disaccharides or monosaccharides
enzymes
nucleotides
DNA, RNA
RNA, DNA
b
a
a
d
c
c
e
a
d
b
polar, nonpolar
hydrogen, covalent
ion
acid, base
carbohydrates
nucleic acids
sodium chloride, products
catalyst
active site
pH
A—carbohydrate; B—lipid; C—protein
Carbohydrates such as the monosaccharide glucose shown here are found
in cells as a source of energy (glucose), as energy storage molecules
(glycogen and starch), or as structural
molecules (cellulose). Lipids such as
the fatty acids shown here are found
in cells as energy storage molecules
(fats) or in cell membranes as structural molecules (phospholipids).
Proteins are found in cells as enzymes
and hemoglobin, as structural proteins
in the body (collagen, hair, muscles),
or in blood as part of blood clot fibers.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
84
Chemistry of Life